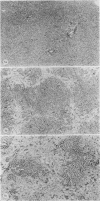
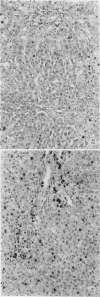
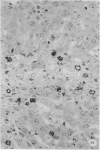
Abstract
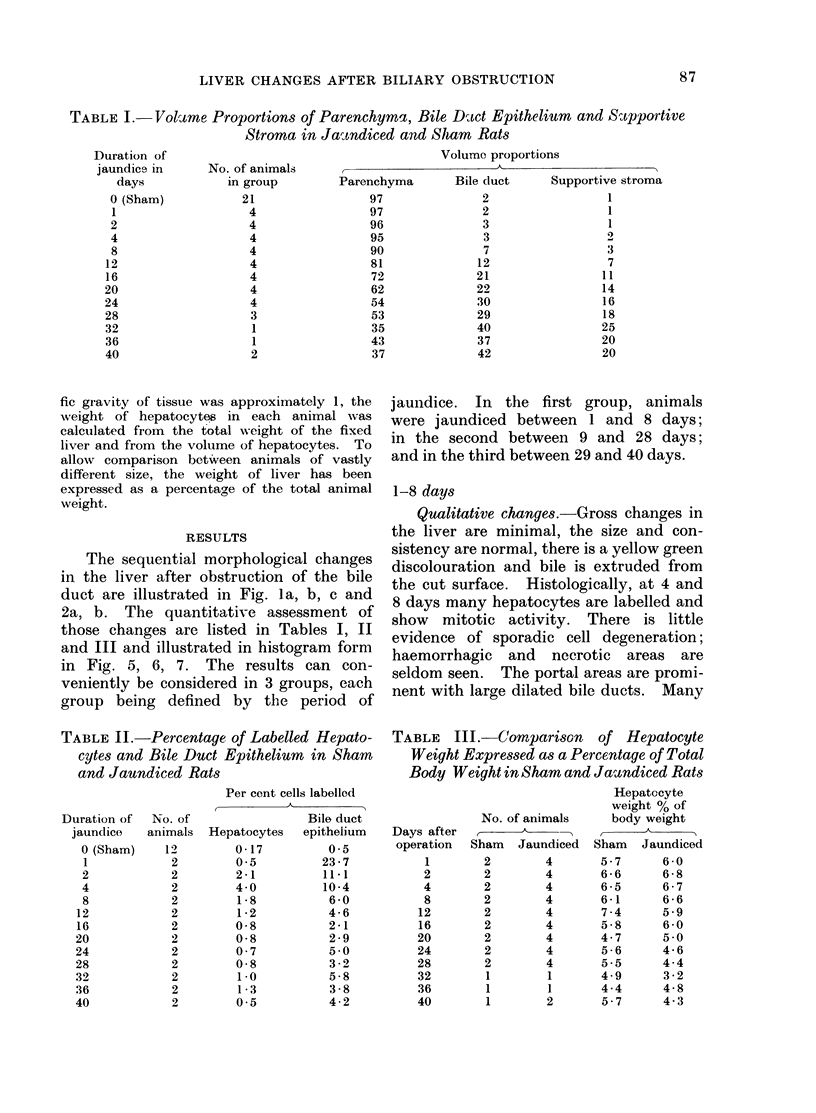
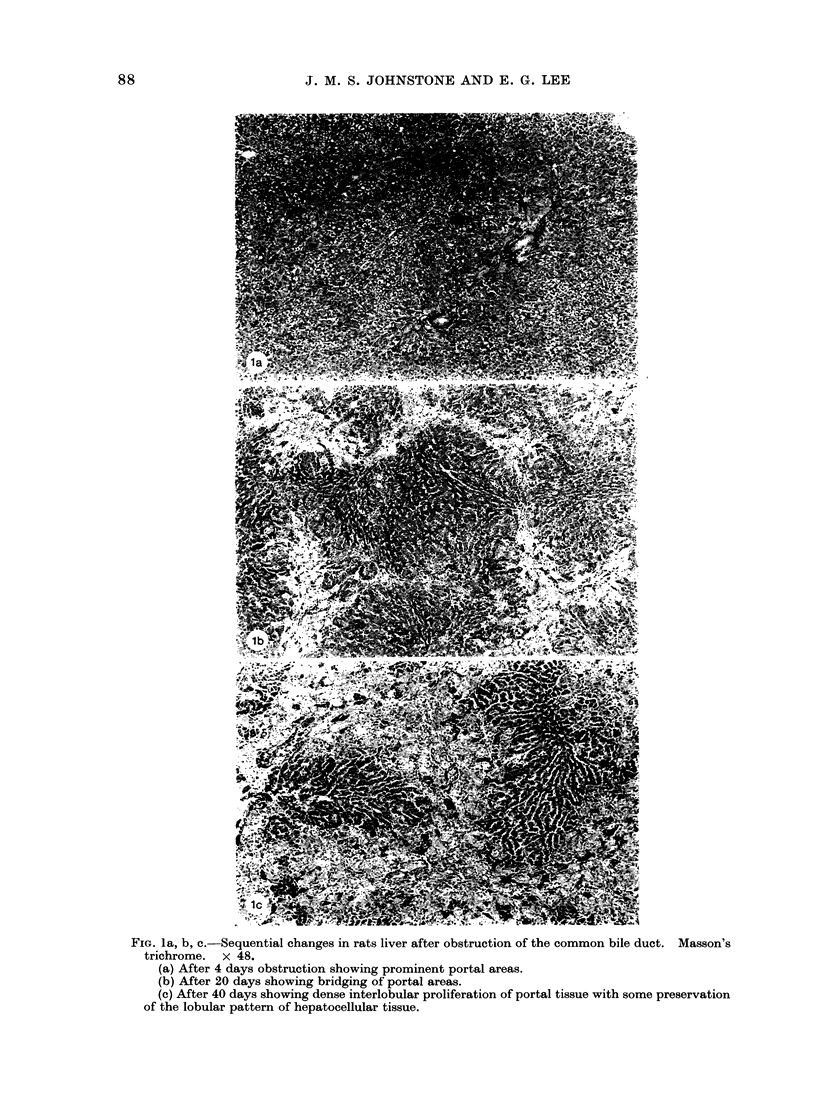
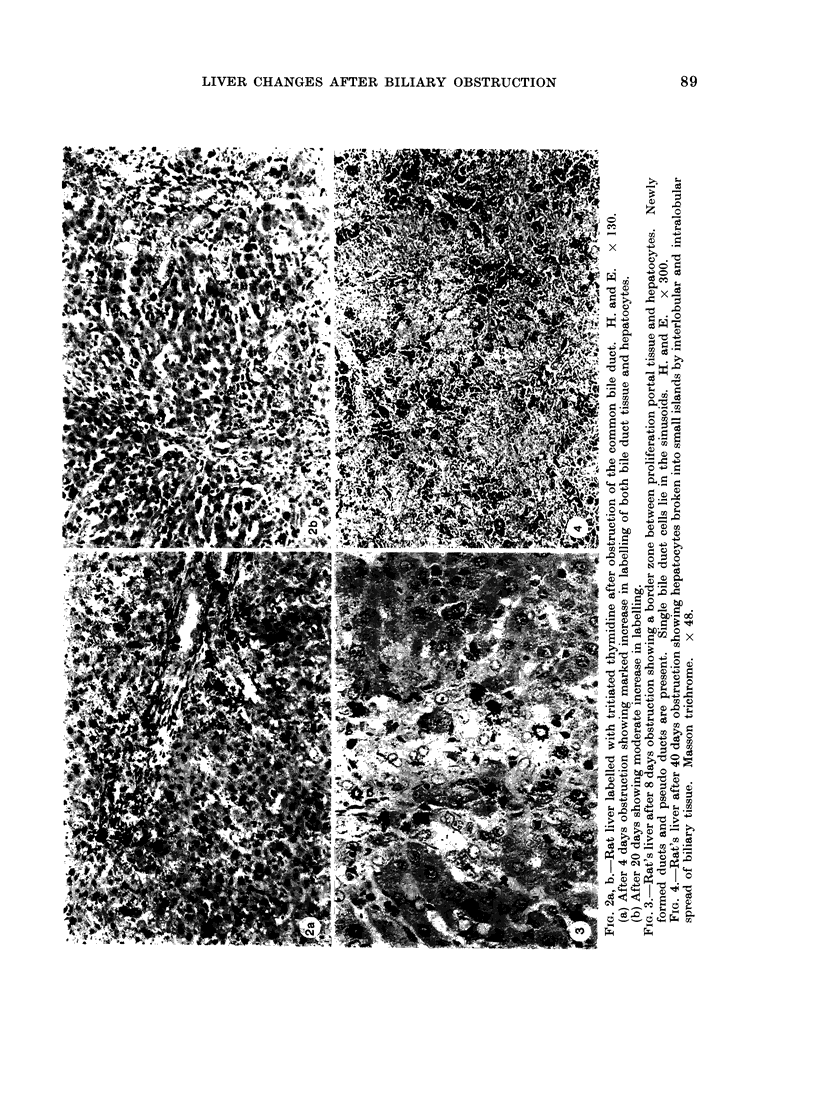
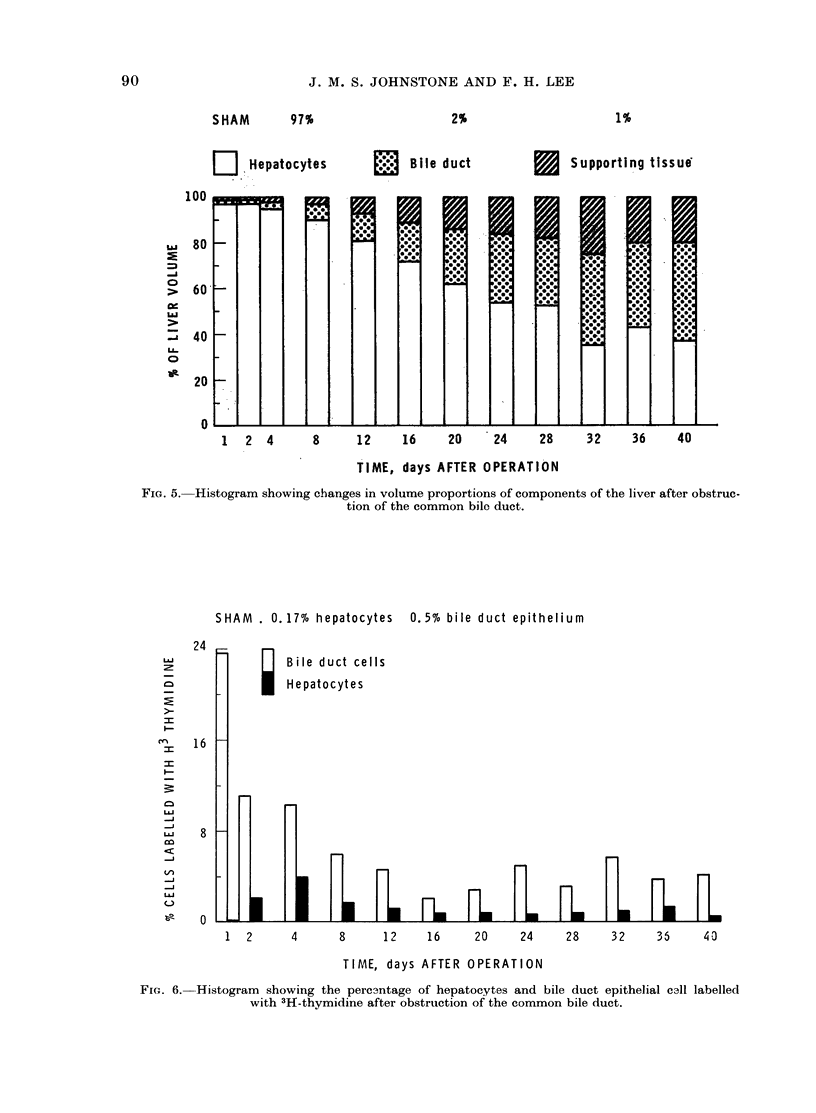
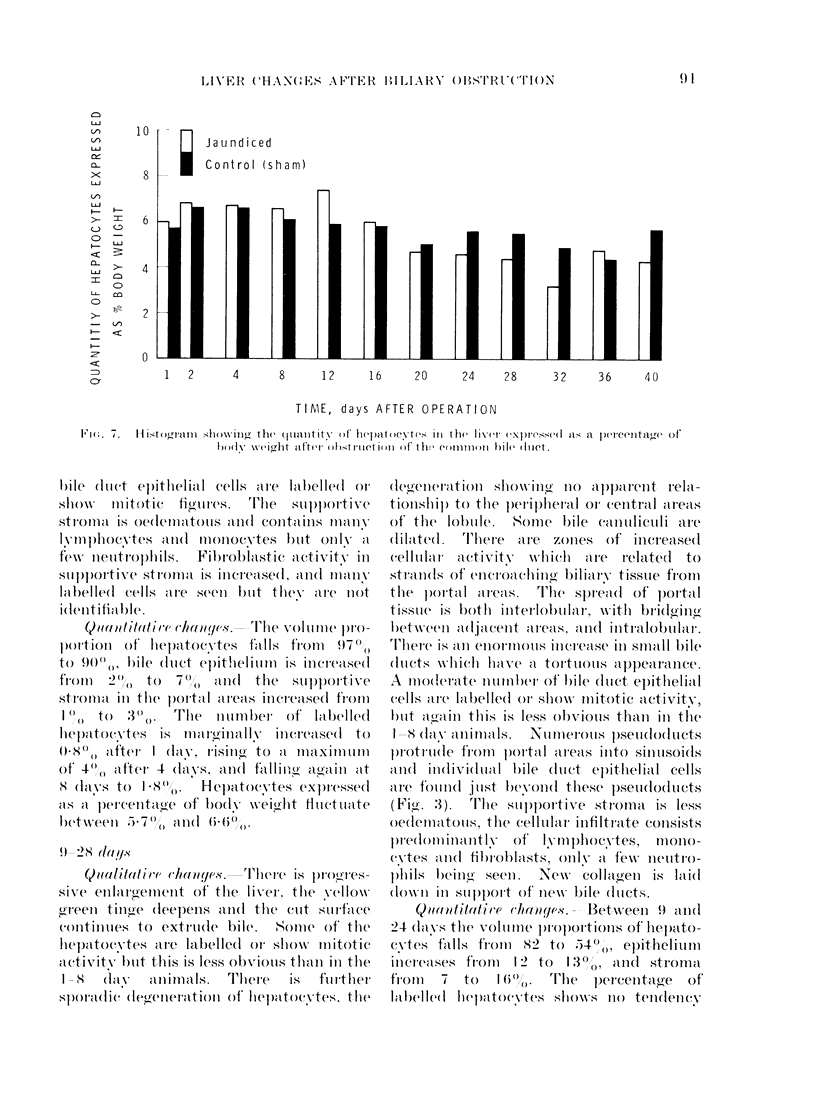
A study has been made of sequential changes in the rat's liver from 1 to 40 days after obstruction of the common bile duct. The qualitative changes have been described and illustrated. The volume proportions of hepatocytes, bile duct epithelium and biliary stroma have been quantified by histological analysis using a point counting technique. The proliferation of hepatocytes and bile duct cells have been measured by labelling with tritiated thymidine. The absolute quantity of