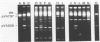Abstract
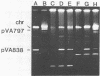
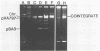
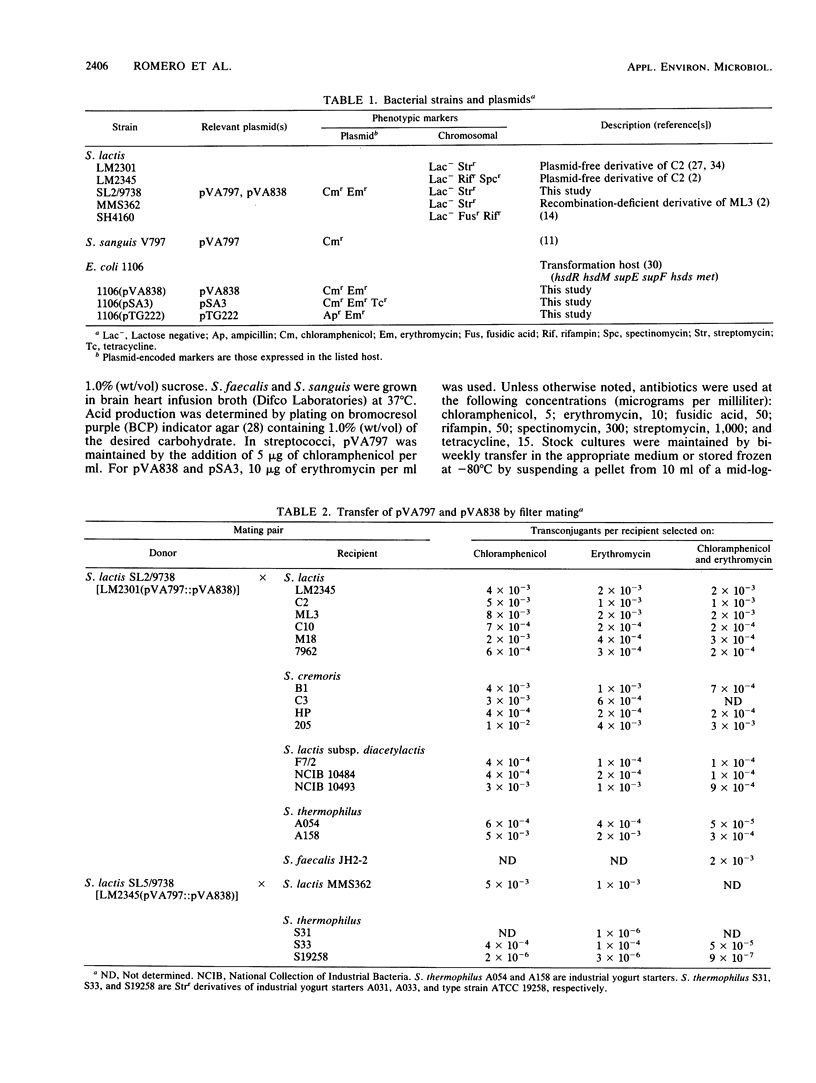
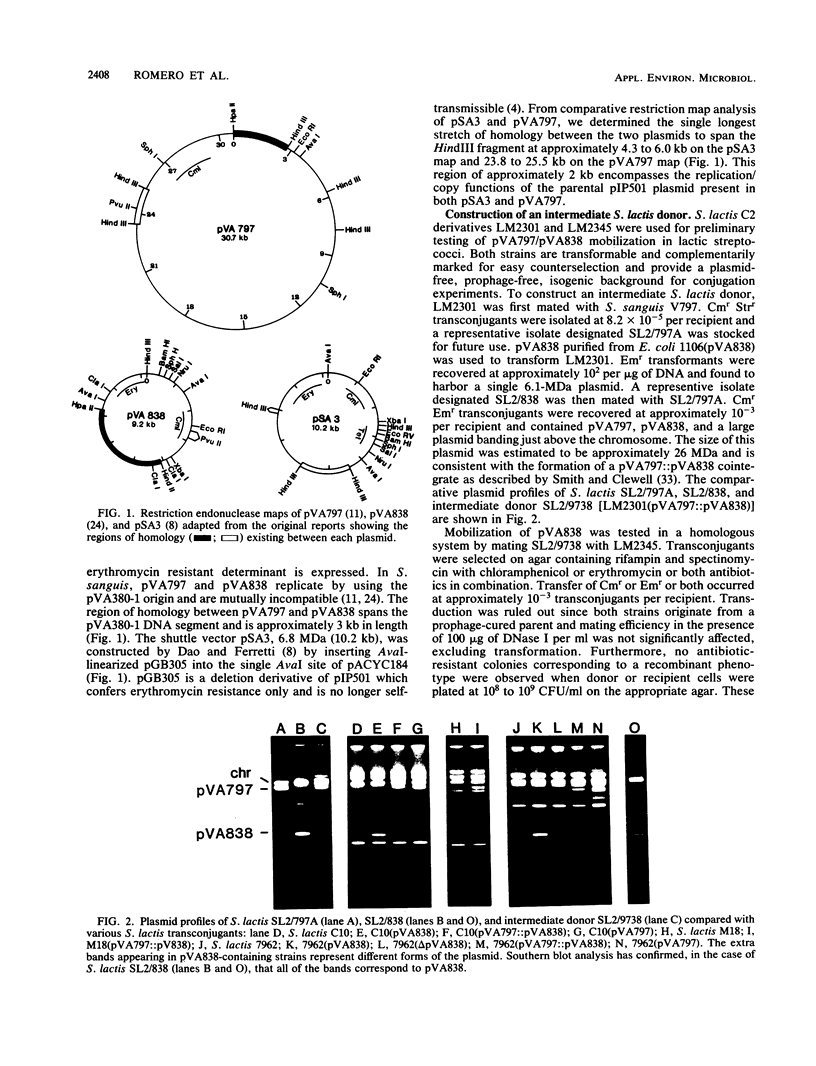
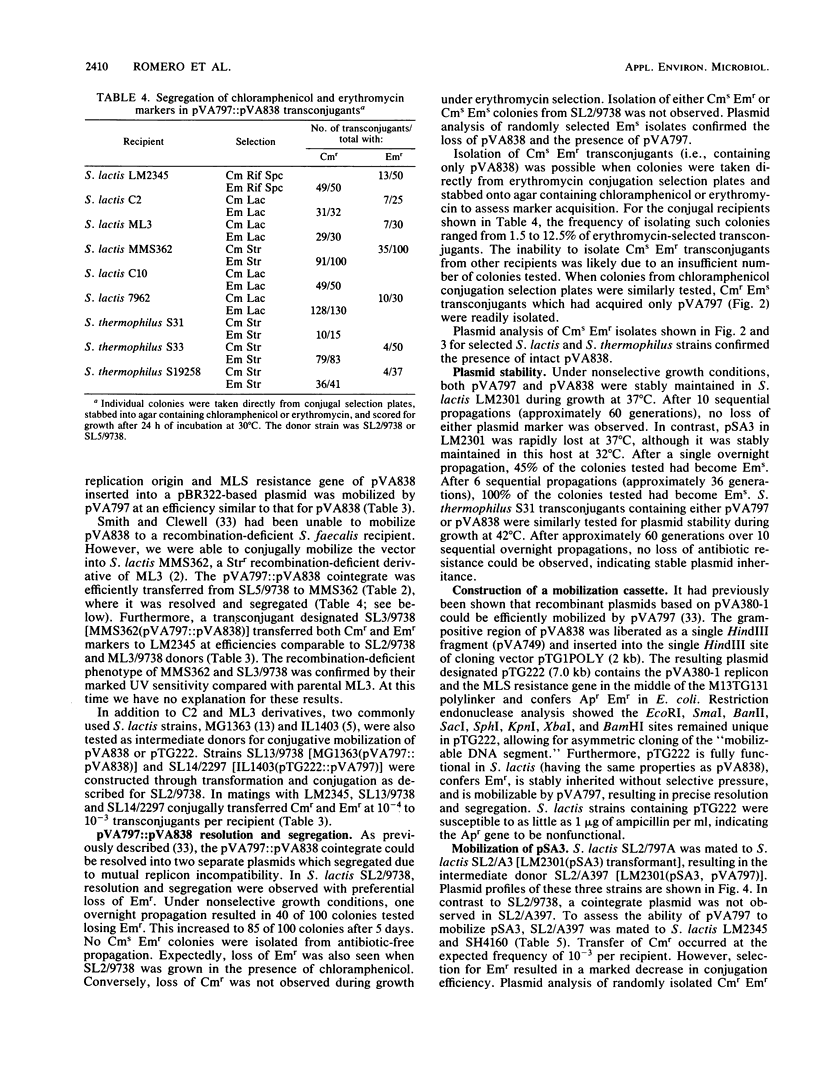
Due to the current variability in applying polyethylene glycol-mediated protoplast transformation to lactic streptococci, a study was undertaken to assess the feasibility of conjugative mobilization as an alternative method for vector delivery. By using the broad-host-range conjugative plasmid pVA797, the partially homologous cloning vector pVA838 was successfully introduced into various strains of Streptococcus lactis, Streptococcus cremoris, Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis, Streptococcus thermophilus, and Streptococcus faecalis. Frequencies ranged from 10(-2) to 10(-6) transconjugants per recipient. Both pVA797 and pVA838 were acquired intact, without alteration in functionality. Also, the shuttle vector pSA3, which shares partial homology with pVA797, was mobilized via conjugation. The use of S. lactis LM2301 as the intermediate donor allowed the use of physiologic and metabolic characteristics for recipient differentiation. The construction of a vector containing a "DNA cassette" conferring mobilization and the resolution, segregation, and stability of the cointegrates, pVA797, pVA838, and pSA3, are also reported.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Genetic and physical characterization of recombinant plasmids associated with cell aggregation and high-frequency conjugal transfer in Streptococcus lactis ML3. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):954–962. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.954-962.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. In Vivo Cloning of lac Genes in Streptococcus lactis ML3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.245-249.