Abstract
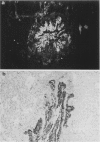
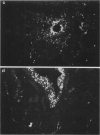
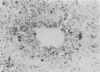
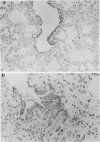
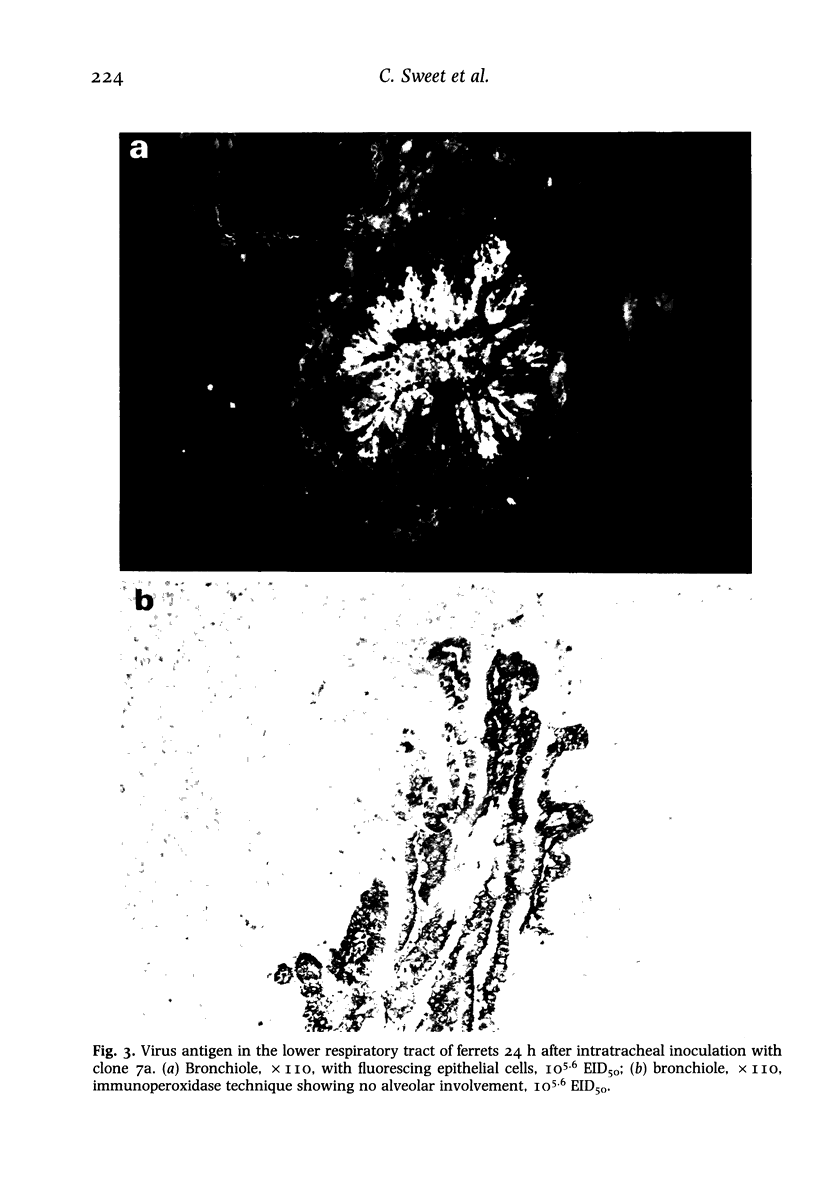
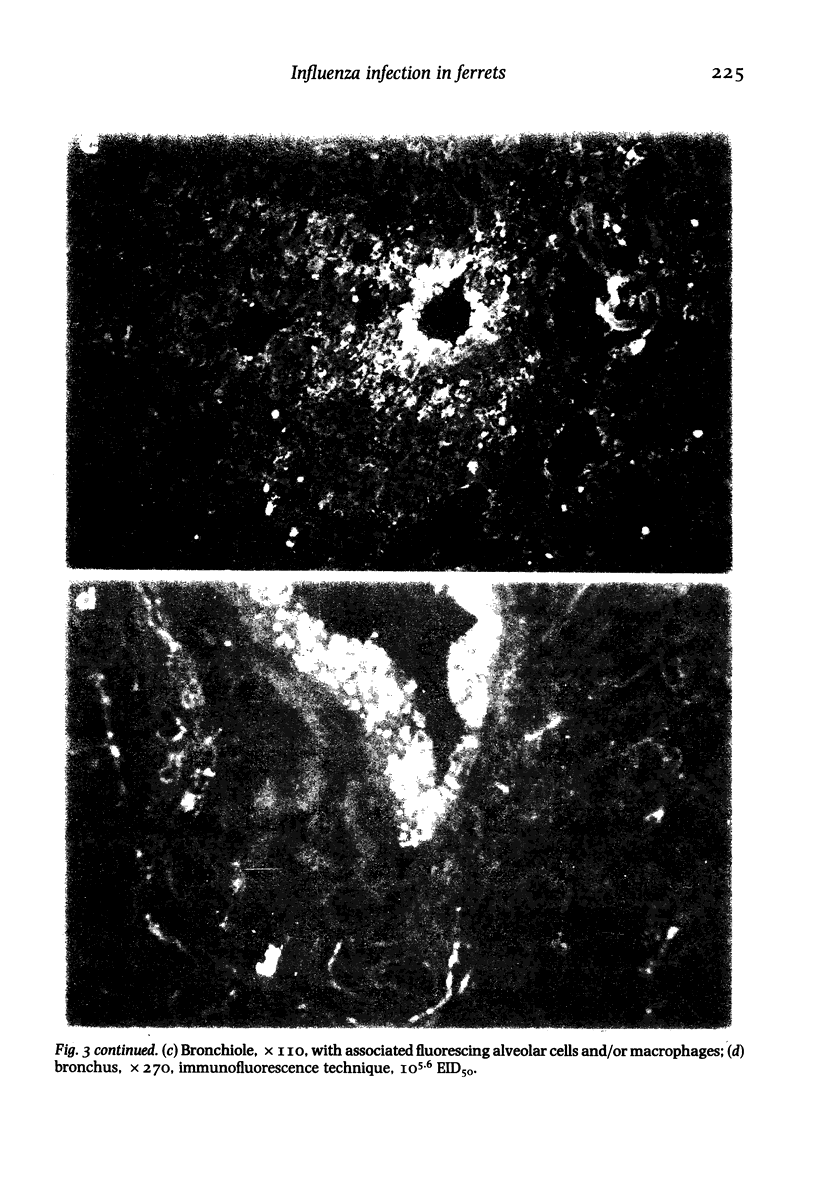
