Abstract
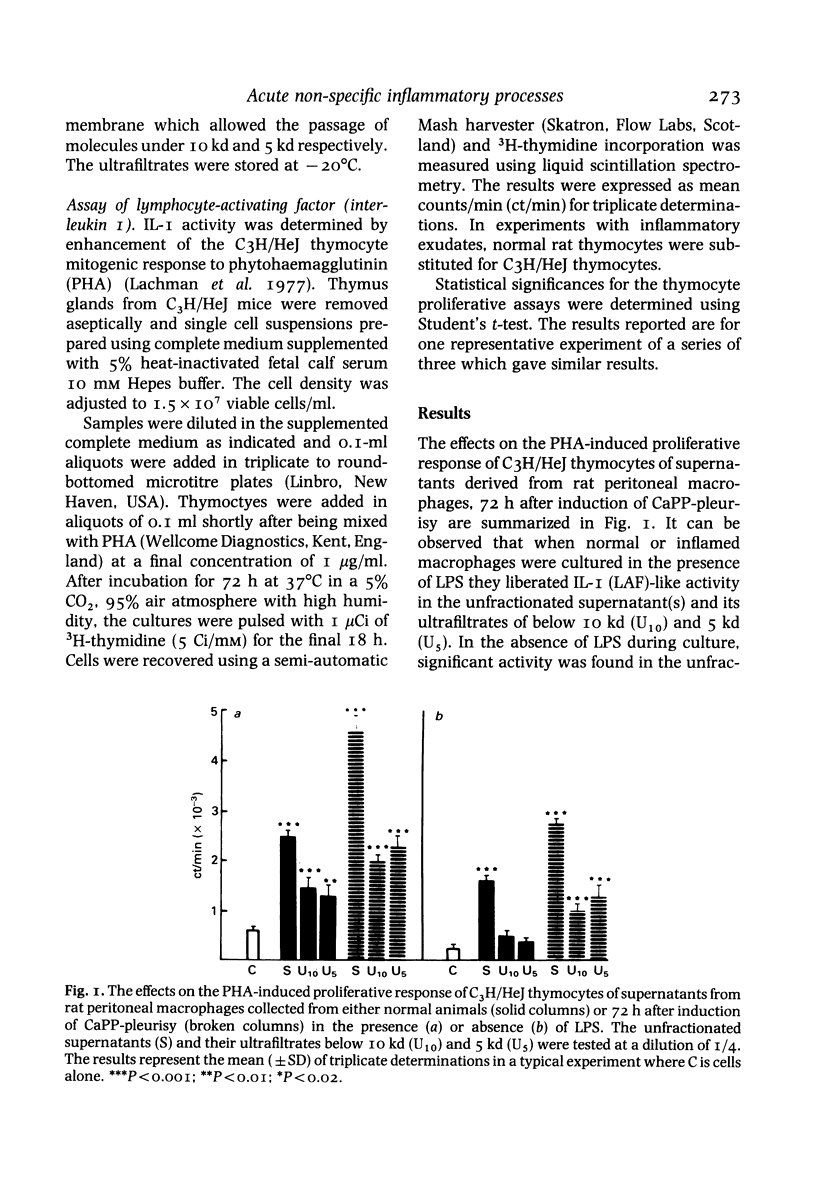
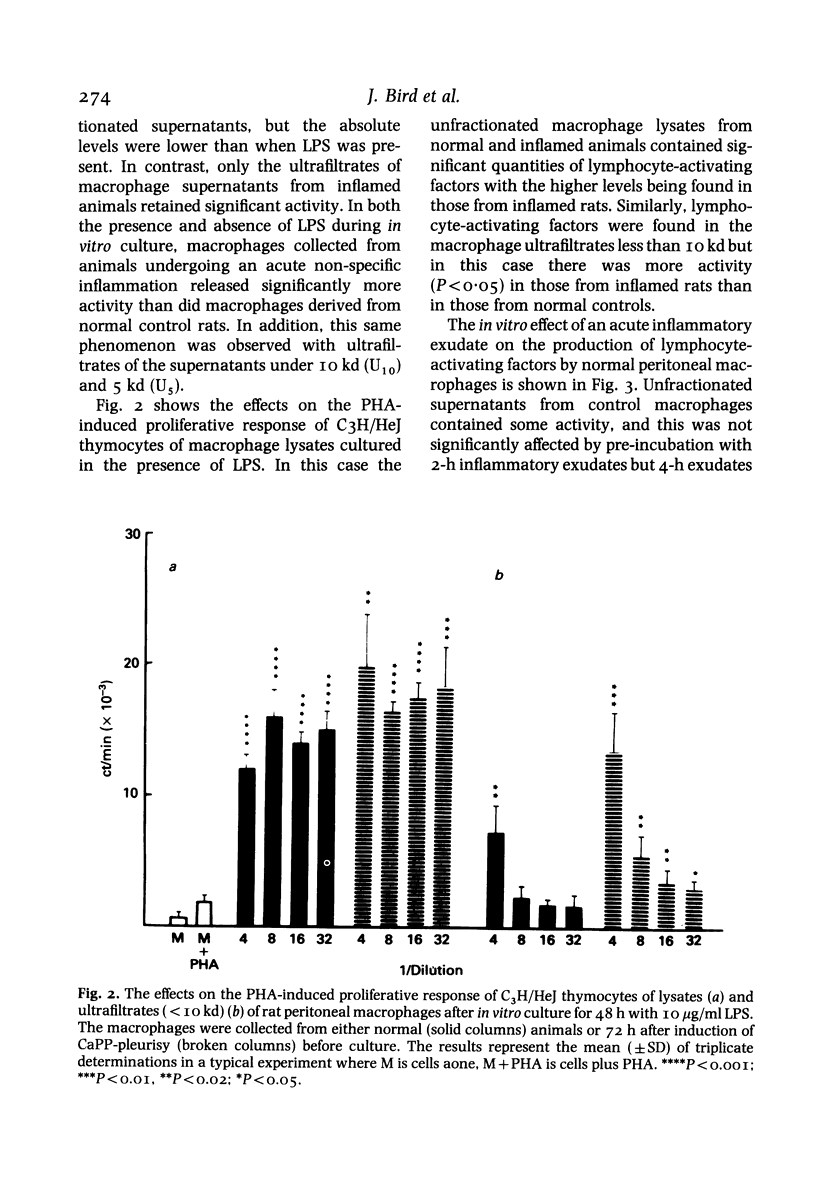
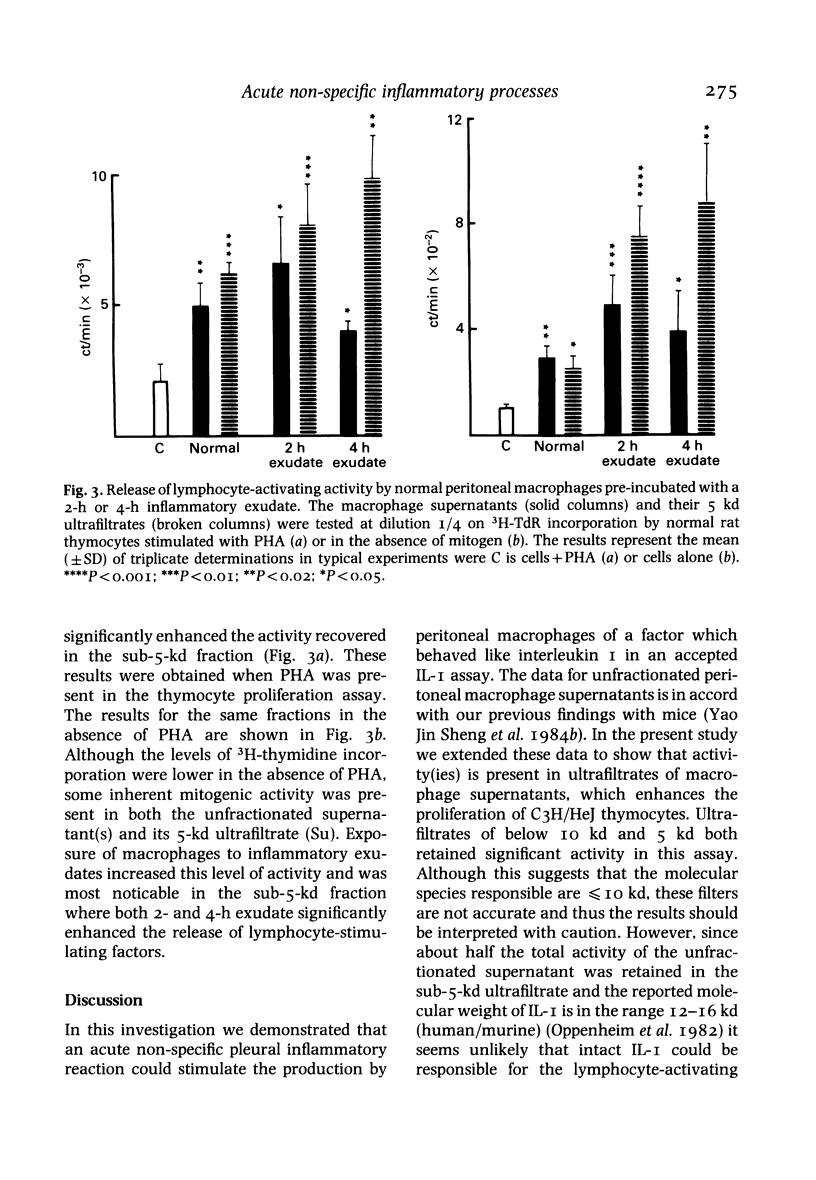
Peritoneal macrophages harvested from rats undergoing an acute non-specific inflammatory reaction induced by an injection of calcium pyrophosphate (CaPP) into the pleural cavity released increased amounts of interleukin I (IL-I)-like material. Lymphocyte-activating factors were also found in ultrafiltrates of the macrophage supernatants below 10 kd and 5 kd. A similar pattern of activity was observed when lysates of the macrophages were tested. In addition pre-exposure of normal peritoneal macrophages to an acute pleural inflammatory exudate before supernatant production enhanced the release of lymphocyte-activating factors found both in the unfractionated supernatant and a sub-5-kd ultrafiltrate. Thus these results demonstrate that an acute inflammatory reaction, initiated by a non-antigenic stimulus is