Abstract
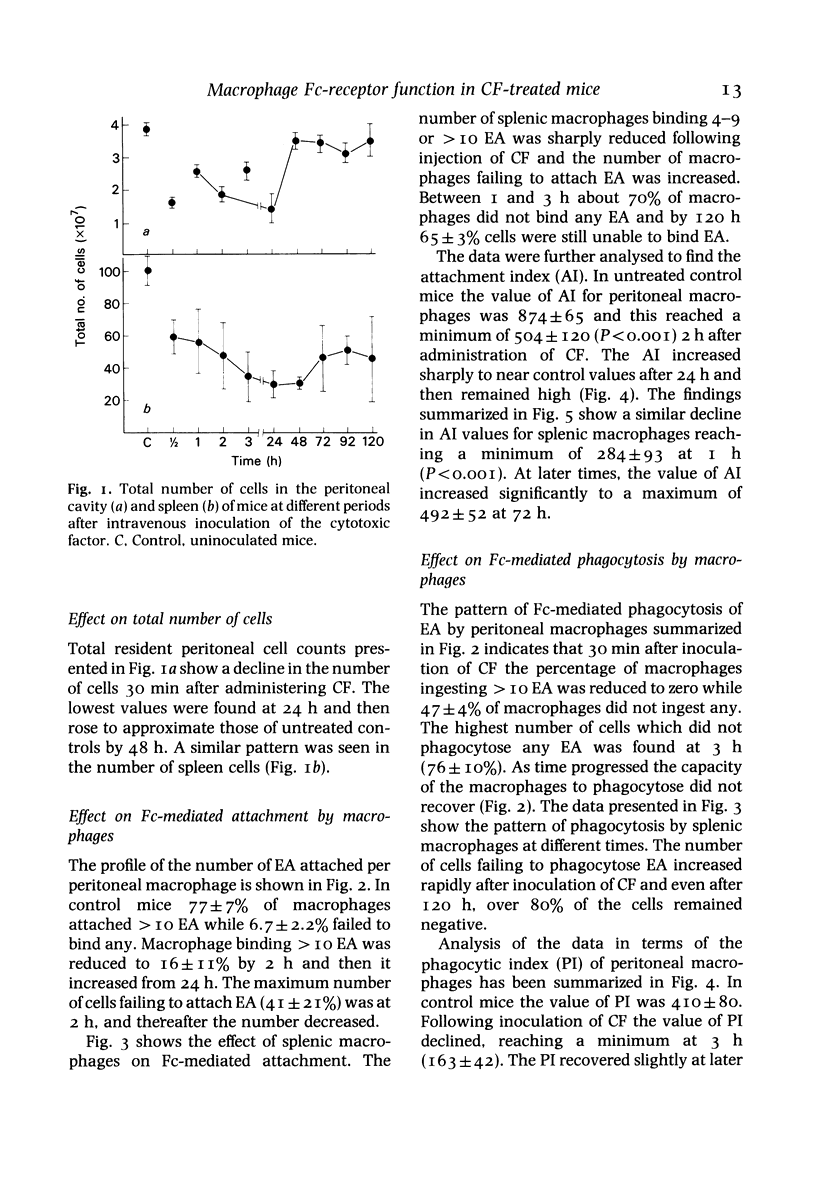
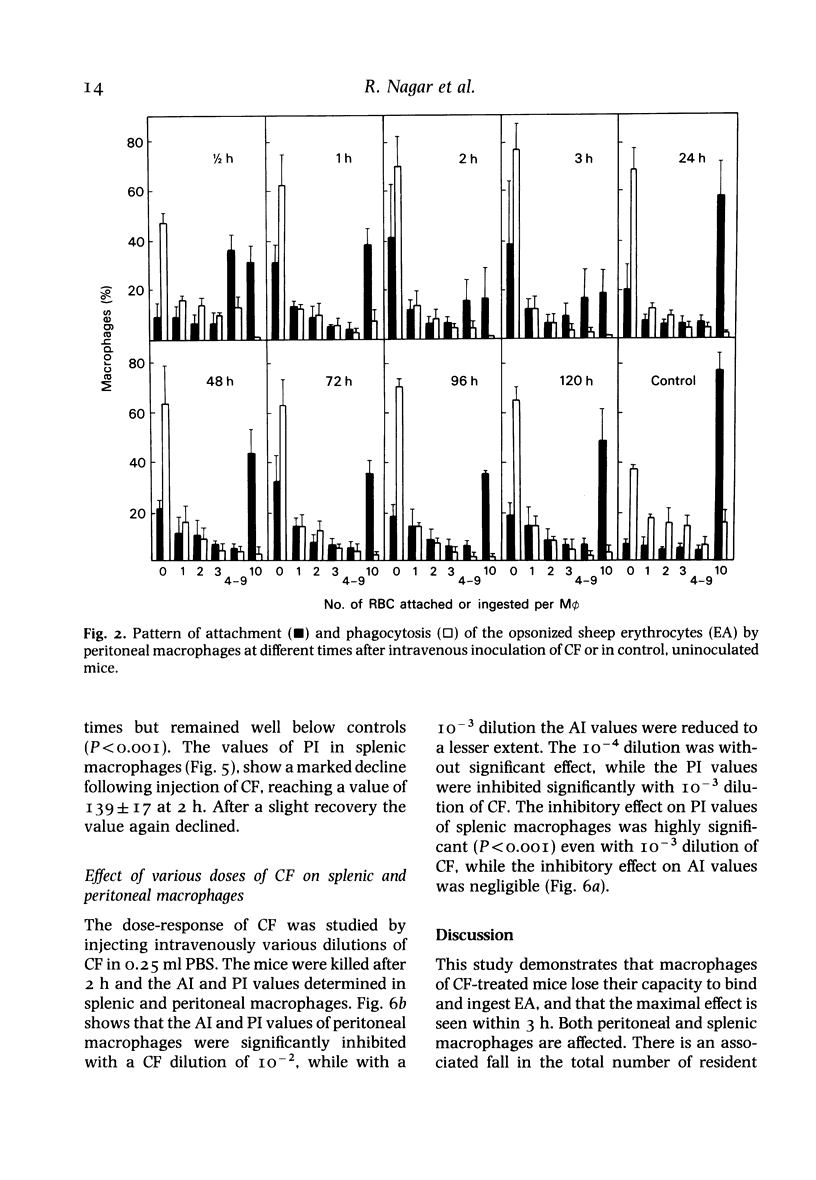
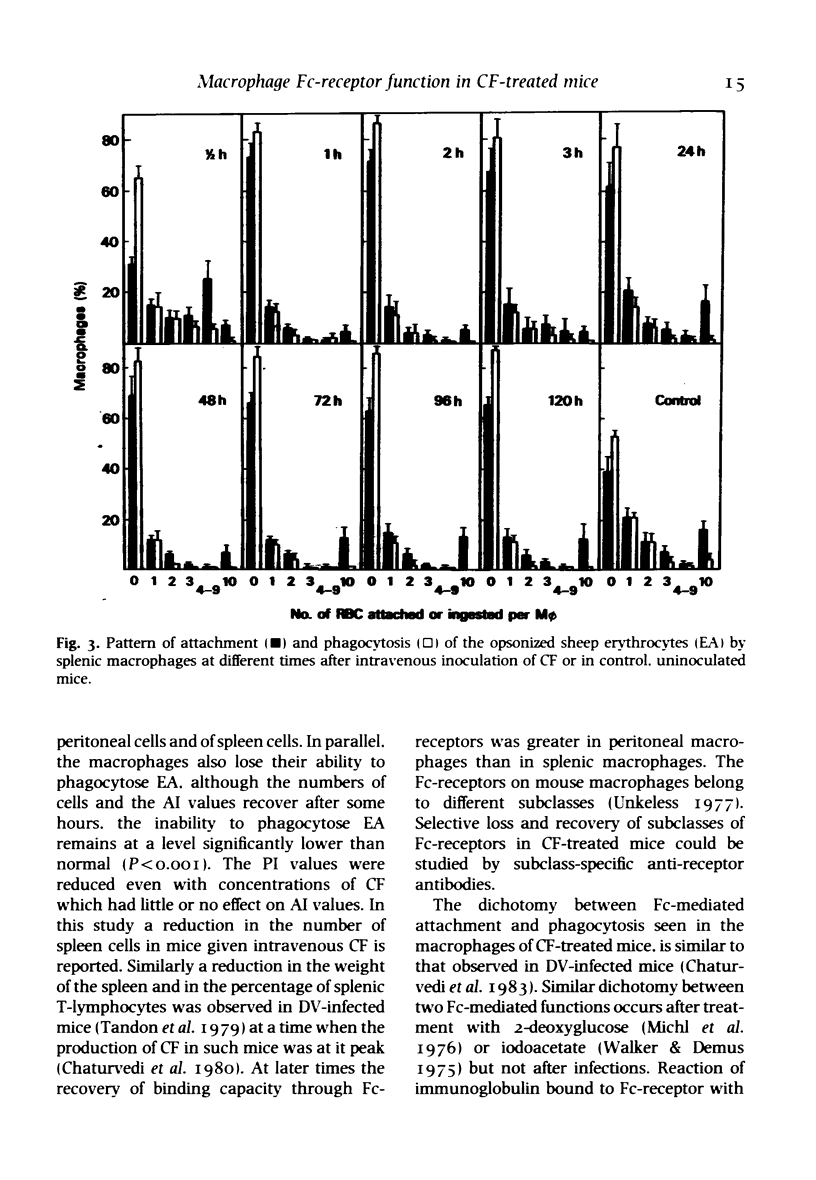
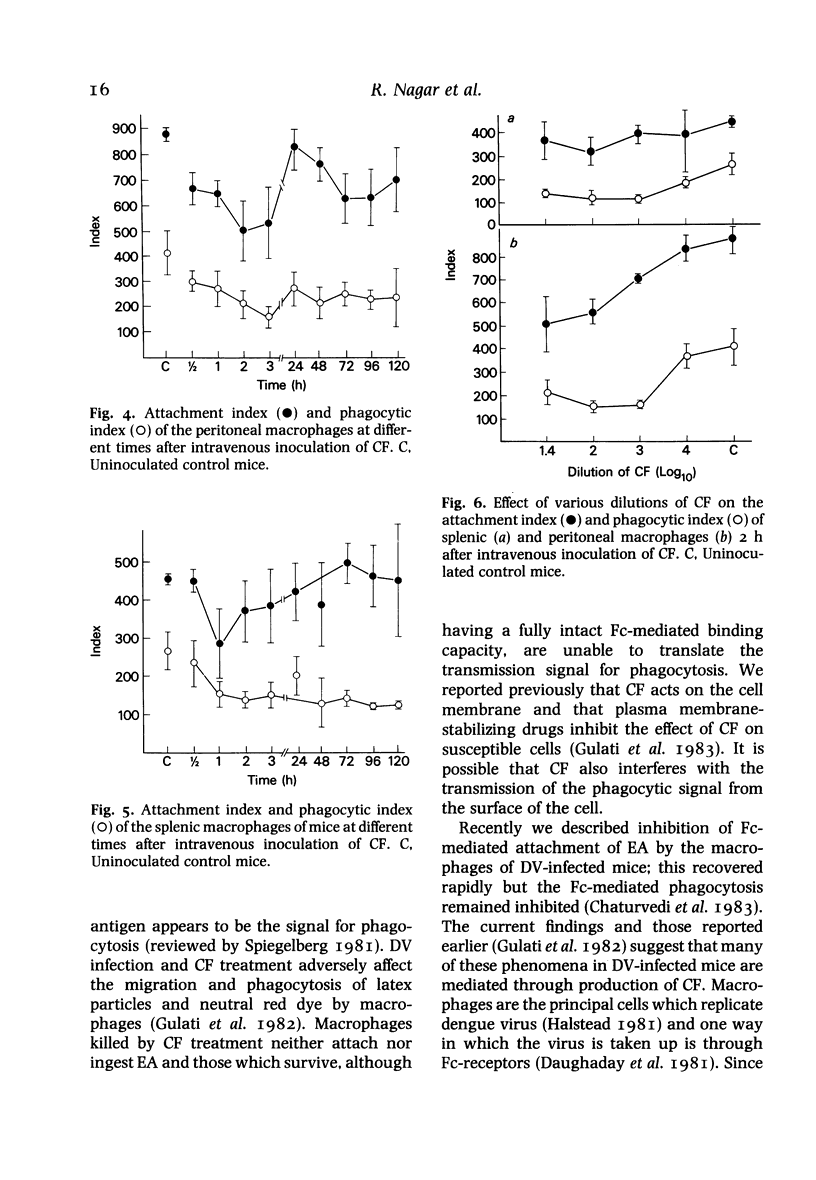
Many defects in macrophage functions in dengue type 2 virus (DV) infection have been shown to be mediated by production of the virus-induced cytotoxic factor (CF). An attempt has been made to determine whether the alterations in Fc-mediated functions of macrophages in DV-infected mice are due to CF. Mice given CF intravenously show a rapid fall in total numbers of peritoneal and spleen cells. The number of cells in the peritoneal cavity recovered in 48 h. but recovery in the spleen was not significant. The capacity of the splenic and peritoneal macrophages to attach and ingest opsonized sheep erythrocytes was significantly reduced, the lowest values of attachment index (AI) and phagocytic index (PI) being observed within 2-3 h. At later periods the AI values increased markedly but the PI values remained depressed. The effect was dose-dependent. The effect on Fc-receptor functions of macrophages in DV-infected mice thus appears to be mediated through CF.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaturvedi U. C., Bhargava A., Mathur A. Production of cytotoxic factor in the spleen of dengue virus-infected mice. