Abstract
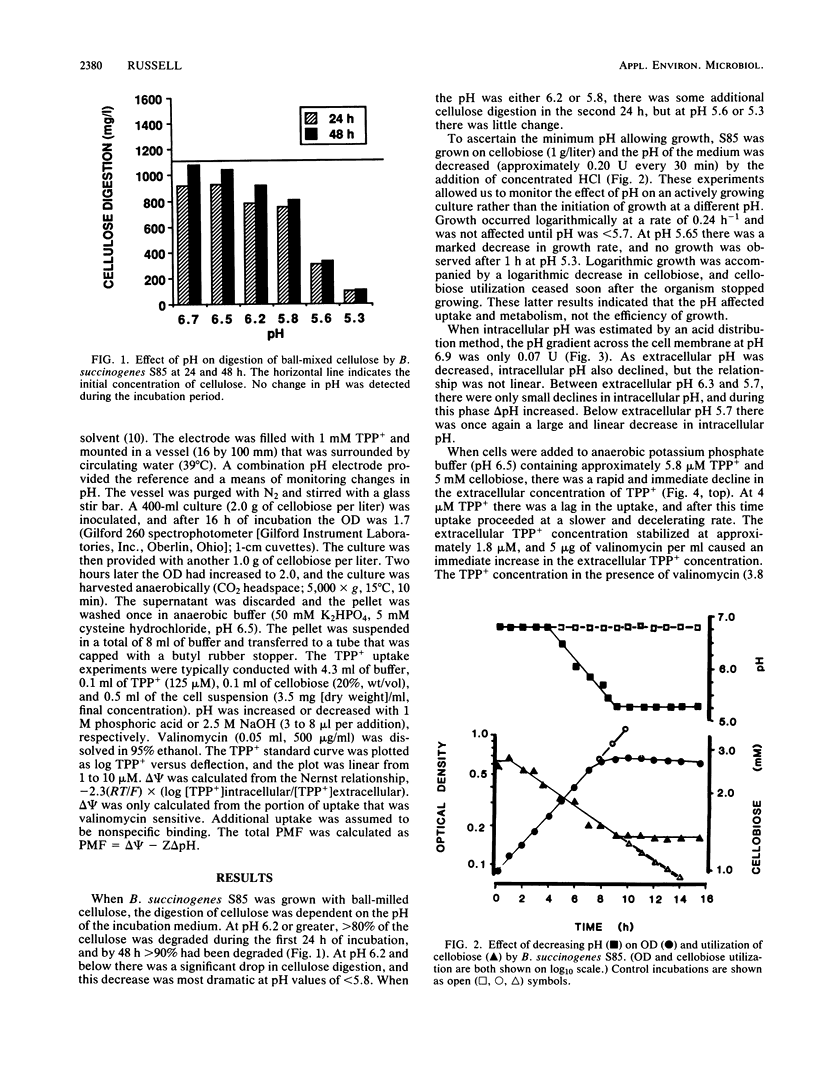
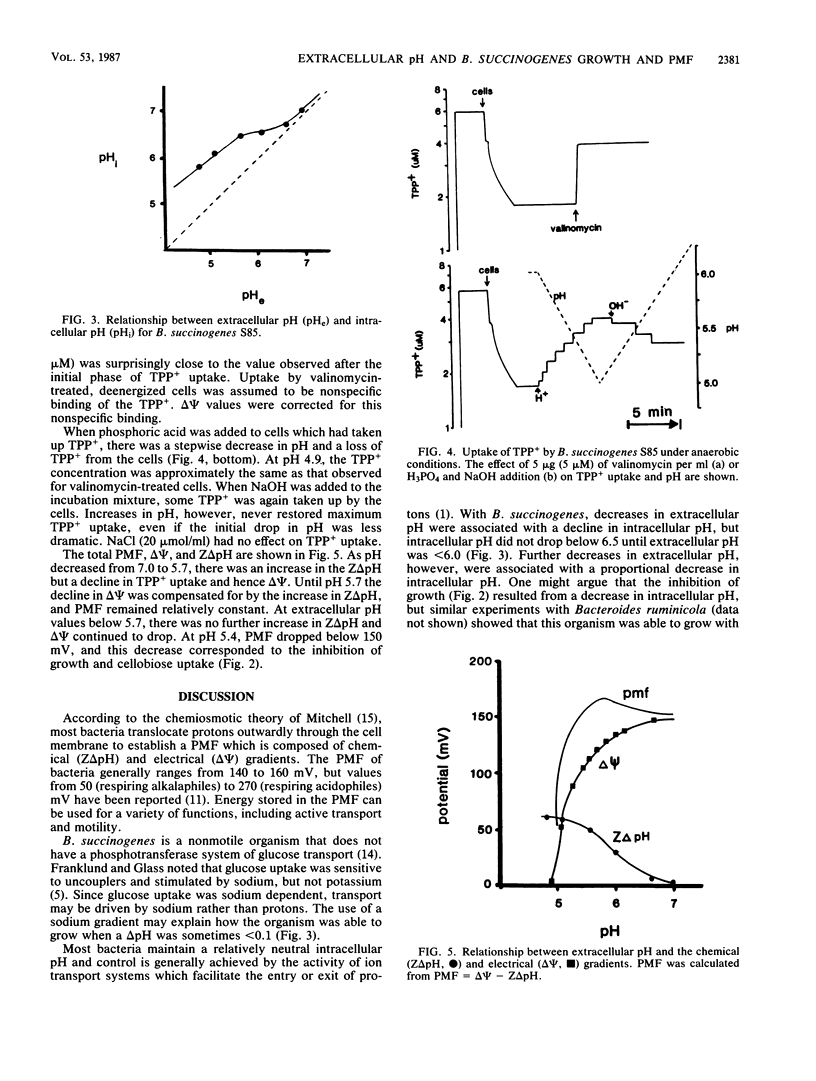
The utilization of cellulose or cellobiose by Bacteroides succinogenes S85 was severely inhibited at pH values of less than 5.7. Since low pH inhibited the utilization of both cellobiose and cellulose, changes in cellulase activity could not explain the effect. At an extracellular pH of 6.9, the pH gradient (delta pH) across the cell membrane was only 0.07 U. As extracellular pH declined from 6.9 to 5.7, intracellular pH decreased to a smaller extent than extracellular pH and delta pH increased. Below pH 5.7, there was a linear and nearly proportional decrease in intracellular pH. B. succinogenes took up the lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium ion (TPP+) in the presence of cellobiose, and uptake was sensitive to the ionophore valinomycin. As pH was decreased with phosphoric acid, the cells lost TPP+ and electrical potential, delta psi, decreased. From extracellular pH 6.9 to 5.7, the decrease in delta psi was compensated for by an increase in delta pH, and the proton motive force ranged from 152 to 158 mV. At a pH of less than 5.7, there was a large decrease in proton motive force, and this decrease corresponded to the inhibition of cellobiose utilization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional requirements of the predominant rumen cellulolytic bacteria. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Wolin M. J. Effect of monensin and lasalocid-sodium on the growth of methanogenic and rumen saccharolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklund C. V., Glass T. L. Glucose uptake by the cellulolytic ruminal anaerobe Bacteroides succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.500-506.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino T., Russell J. B. Effect of reducing-equivalent disposal and NADH/NAD on deamination of amino acids by intact rumen microorganisms and their cell extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1368–1374. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1368-1374.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamo N., Muratsugu M., Hongoh R., Kobatake Y. Membrane potential of mitochondria measured with an electrode sensitive to tetraphenyl phosphonium and relationship between proton electrochemical potential and phosphorylation potential in steady state. J Membr Biol. 1979 Aug;49(2):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01868720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J. M., Farrand J. R., Montgomery L. Cellulolytic and non-cellulolytic bacteria in rat gastrointestinal tracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1428–1434. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1428-1434.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Russell J. B. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation of hexoses by ruminal bacteria: evidence for the phosphotransferase transport system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1348–1352. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1348-1352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery L., Macy J. M. Characterization of rat cecum cellulolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1435–1443. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1435-1443.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riebeling V., Thauer R. K., Jungermann K. The internal-alkaline pH gradient, sensitive to uncoupler and ATPase inhibitor, in growing Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Dombrowski D. B. Effect of pH on the efficiency of growth by pure cultures of rumen bacteria in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):604–610. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.604-610.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. S. Factors affecting the cellulolytic activity of rumen contents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):497–502. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.497-502.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Pond W. G. Enumeration and activity of cellulolytic bacteria from gestating swine fed various levels of dietary fiber. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):858–862. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.858-862.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


