Abstract
To develop an animal model of the haemolytic-uraemic syndrome during shigellosis, rabbits were injected with lipopolysaccharides (LPS) extracted by the hot phenol-water method from Shigella dysenteriae I and from S. flexneri. Two intravenous injections of LPS spaced by 24 h elicited renal cortical necrosis in a generalized Shwartzman reaction characterized by fibrin deposition in glomerular capillaries and by elevated plasma creatinine concentration. Rabbits rendered leucopenic by busulphan treatment were protected against renal cortical necrosis after injection with LPS derived from S. dysenteriae I. Both LPS preparations derived from Shigella species were also active in producing fever in rabbits, death in rabbits, and gelation of limulus lysate with approximately the same potency as a standard LPS of E. coli 055:B5. These results demonstrated that the LPS of Shigella species given intravenously to rabbits produces renal cortical necrosis, which is caused by leucocyte-mediated intravascular fibrin deposition in renal blood vessels and which resembles histologically the renal lesion in the haemolytic-uraemic during shigellosis in humans.
Full text
PDF


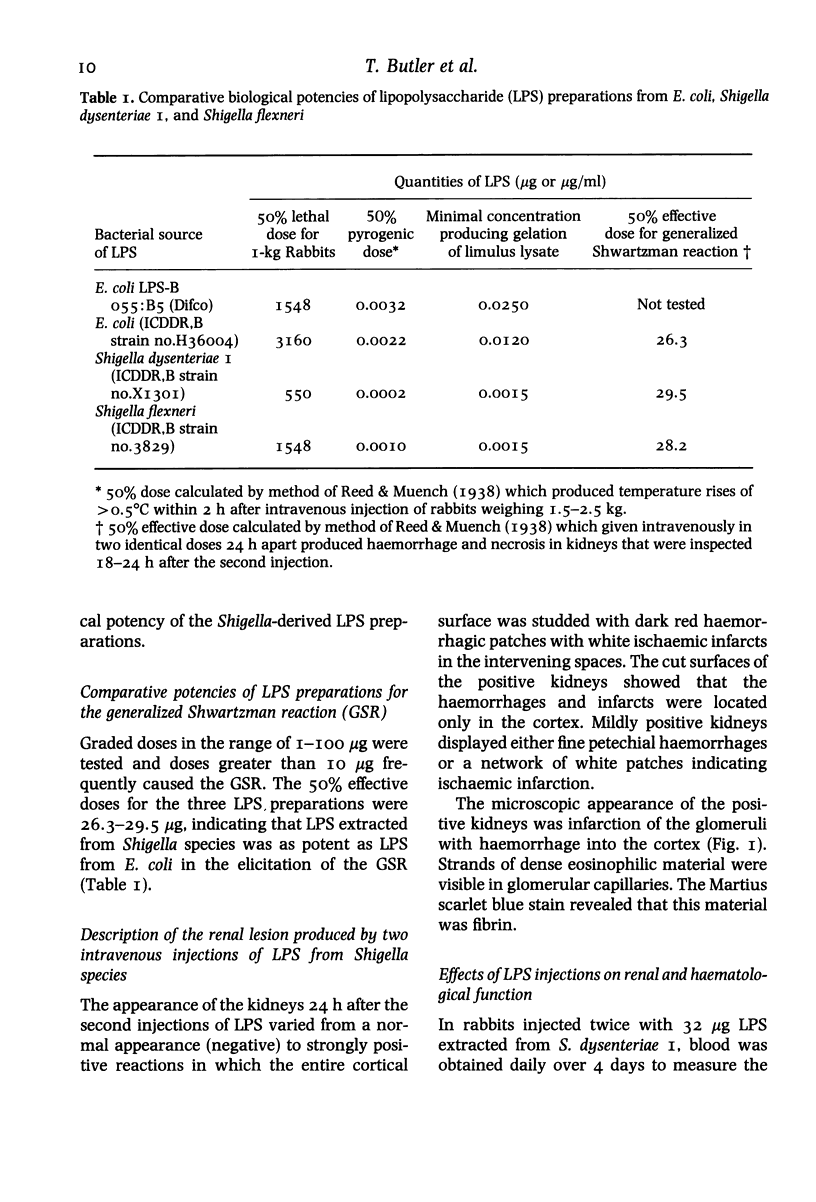
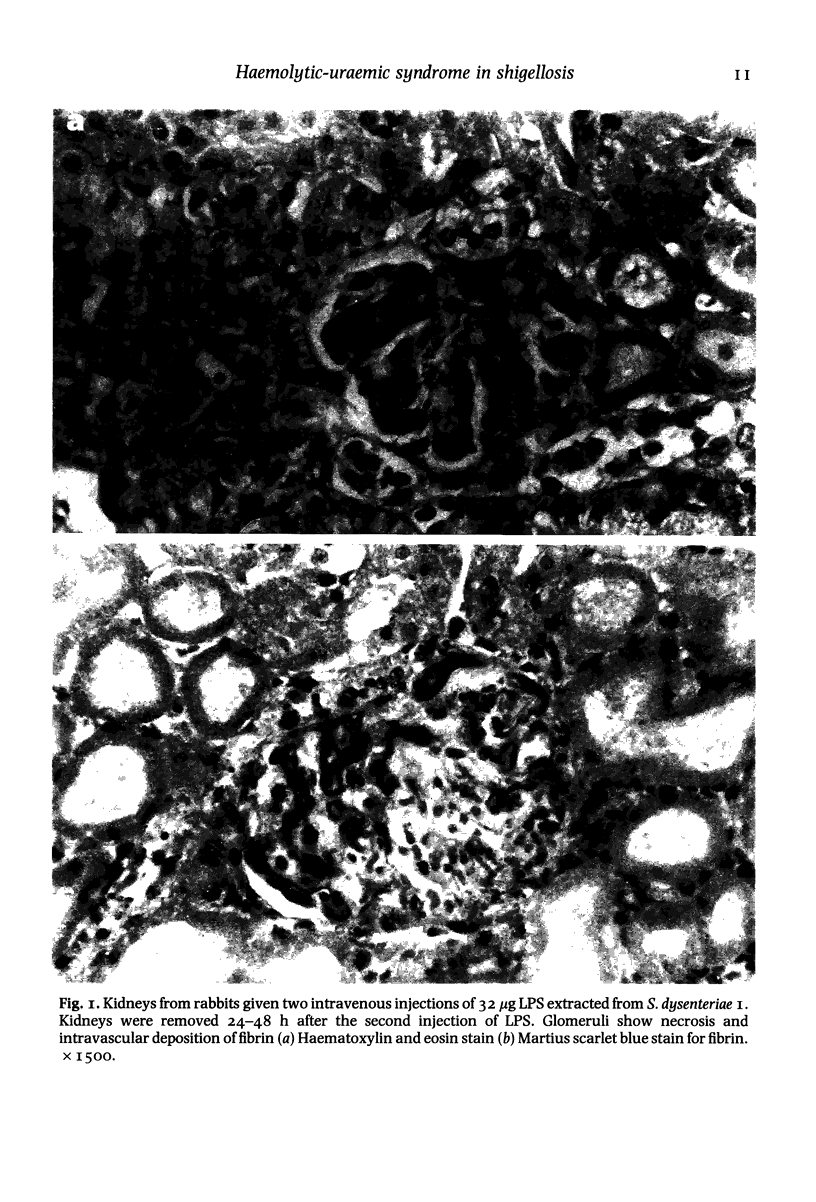
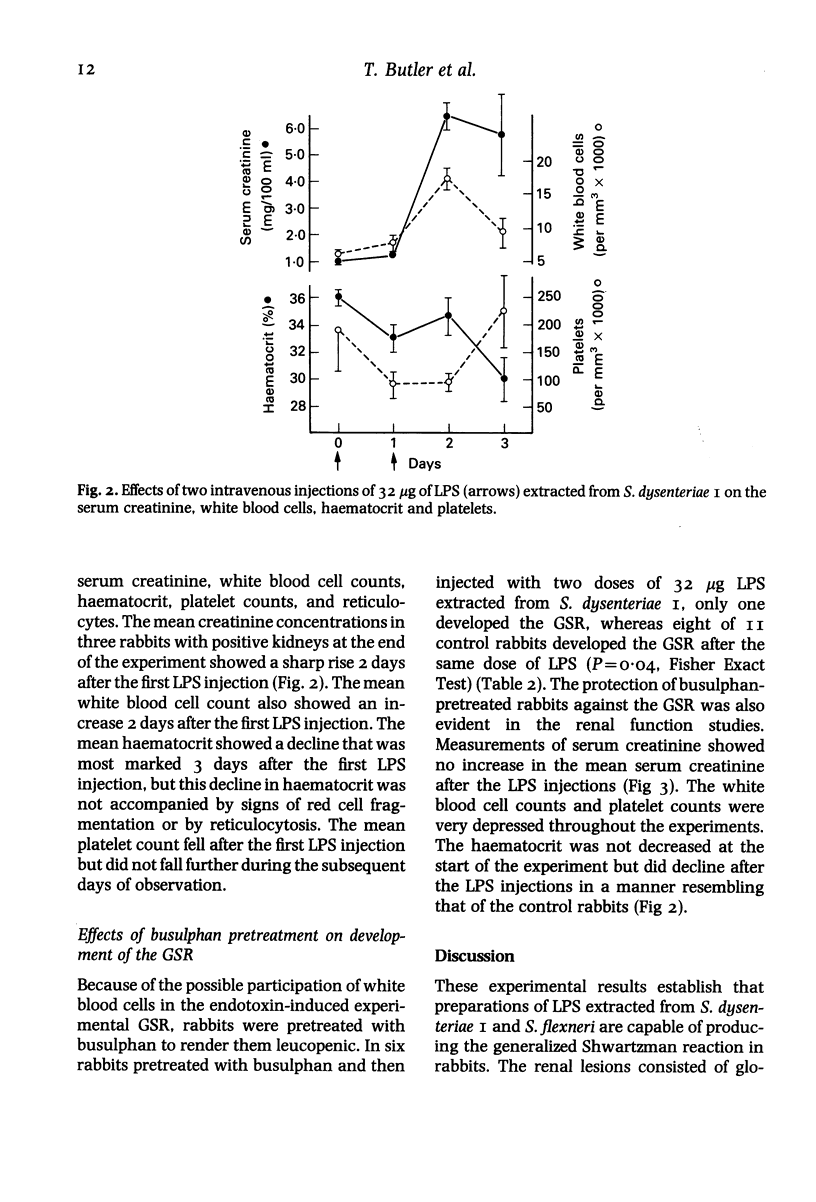


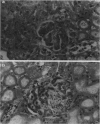
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohn E., Müller-Berghaus G. The effect of leukocyte and platelet transfusion on the activation of intravascular coagulation by endotoxin in granulocytopenic and thrombocytopenic rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1976 Aug;84(2):239–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Islam M. R., Bardhan P. K. The leukemoid reaction in shigellosis. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Feb;138(2):162–165. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140400044010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANANTONIO C., VITACCO M., MENDILAHARZU F., RUTTY A., MENDILAHARZU J. THE HEMOLYTIC-UREMIC SYNDROME. J Pediatr. 1964 Apr;64:478–491. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. W., Kvale P. A., Afable V. L., Stewart S. D., Halverson C. W., Holmes K. K. Single-dose antibiotic treatment of asymptomatic gonorrhea in hospitalized women. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 2;283(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007022830101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanowska E., Pelczarska A., Wnuk W., Mulczyk M., Godzińska H., Slopek S. Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characteristic of Shigella sonnei phase I free endotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., GOOD R. A. Studies on the generalized Shwartzman reaction: I. General observations concerning the phenomenon. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):605–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M. Effect of Shigella flexneri endotoxin on ureagenesis and liver ultrastructure in rabbits. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Jun;32(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]