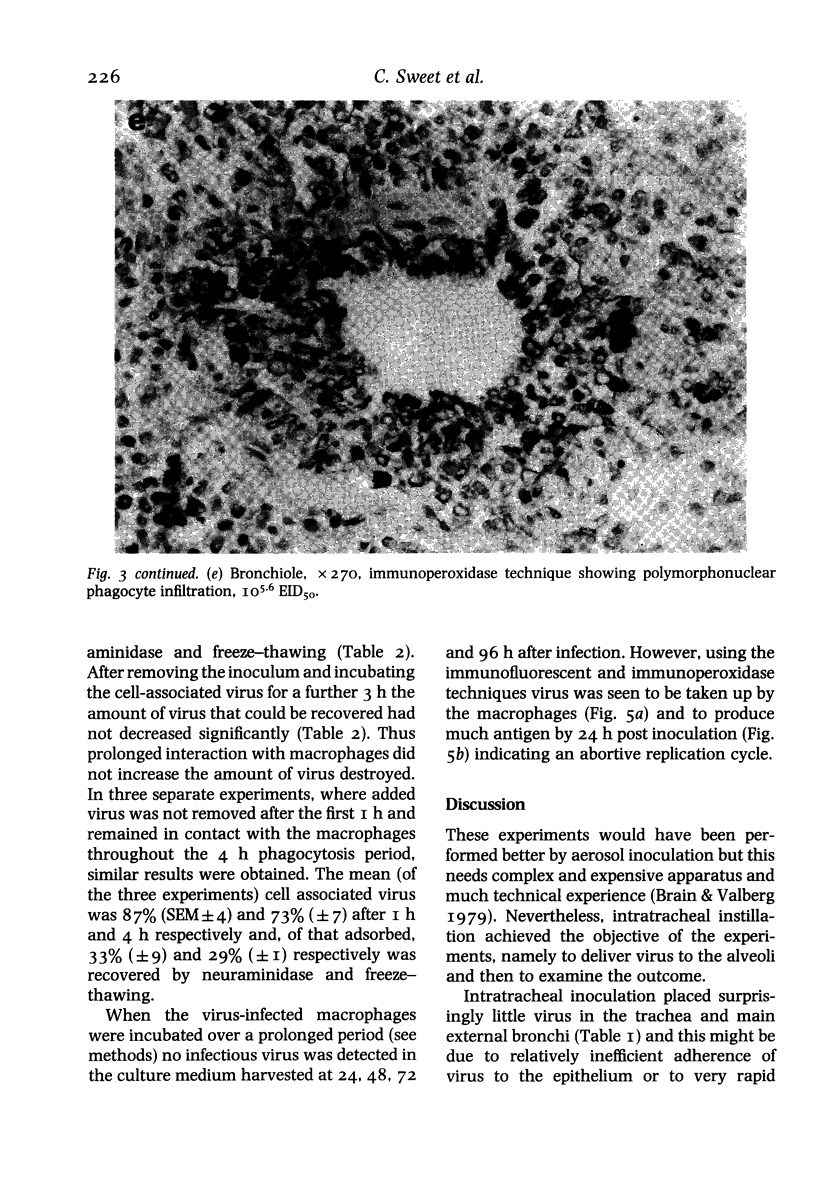
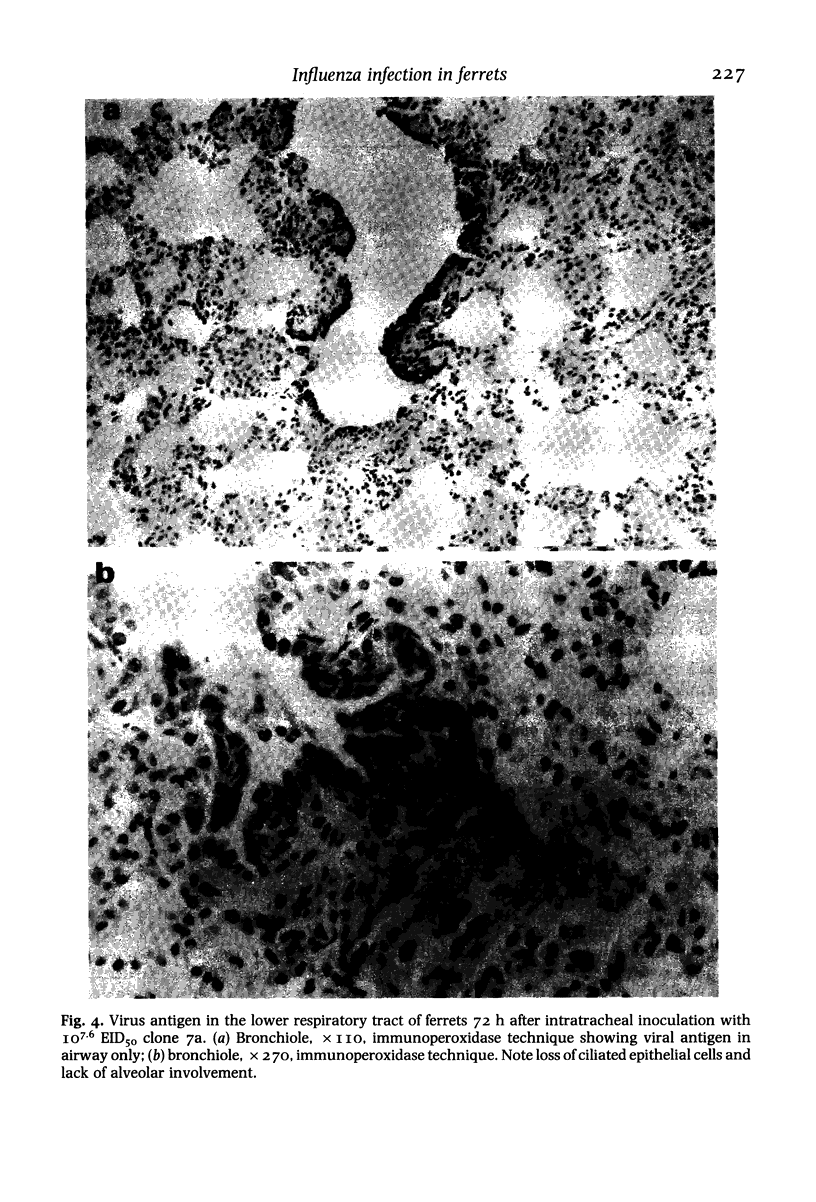
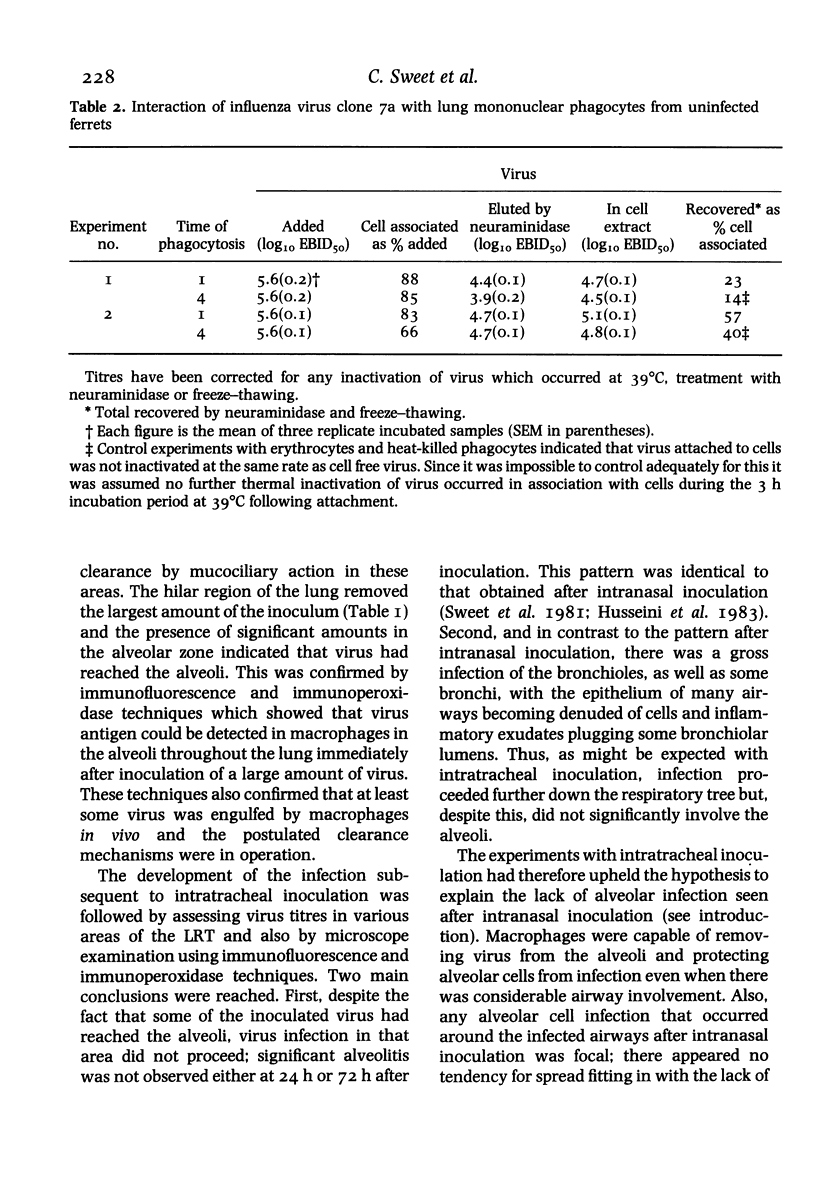
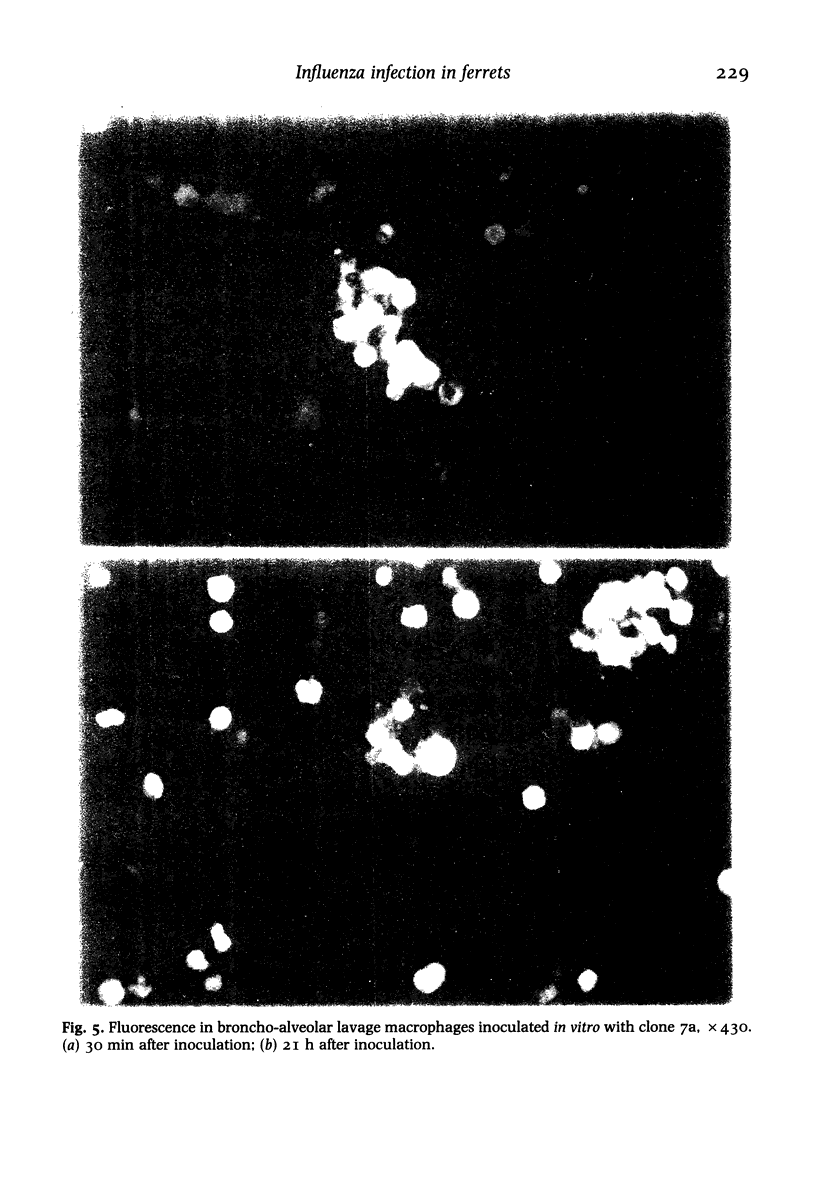
Intratracheal inoculation of influenza virus in the ferret was followed by a more severe airway infection than that produced by nasal infection and was mainly bronchiolar rather than bronchial. Also, virus isolation from the alveolar zone of the lung together with immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase techniques showed that some virus reached the alveoli. Nevertheless, there was no subsequent alveolitis suggesting the existence of a clearance phenomenon. Alveolar macrophages were shown to have phagocytosed virus in vivo and phagocytosis studies in vitro showed that two mechanisms could operate to eradicate the virus. First, a rapid destruction of virus and second an abortive cycle of replication which produced virus antigen but not infectious virus. Experiments with large doses of virus indicated that after intranasal inoculation little virus reached the alveoli so it would probably be quickly cleared by the macrophages.
