Abstract
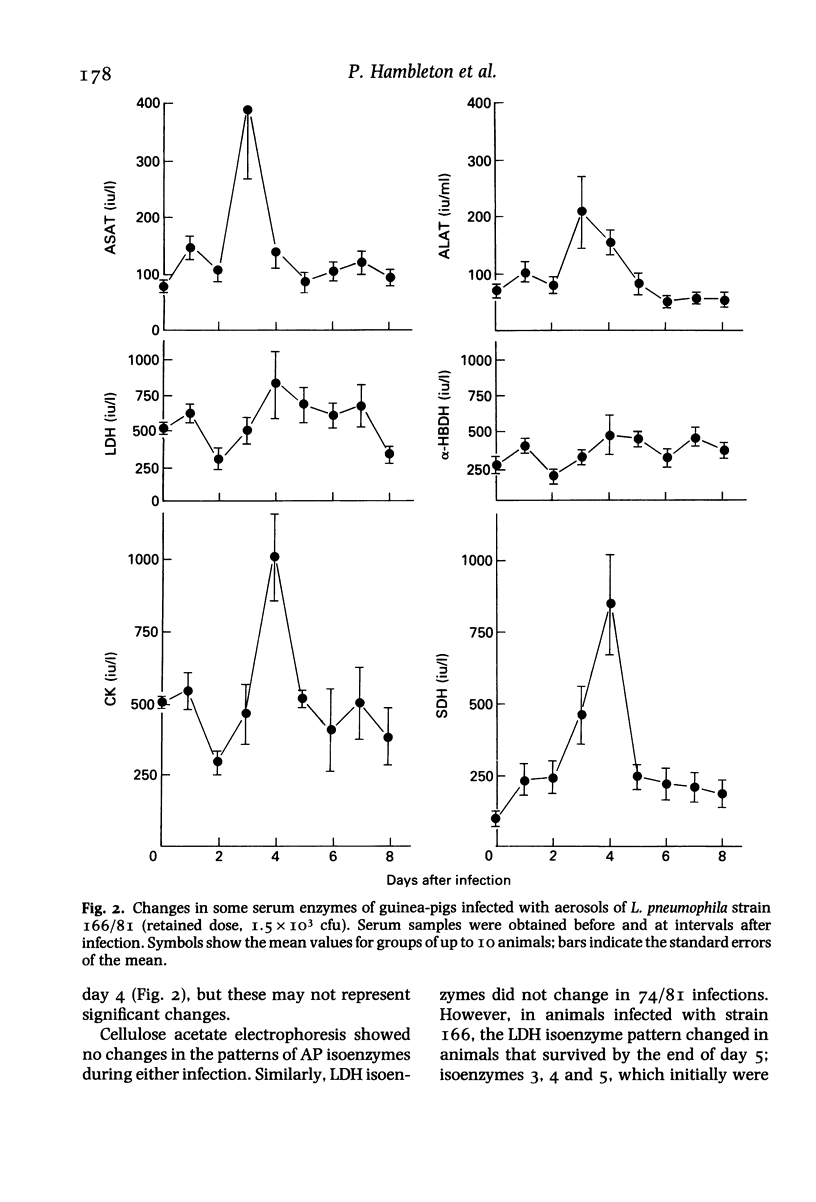
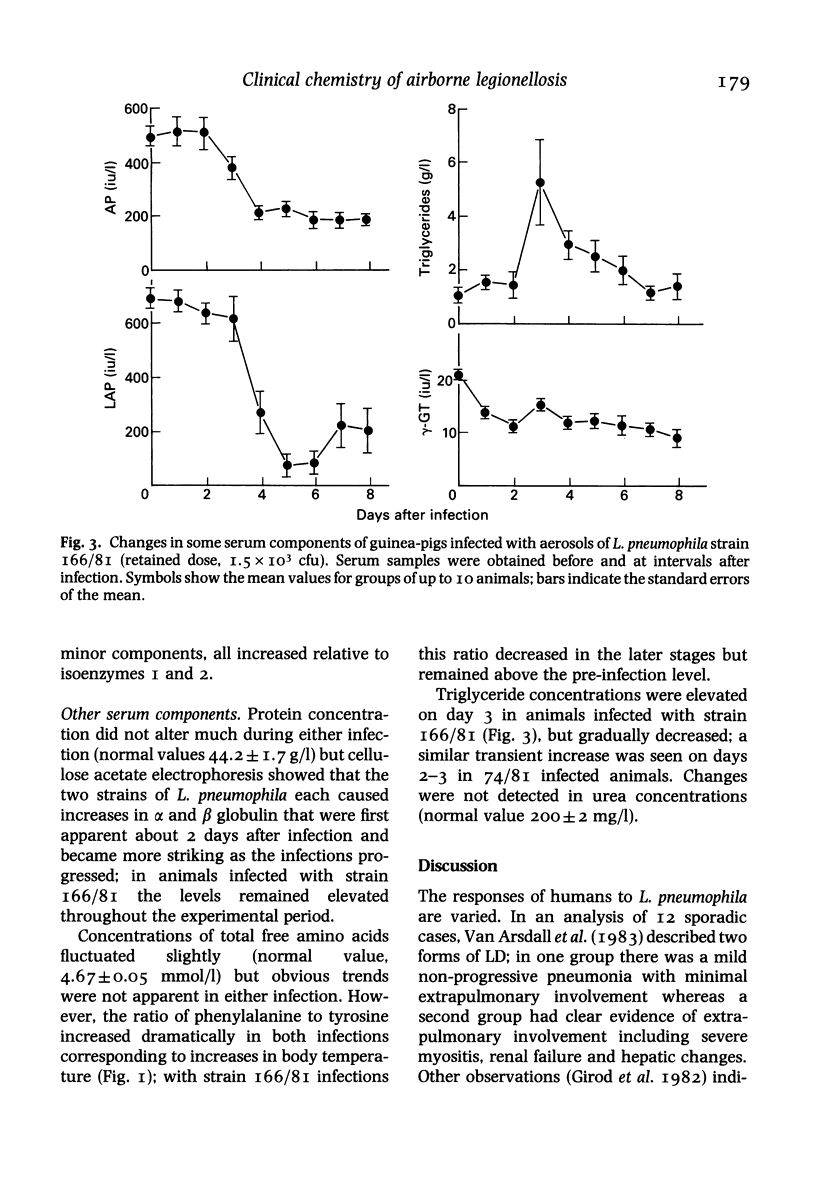
Legionella pneumophila infection of guinea-pigs by the aerosol route with either of two strains, one (serogroup I) giving an acute the other (serogroup 3) giving a protracted illness, induced a pyrexia and similar pneumonic lesions. With both strains there was a bacteraemia with early decreases in serum iron and zinc and increases in serum copper concentrations. Marked changes in other serum components were evident only in those animals which had protracted illness (serogroup 3-infected animals). These included transient increases in aminotransferase, creatine kinase and sorbitol dehydrogenase activities and triglyceride levels, together with gradual decreases in alkaline phosphatase and leucine aminopeptidase activities. Serum lysozyme activity and acute-phase protein synthesis increased, as did the ratio of phenylalanine to tyrosine. The findings confirm the relevance of the aerosol-infected guinea-pig model for the investigation of the disease processes and evaluation of therapeutic measures for use in man.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Kaufmann A. F. Exotoxin activity associated with the Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):453–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.453-456.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H., Miller R. D. Identification of a cytotoxin produced by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.271-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girod J. C., Reichman R. C., Winn W. C., Jr, Klaucke D. N., Vogt R. L., Dolin R. Pneumonic and nonpneumonic forms of legionellosis. The result of a common-source exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):545–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton P., Baskerville A., Harris-Smith P. W., Bailey N. E. Changes in whole blood and serum components of grivet monkeys with experimental respiratory Francisella tularensis infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Dec;59(6):630–639. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton P., Baskerville A., Marshall R. B., Harris-Smith P. W., Adams G. D. Metabolic sequelae of experimental leptospirosis in grivet monkeys. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Feb;61(1):16–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton P., Stephenson J. R., Baskerville A., Wiblin C. N. Pathogenesis and immune response of vaccinated and unvaccinated rhesus monkeys to tick-borne encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):995–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.995-1003.