able to stimulate macrophages remote from the inflammatory site to produce a factor which behaves like IL-I in a standard IL-I assay. The presence of low-molecular-weight factors (less than 5 kd) with similar activity may suggest that degradation of IL-I has taken place to yield active fragments. Acute inflammatory exudate also augments release of these factors which may be important in the pathogenesis of inflammation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gery I., Davies P., Derr J., Krett N., Barranger J. A. Relationship between production and release of lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1) by murine macrophages. 1. Effects of various agents. Cell Immunol. 1981 Nov 1;64(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroud J. P., Pelletier M., Girre C. Pouvoir mitogène de sérums de rats porteurs d'une inflammation aiguë vis-à-vis de macrophages en culture. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1977 Oct 31;285(11):1143–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girre C., Pelletier M., Giroud J. P. Mise en évidence, au cours de réactions inflammatoires aiguës, d'un facteur sérique mitogène pour les macrophages. J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr-Jun;12(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa Y., Sawada S., Sawada J., Osawa T. Lymphocyte-potentiating factor from human peripheral blood adherent cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;57(5):451–461. doi: 10.1159/000232137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier M., Girre C., Dunn C. J., Willoughby D. A., Giroud J. P. Induction of macrophage DNA synthesis in vitro by non-immunological inflammatory exudates: effect of irradiation and thymus or bone marrow cell reconstitution. J Pathol. 1978 Oct;126(2):95–101. doi: 10.1002/path.1711260207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