Full text
PDF


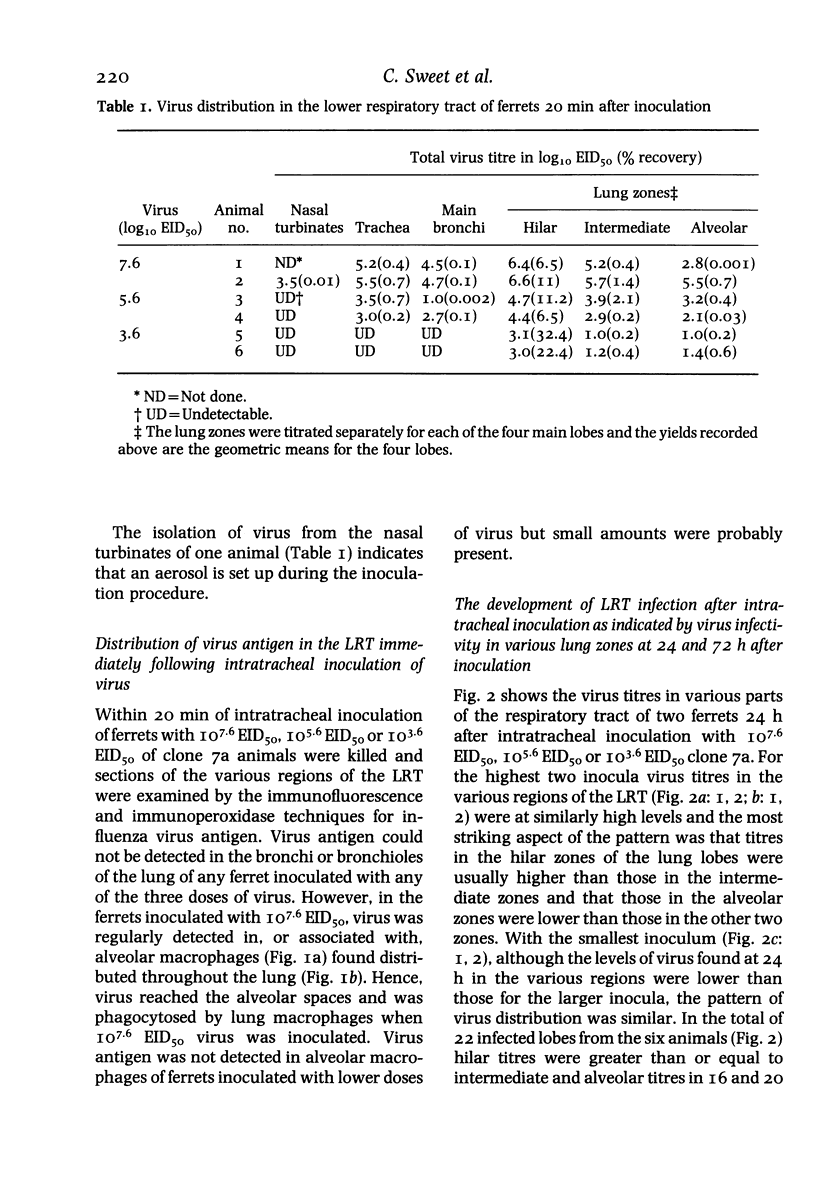
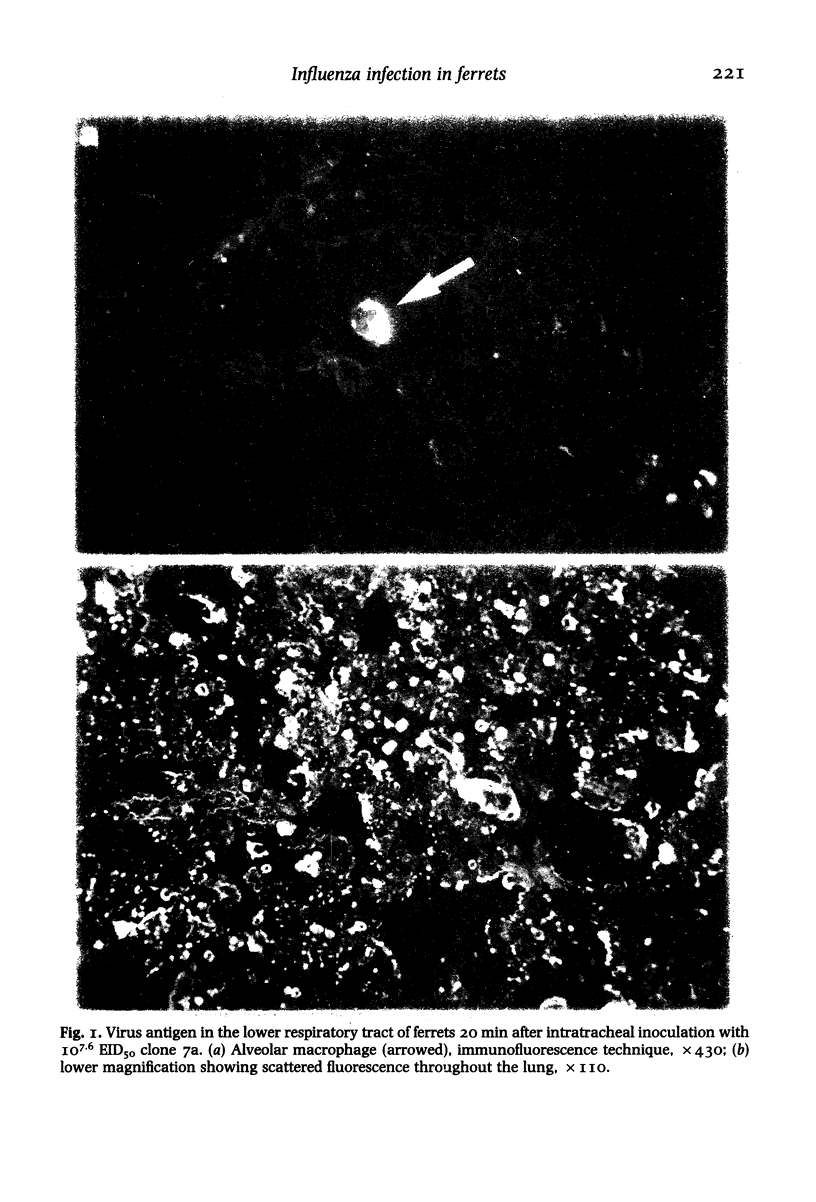
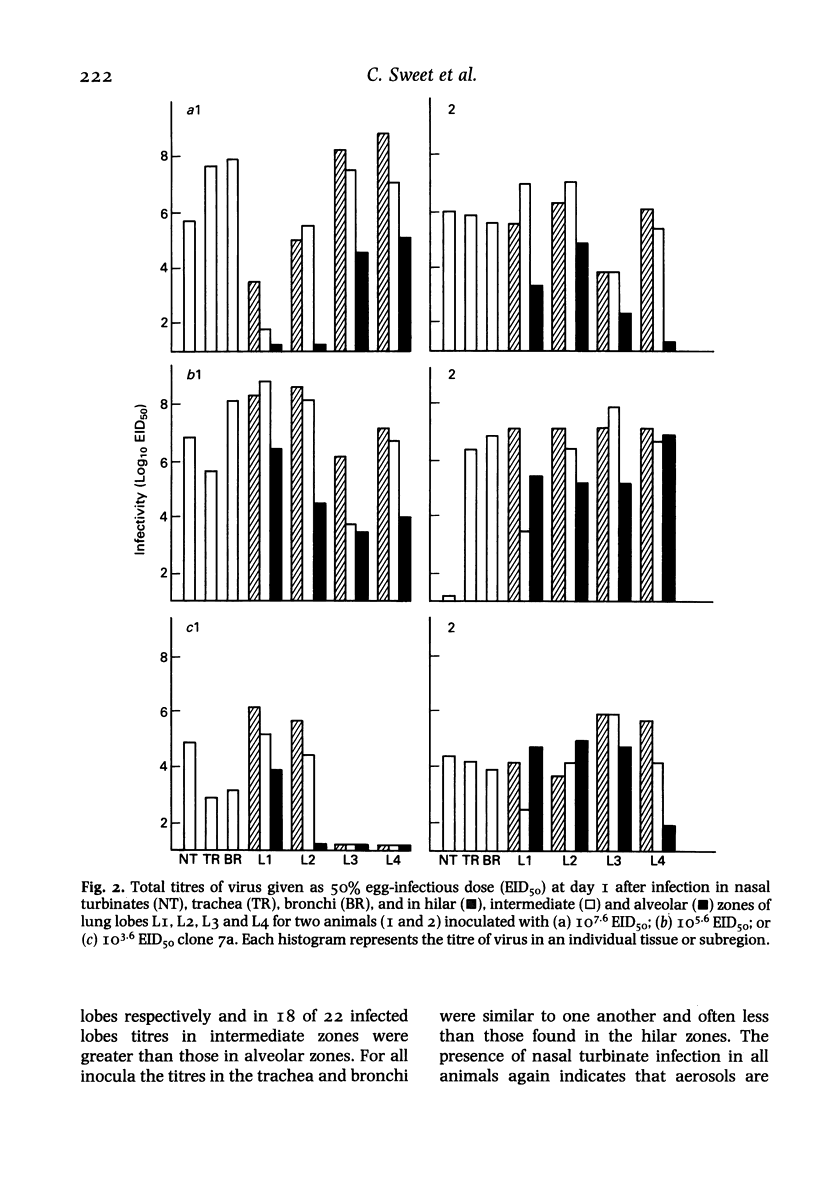



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain J. D., Valberg P. A. Deposition of aerosol in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1325–1373. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Mitkis F., Sweet C., Collie M. H., Smith H. The localization of influenza virus in the respiratory tract of ferrets: susceptible nasal mucosa cells produce and release more virus than susceptible lung cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):505–514. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould E. A., Ratcliffe N. A., Basarab O., Smith H. Studies of the basis of localization of influenza virus in ferret organ cultures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Feb;53(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie A. J., Brown G., Fisher A. G., Khan M. Widespread distribution in human tissues of an antigenic determinant of granulocytes. J Clin Pathol. 1984 May;37(5):555–559. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.5.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husseini R. H., Sweet C., Bird R. A., Collie M. H., Smith H. Distribution of viral antigen with the lower respiratory tract of ferrets infected with a virulent influenza virus: production and release of virus from corresponding organ cultures. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):589–598. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Yeakel-Houlihan D., Lyons C. R., Gleason R. R., Stein-Streilein J. Persistence of influenza as an immunogen in pulmonary antigen-presenting cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.965-972.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B. C., Mims C. A. Influenza virus replication in human alveolar macrophages. J Med Virol. 1982;9(3):177–184. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B. C., Mims C. A. Role of macrophage activation and interferon in the resistance of alveolar macrophages from infected mice to influenza virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1154–1159. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1154-1159.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B., Mims C. A. Interaction of influenza virus with mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.751-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C., Macartney J. C., Bird R. A., Cavanagh D., Collie M. H., Husseini R. H., Smith H. Differential distribution of virus and histological damage in the lower respiratory tract of ferrets infected with influenza viruses of differing virulence. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):103–114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]