Abstract
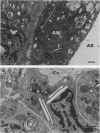
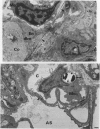
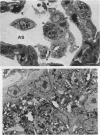
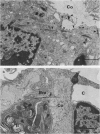
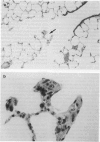
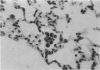
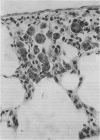
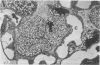
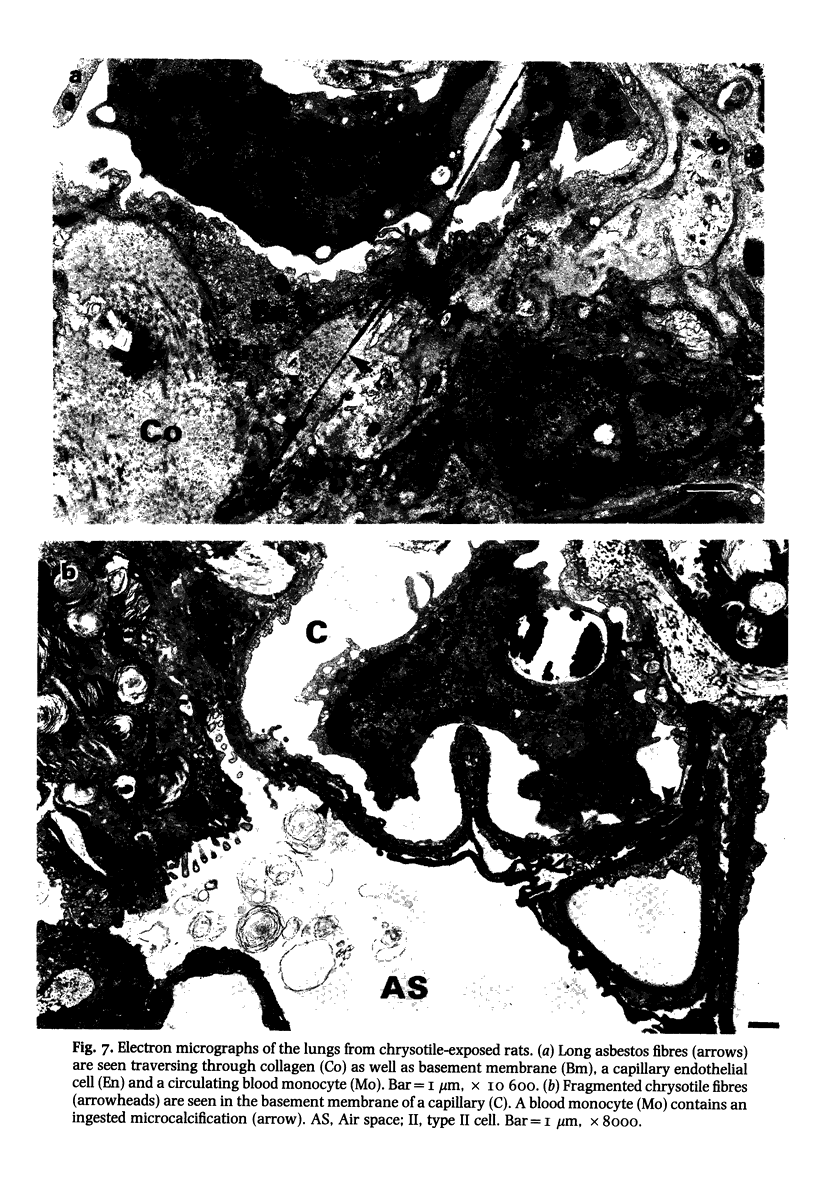
Although all commercial types of asbestos can cause pulmonary fibrosis, little is known about ultrastructural differences in the evolution of pulmonary lesions induced by amphiboles and serpentines. The present study was designed to compare the histological and ultrastructural effects produced by chronic inhalation of either crocidolite (amphibole) or chrysotile (serpentine) asbestos in the rat. Animals, exposed by intermittent inhalation for 3 months, were killed after 2 to 16 months. When inhaled, both types of asbestos caused thickened alveolar duct bifurcations associated with macrophage aggregates. Crocidolite inhalation also produced subpleural collections of alveolar macrophages and lymphocytes. Electron microscopy revealed some similarities, but also distinct differences, in the pulmonary distribution of inhaled chrysotile and crocidolite. Whereas both asbestos varieties were identified within the pulmonary interstitium, only crocidolite was detected inside alveolar macrophages. Chrysotile fibres were seen infrequently within the vascular compartment. Microcalcifications were noted after chrysotile inhalation, but were never observed following crocidolite exposure. Both asbestos types induced slight pulmonary fibrosis. These findings indicate that crocidolite and chrysotile produce different pathogenetic features, although both are fibrogenic.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry B. E., Wong K. C., Brody A. R., Crapo J. D. Reaction of rat lungs to inhaled chrysotile asbestos following acute and subchronic exposures. Exp Lung Res. 1983 Jul;5(1):1–21. doi: 10.3109/01902148309061501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botham S. K., Holt P. F. The effects of inhaled crocidolites from Transvaal and North-west Cape mines on the lungs of rats and guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Dec;53(6):612–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Hill L. H., Adkins B., Jr, O'Connor R. W. Chrysotile asbestos inhalation in rats: deposition pattern and reaction of alveolar epithelium and pulmonary macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):670–679. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Hill L. H. Interstitial accumulation of inhaled chrysotile asbestos fibers and consequent formation of microcalcifications. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):107–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., Mossman B. T. The pathogenesis of asbestos-associated diseases. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 17;306(24):1446–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206173062403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. M. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF ASBESTOS DUST ON THE LUNG. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:454–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern S. W., Mandel W. J. The significance of exercise-induced ventricular arrhythmias. Chest. 1980 Jan;77(1):1–2. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. F., Mills J., Young D. K. Experimental asbestosis in the guinea-pig. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):185–195. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. F., Mills J., Young D. K. Experimental asbestosis with four types of fibers: importance of small particles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):87–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan E., Oghiso Y., Hartmann D. P. The effects of chrysotile and crocidolite asbestos on the lower respiratory tract: analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage constituents. Environ Res. 1983 Dec;32(2):382–397. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(83)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Kunkel R. G., Phan S. H. The role of strain variation in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):63–66. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Churg J. Formation of the asbestos body. A comparative study with three types of asbestos. Environ Res. 1970 Mar;3(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(70)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G., Skidmore J. W., Timbrell V. The effects of the inhalation of asbestos in rats. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):252–269. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]