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: clinical features of 24 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):297–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattimer G. L., Rhodes L. V., 3rd Legionnaires' disease. Clinical findings and one-year follow-up. JAMA. 1978 Sep 8;240(11):1169–1171. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.11.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae A. D., Lewis M. J. Legionnaires' disease in Nottingham. Lancet. 1977 Dec 10;2(8050):1225–1226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Edwards M. L., Smith D. W. Changes in iron and transferrin levels and body temperature in experimental airborne legionellosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):302–307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E. Proteolytic action of Legionella pneumophila on human serum proteins. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):51–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.51-53.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Kallings I., Dahnsjö H., Clemens F. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease in Sweden: report of sixty-eight cases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(1):43–55. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-1.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., George J. R., Reeves M. W., Harrell W. K. Development of a chemically defined liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):615–626. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.615-626.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Neilands J. B., Balows A. Absence of siderophore activity in Legionella species grown in iron-deficient media. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):324–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.324-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D., Grist N. R., Nájera R. Illness associated with "package tours": a combined Spanish-Scottish study. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(1):117–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, DuPont H. L., Pekarek R. S., Powanda M. C., Schwartz A., Hornick R. B., Beisel W. R. An endogenous mediator of depression of amino acids and trace metals in serum during typhoid fever. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):77–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Davis G. S., Gump D. W., Craighead J. E., Beaty H. N. Legionnaires' pneumonia after intratracheal inoculation of guinea pigs and rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):568–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