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):665–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi U. C., Nagar R., Mathur A. Effect of dengue virus infection on Fc-receptor functions of mouse macrophages. J Gen Virol. 1983 Nov;64(Pt 11):2399–2407. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-11-2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday C. C., Brandt W. E., McCown J. M., Russell P. K. Evidence for two mechanisms of dengue virus infection of adherent human monocytes: trypsin-sensitive virus receptors and trypsin-resistant immune complex receptors. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):469–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.469-473.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati L., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Depressed macrophage functions in dengue virus-infected mice: role of the cytotoxic factor. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Apr;63(2):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab G. J., Warr G. A., Sannes P. L. Alveolar macrophage ingestion and phagosome-lysosome fusion defect associated with virus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):960–968. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.960-968.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl J., Ohlbaum D. J., Silverstein S. C. 2-Deoxyglucose selectively inhibits Fc and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Description of the inhibitory effect. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen S. C. Role of macrophages in natural resistance to virus infections. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):1–26. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.1-26.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. M., Pesanti E. L. Effect of influenza infection on the phagocytic and bactericidal activities of pulmonary macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):651–657. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.651-657.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley J. D., Pesanti E. L. Effects of antiviral agents on murine cytomegalovirus-induced macrophage dysfunction. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):918–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.918-923.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S., Demus A. Antibody-dependent cytolysis of chicken erythrocytes by an in vitro-established line of mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



