Abstract
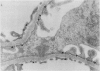
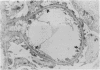
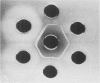
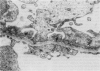
This reports a perfusion study using avidin, a native cation macromolecule, followed by rat anti-avidin antibody given directly into the rat renal artery. After 10 min perfusion with avidin, an indirect immunofluorescent study revealed a fine granular distribution of rat IgG along the glomerular capillary loops; an electromicroscopic study showed small particles at sites identical to the position of the anionic sites of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). After 10 min perfusion with anti-avidin antibody following avidin, rat IgG was heavily deposited along the glomerular capillary loops and electron-dense deposits were observed subendothelially. Rats were administered also intravenous avidin followed 1 h later by rat anti-avidin antibody. The staining pattern of rat IgG, initially almost linear, became granular along the glomerular capillary loops by 72 h. Twenty-four hours later small electron dense deposits, initially localized subendothelially, were found in the subepithelial region with swelling of epithelial foot processes. These observations show that avidin binds to the anionic sites of the GBM, acts as a planted antigen, and results in in situ immune-complex formation.
Full text
PDF

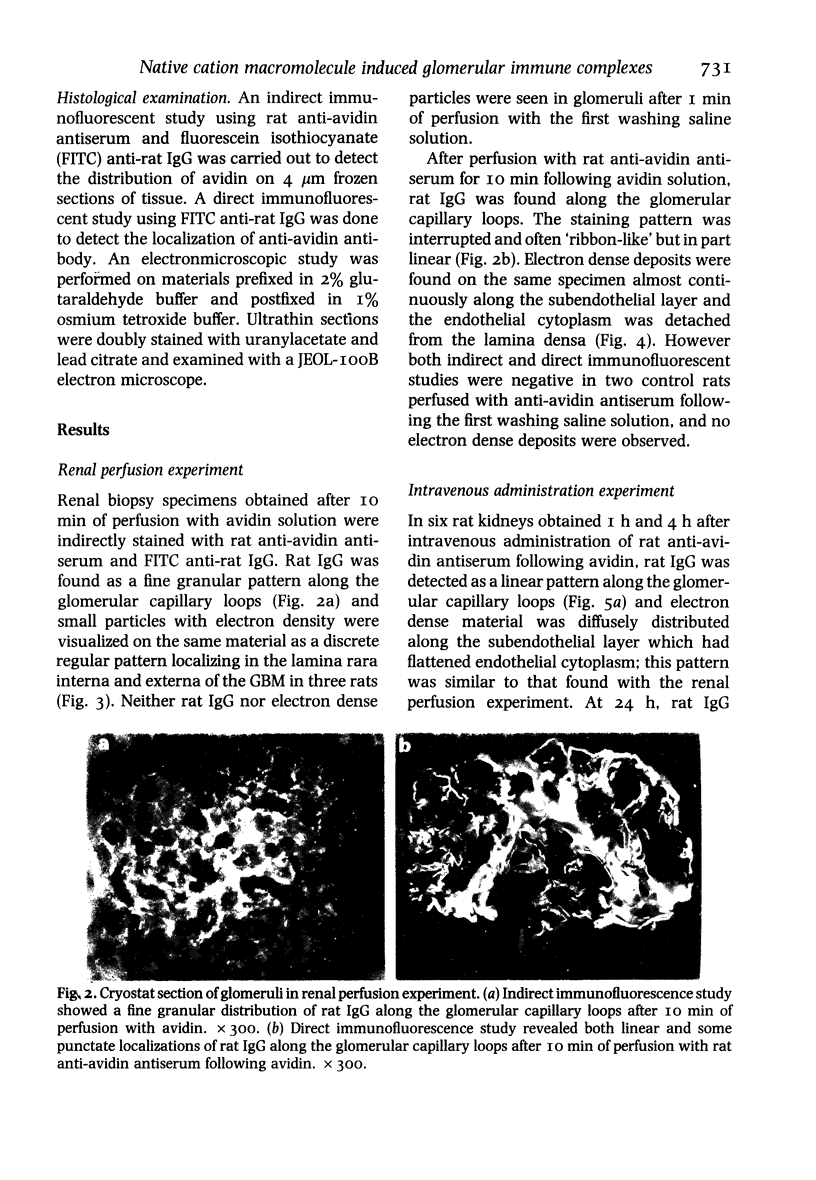
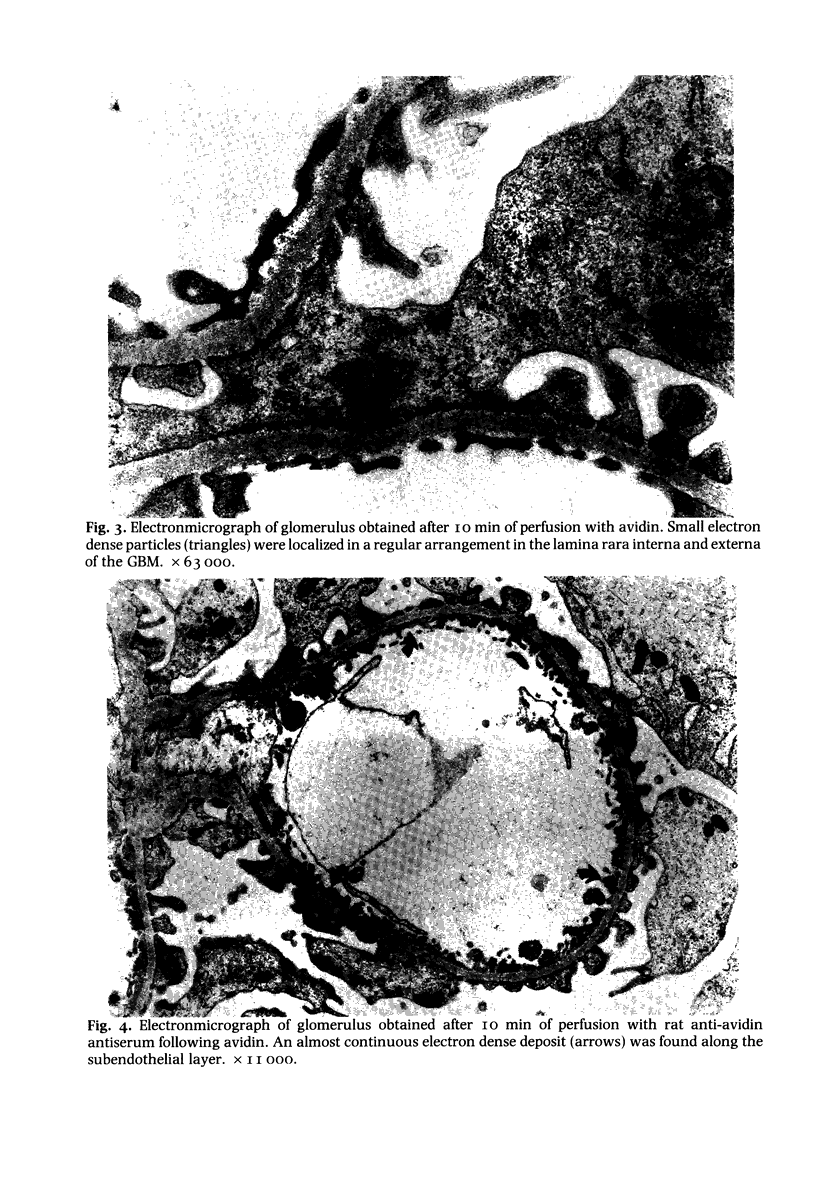
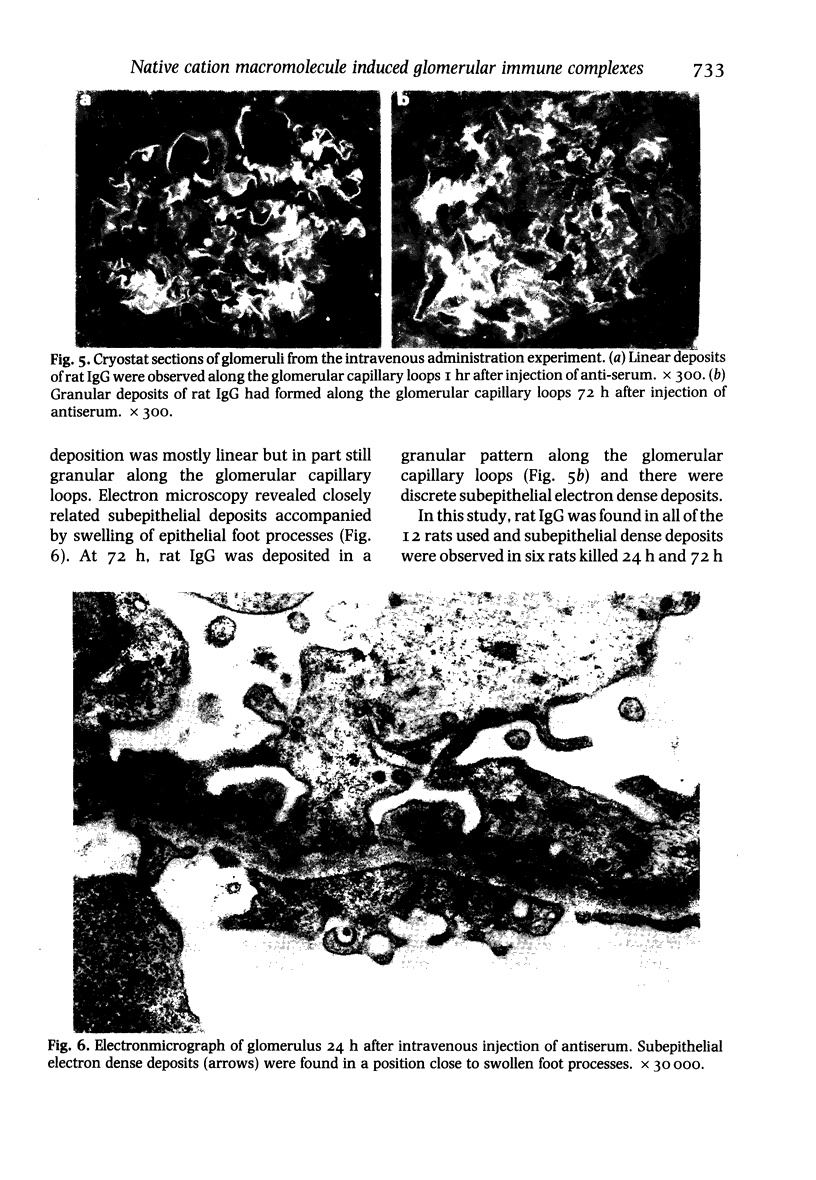


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batsford S. R., Takamiya M., Vogt A. A model of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat employing cationized ferritin. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Nov;14(5):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H. Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):451–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI110469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Salant D. J. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. D., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F. The ultrastructure of the functioning kidney. Lab Invest. 1967 Feb;16(2):220–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Bricteux N., Salmon J., Miescher P. A. Dynamics of immune complex nephritis during antibody excess. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(1):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000231026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Batsford S., Rodríguez-Iturbe B., García R. Cationic antigens in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Dec;20(6):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Rohrbach R., Shimizu F., Takamiya H., Batsford S. Interaction of cationized antigen with rat glomerular basement membrane: in situ immune complex formation. Kidney Int. 1982 Jul;22(1):27–35. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]