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Gilmore M. S. Location of antibiotic resistance determinants, copy control, and replication functions on the double-selective streptococcal cloning vector pGB301. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):115–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00271206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin A., Chopin M. C., Moillo-Batt A., Langella P. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin M. C., Chopin A., Rouault A., Simon D. Cloning in Streptococcus lactis of plasmid-mediated UV resistance and effect on prophage stability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):233–237. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao M. L., Ferretti J. J. Streptococcus-Escherichia coli shuttle vector pSA3 and its use in the cloning of streptococcal genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.115-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou J. D., McKay L. L. Inorganic salts resistance associated with a lactose-fermenting plasmid in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.257-265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Genetic transfer systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):275–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00399503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Transformation of Streptococcus lactis Protoplasts by Plasmid DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1213–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1213-1215.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Evans R. P., Tobian J. A., Hartley D. L., Clewell D. B., Jones K. R. Novel shuttle plasmid vehicles for Escherichia-Streptococcus transgeneric cloning. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P., Clewell D. B. A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P. Molecular cloning in the Streptococci. Basic Life Sci. 1982;19:195–210. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4142-0_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Zottola E. A. Loss of lactose metabolism in lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1090-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Cords B. R., Baldwin K. A. Transduction of lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis C2. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.810-815.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L. Functional properties of plasmids in lactic streptococci. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):259–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00399502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Rouault A., Chopin M. C. High-efficiency transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):394–395. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.394-395.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Clewell D. B. Return of Streptococcus faecalis DNA cloned in Escherichia coli to its original host via transformation of Streptococcus sanguis followed by conjugative mobilization. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1109–1114. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1109-1114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snook R. J., McKay L. L. Conjugal Transfer of Lactose-Fermenting Ability Among Streptococcus cremoris and Streptococcus lactis Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):904–911. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.904-911.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wright A., Taimisto A. M., Sivelä S. Effect of Ca2+ ions on plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1100-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]