hepatocytes in each liver has been estimated and expressed as a percentage of body weight. Over 40 days there is a relative fall in the volume proportion of hepatocytes and an increase in bile duct cells and biliary stroma. These changes in volume proportions are related directly to the period of jaundice. Biliary stroma increases in support of new bile duct tissue and there is no excessive fibrosis. Hepatocytes proliferate at a greater rate than normal after obstruction of the common bile duct and the degree of proliferation reaches a maximum of 24 times that of normal 4 days after obstruction. Similarly, the proliferation of bile duct epithelium is increased in obstructive jaundice but in this instance it reaches a maximum of 50 times that of normal 24 h after ligation of the common bile duct. The absolute quantity of hepatocytes in the liver probably falls during the period of jaundice. However, the fall is less than anticipated from the volume proportion of hepatocytes because of the overall increase in liver size.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMERON G. R., MUZAFFAR HASAN S. Disturbances of structure and function in the liver as the result of biliary obstruction. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(2):333–349. doi: 10.1002/path.1700750212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALL E. A., DOBROGORSKI O. HEPATIC ALTERATIONS IN OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Feb;41:126–139. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/41.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E., Ross B. D., Haines J. R. The effect of experimental bile-duct obstruction on critical biosynthetic functions of the liver. Br J Surg. 1972 Jul;59(7):564–568. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800590716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. The effect of obstructive jaundice on the migration of reticulo-endothelial cells and fibroblasts into early experimental granulomata. Br J Surg. 1972 Nov;59(11):875–877. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800591107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER J. W., CARRUTHERS J. S., KALIFAT S. R. The ductular cell reaction of rat liver in extrahepatic cholestasis. I. Proliferated biliary epithelial cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 1962 Apr;1:162–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(62)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]