Abstract
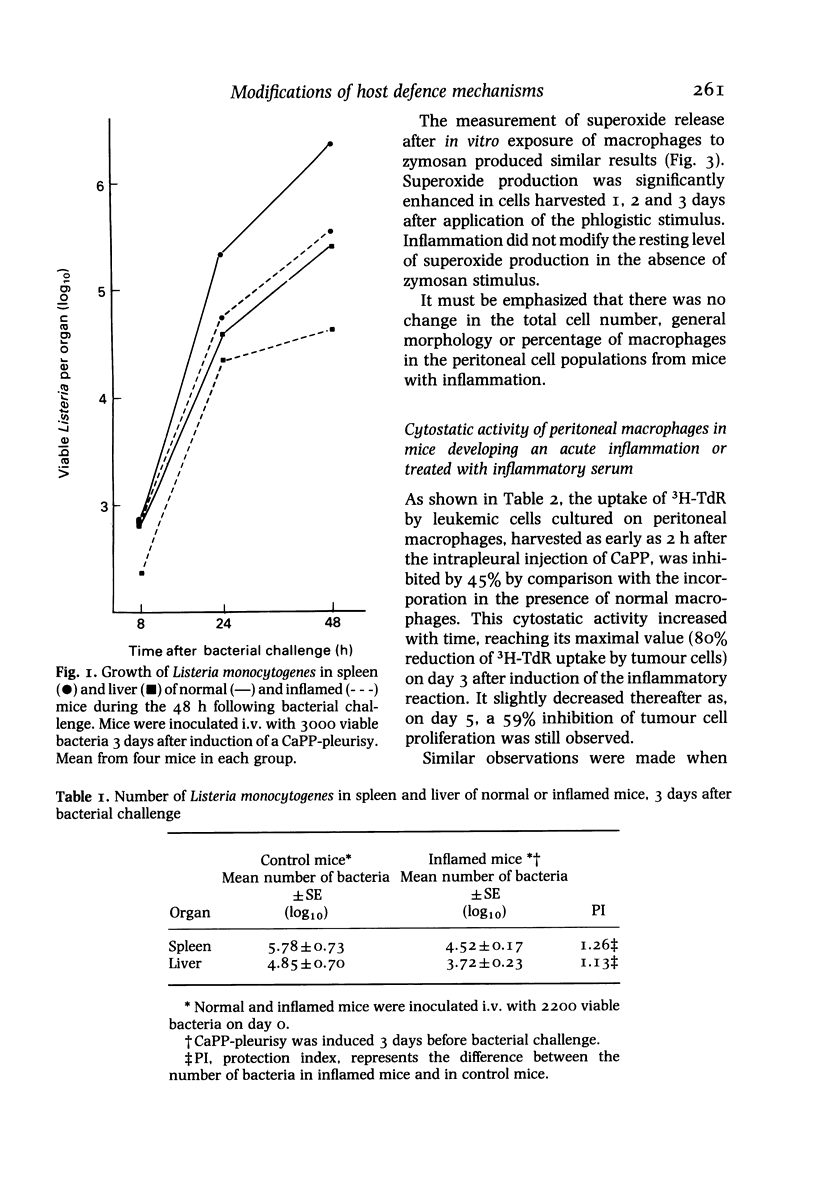
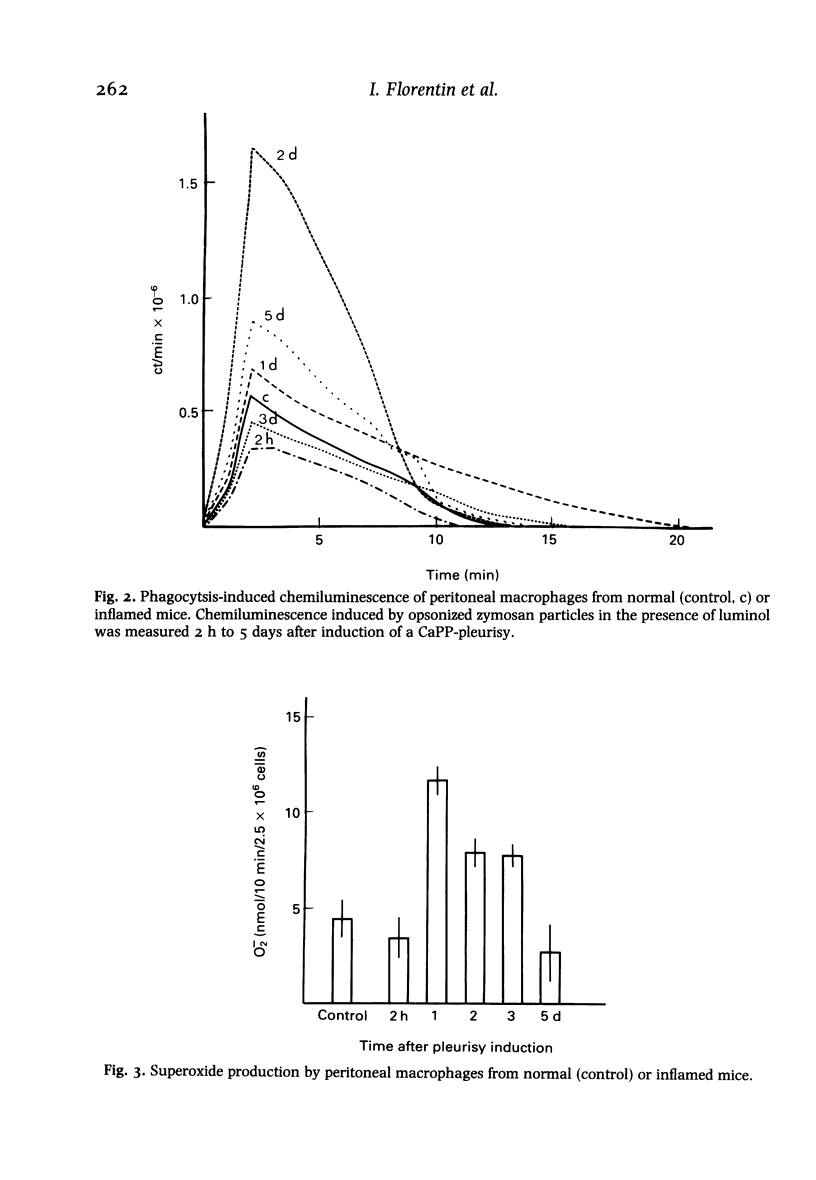
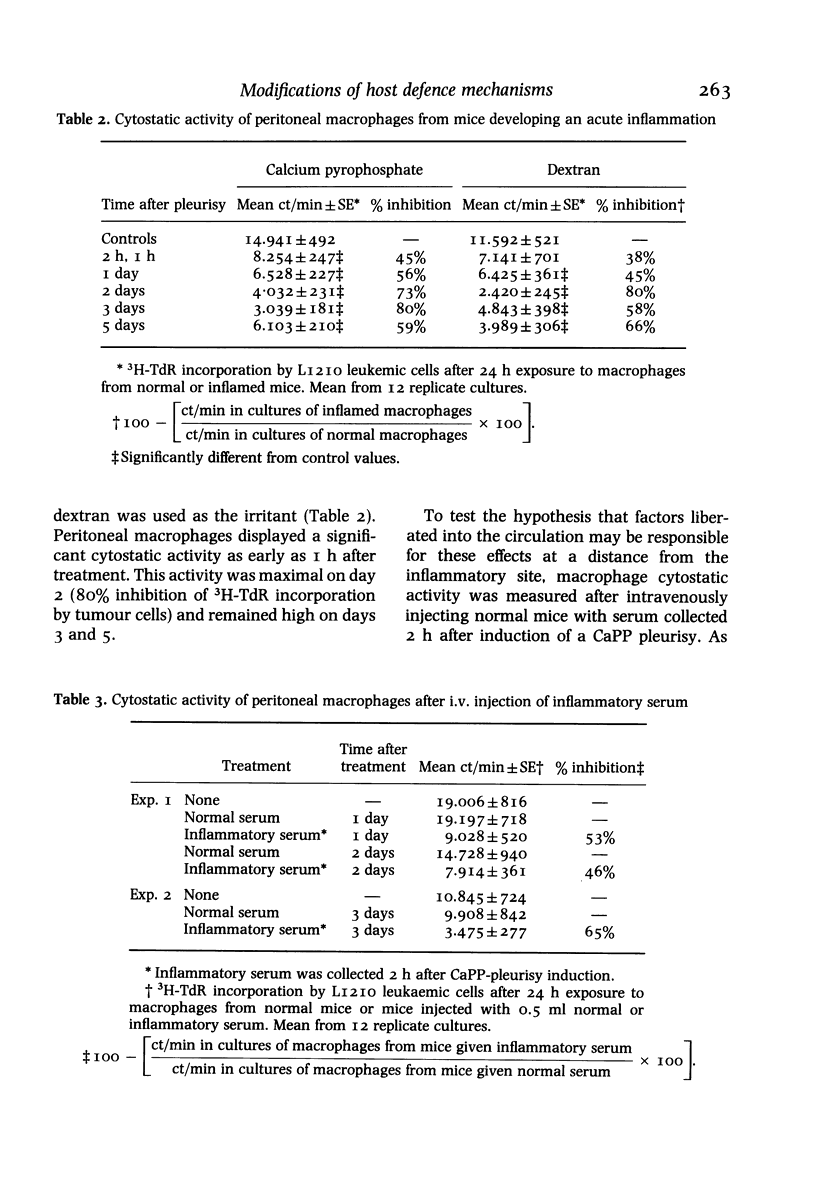
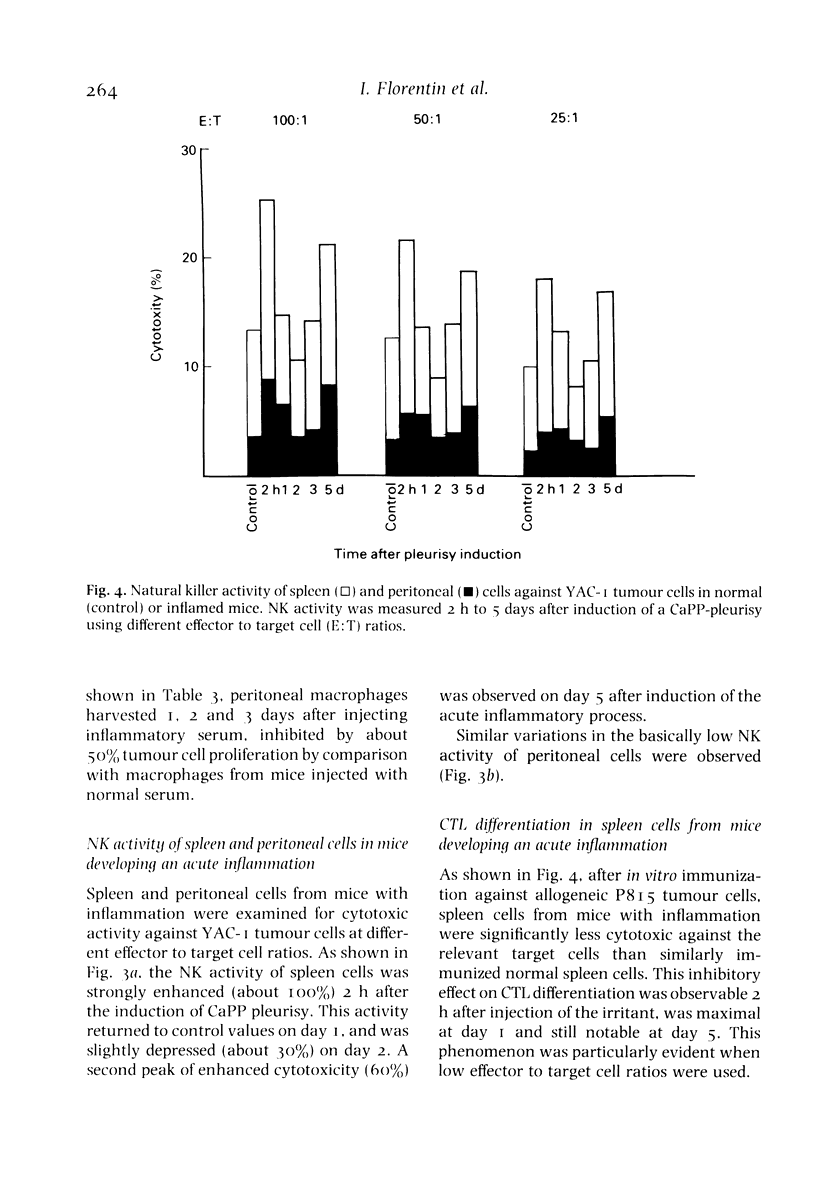
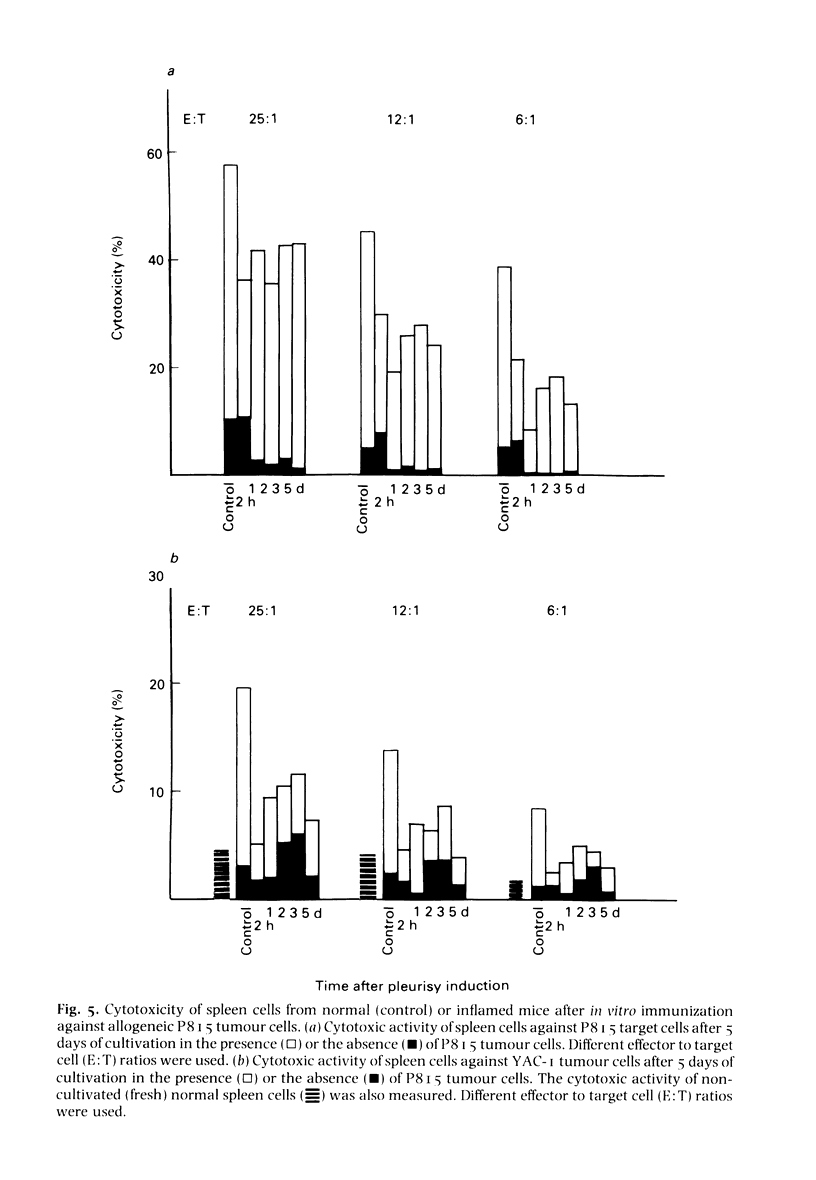
Mice developing an acute non-immunological inflammatory reaction were examined for modification of specific and non-specific defence mechanisms on the basis of previous observations that these animals displayed an increased resistance to bacterial and parasitic infections but an impaired resistance to neoplasia. Local acute inflammation was induced by injection into the pleural cavity of a non-antigenic, endotoxin-free irritant--calcium pyrophosphate microcrystals or low-molecular-weight dextran. Effector functions of macrophages at remote sites from the inflammatory focus were markedly stimulated. This was shown by: (a) an accelerated elimination of Listeria monocytogenes in the liver and spleen of mice with inflammation; (b) the