Abstract
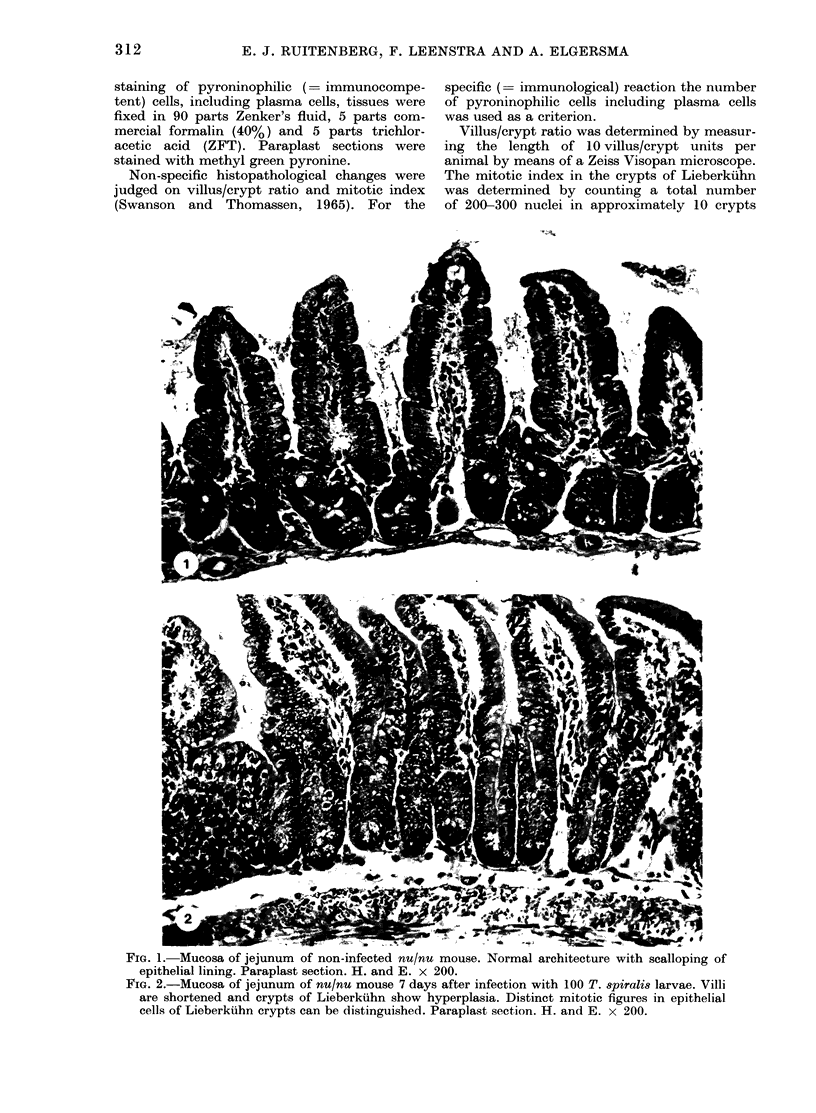
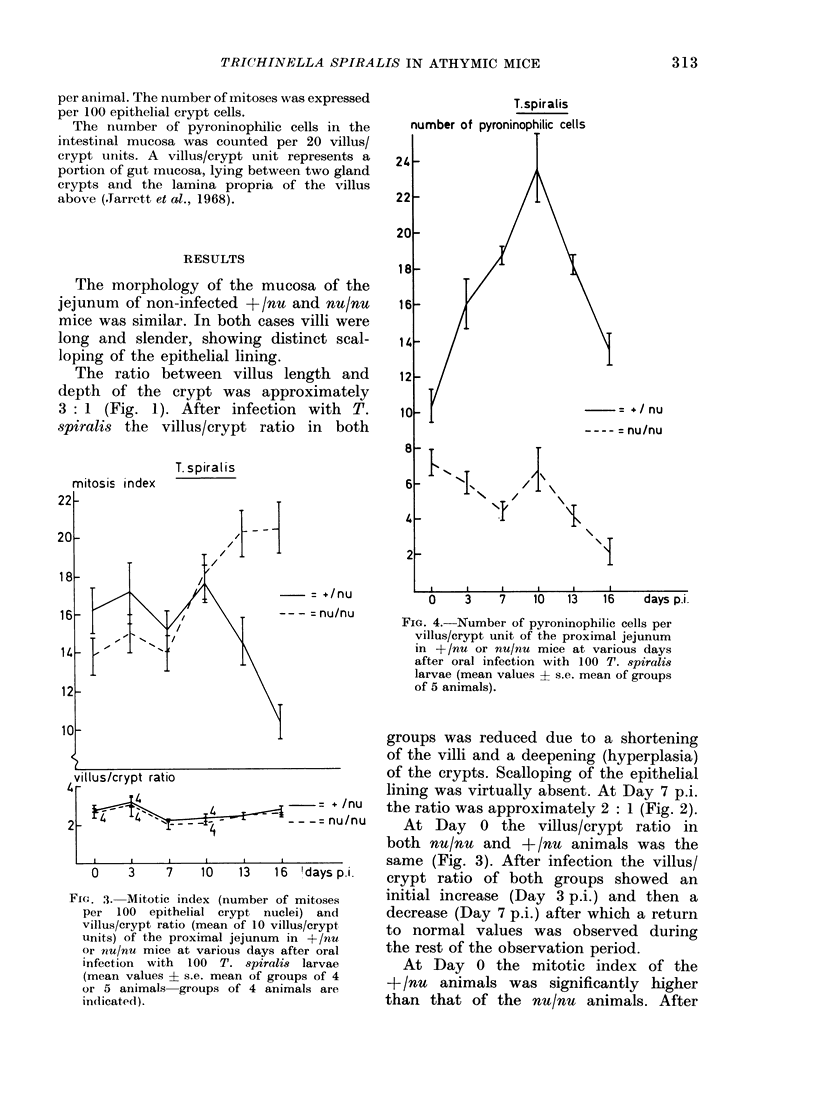
The hypothesis that non-specific histopathological gut changes are thymus-dependent was tested in a helminth infection--the nematode Trichinella spiralis. The study was performed in congenitally athymic (nu/nu) mice and their thymus-bearing heterozygous litter-mates (+/mu). The non-specific histopathological changes of the small intestine were judged on villus/crypt ratio and mitotic index; for the specific (= immunological) reaction the number of pyroninophilic cells in the small intestine was used as criterion. T. spiralis induced non-specific histopathological reactions both in nu/nu and +/nu mice, whereas the number of pyroninophilic cells was only increased in +/nu mice. It was concluded that the immunological reaction was dependent on the immune status of the host, whereas the non-specific histopathological changes were not, i.e. they were thymus-independent.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ferguson A., Jarrett E. E. Hypersensitivity reactions in small intestine. I Thymus dependence of experimental 'partial villous atrophy'. Gut. 1975 Feb;16(2):114–117. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Steerenberg P. A. Intestinal phase of Trichinella spiralis in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. J Parasitol. 1974 Dec;60(6):1056–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSON V. L., THOMASSEN R. W. PATHOLOGY OF THE JEJUNAL MUCOSA IN TROPICAL SPRUE. Am J Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:511–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