acquisition of cytostatic activity for tumour cells by peritoneal macrophages; and (c) an enhancement of chemiluminescence emission and superoxide production in response to phagocytosis. Natural killer activity of spleen and peritoneal cells was stimulated in a biphasic manner. In contrast, cytolytic T cell differentiation upon in vitro immunization of spleen cells against allogeneic tumour cells was impaired. All these effects were observed very early (2 h) after the onset of inflammation and were still detectable at least 3 days after the inflammatory process had disappeared.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunda M. J., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Inhibition of murine natural killer cell activity by prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Differences in susceptibility of various mouse strains to haemoprotozoan infections: possible correlation with natural killer activity. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Winter;2(4):277–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Haverty T., Fulcher C., Redelman D., Mendelsohn J. Inhibition of human natural cytotoxicity by macromolecular antiproteases. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1569–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Juangbhanich C. W., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. II. The role of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):950–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular kinetics associated with the development of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):299–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G. The tumoricidal properties of inflammatory tissue macrophages and multinucleate giant cells. Am J Pathol. 1979 Aug;96(2):595–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Masucci G., Poros A., Klein E., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. II. Anti-K562 effectors are distinct from allospecific CTL and can be generated from NK-depleted T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1303–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Weidemann M. J. Reactive oxygen production associated with arachidonic acid metabolism by peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91472-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn R. M. Murine T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against syngeneic and allogeneic cell lines induced by fetal calf serum. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 15;54(1):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Miake S., Matsumoto T., Nomoto K., Takeya K. Relationship between non-specific activity of macrophages and immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes. Immunology. 1980 Jul;40(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


