Abstract
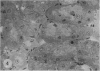
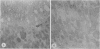
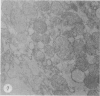
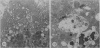
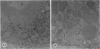
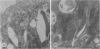
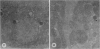
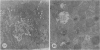
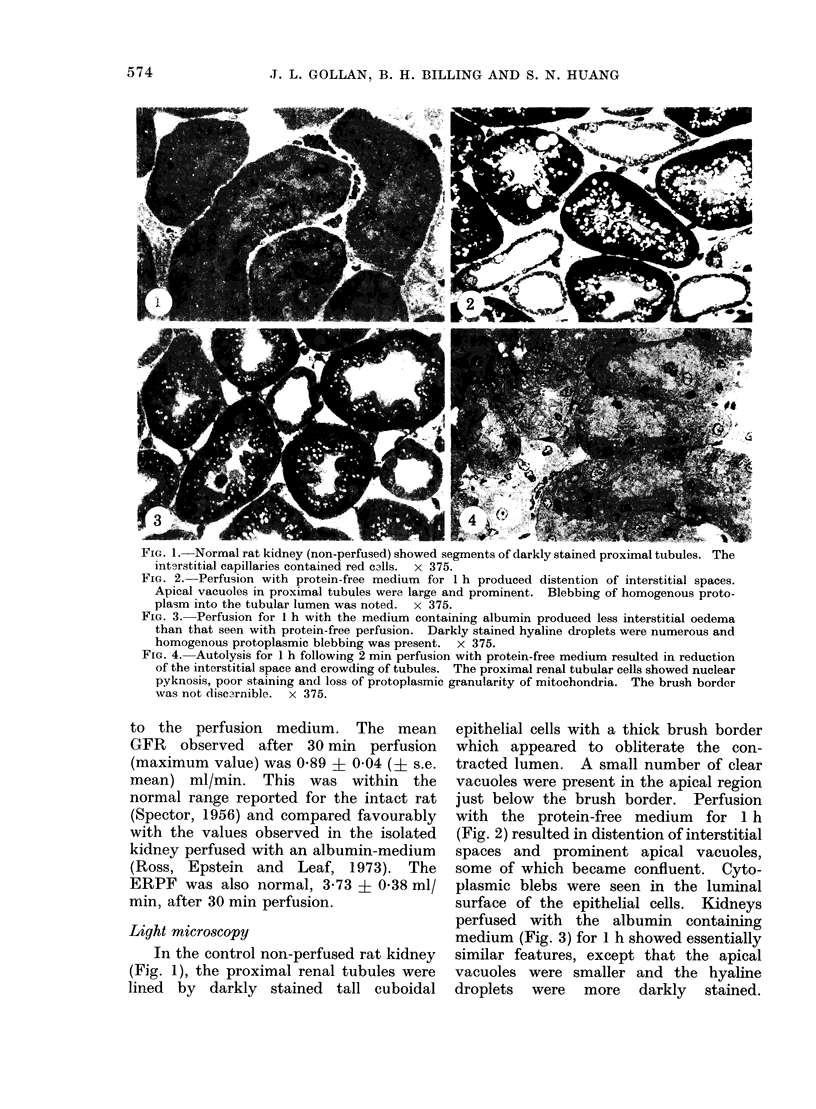
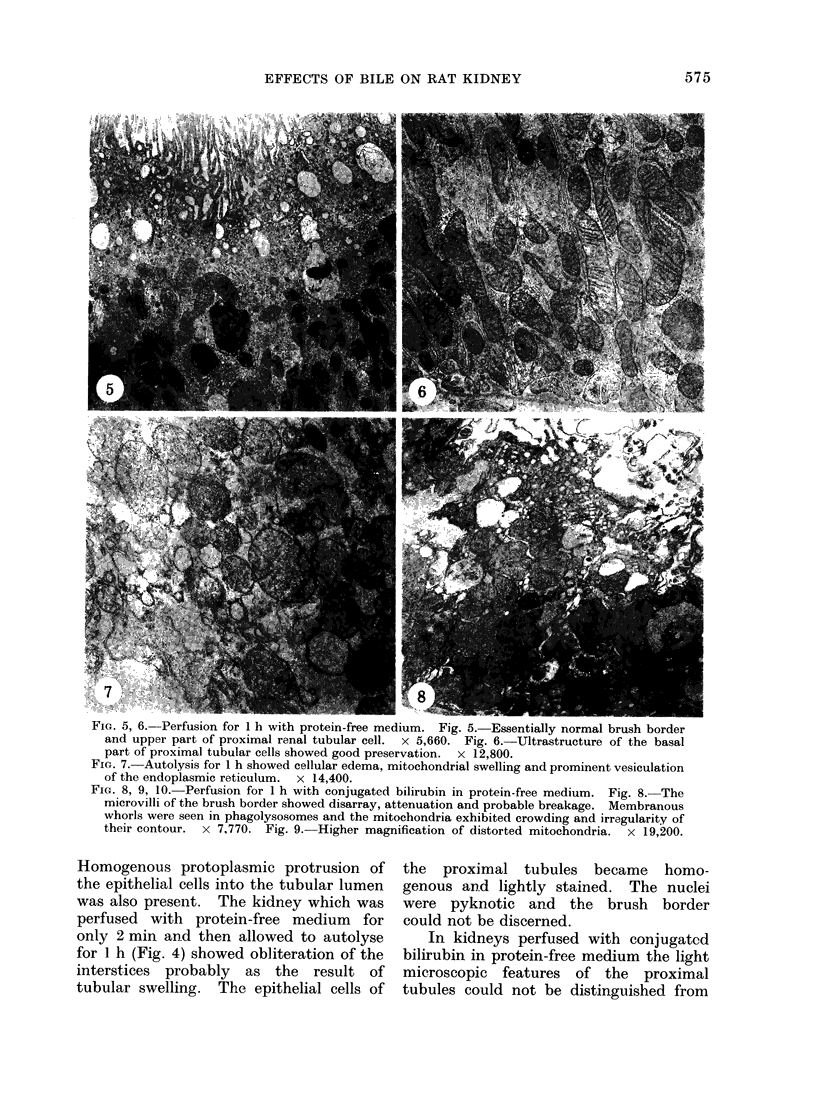
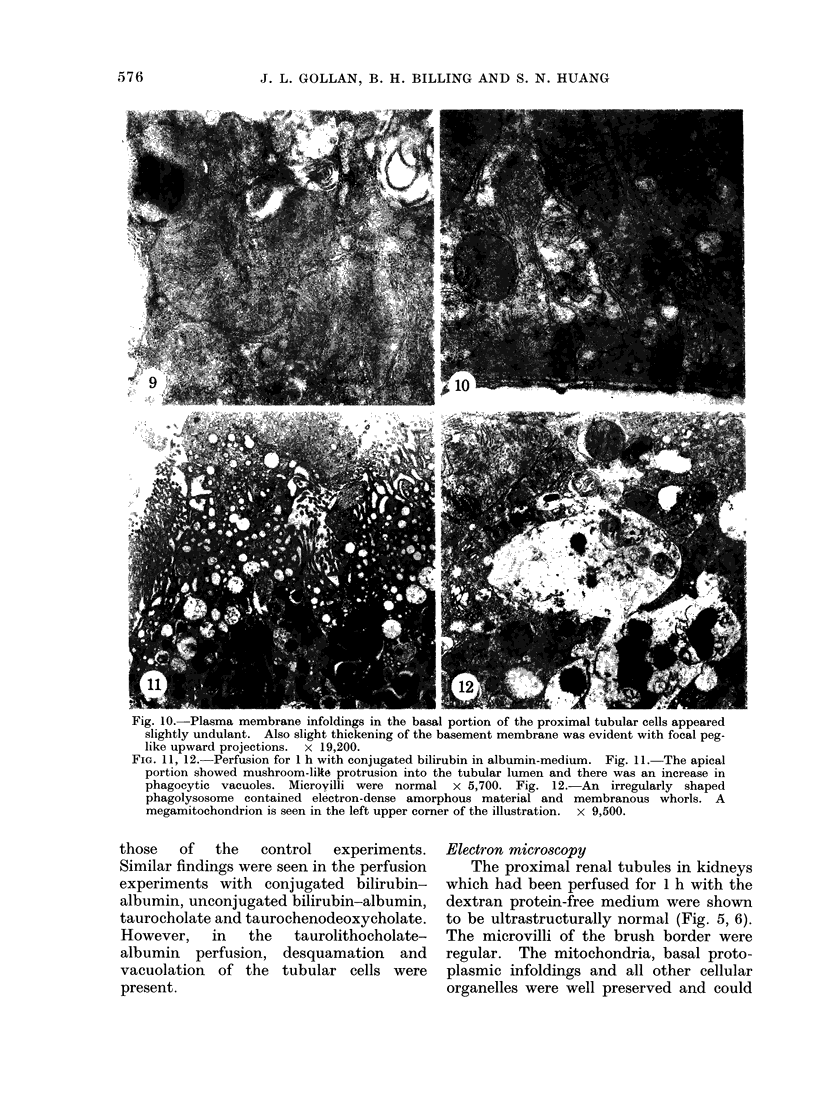
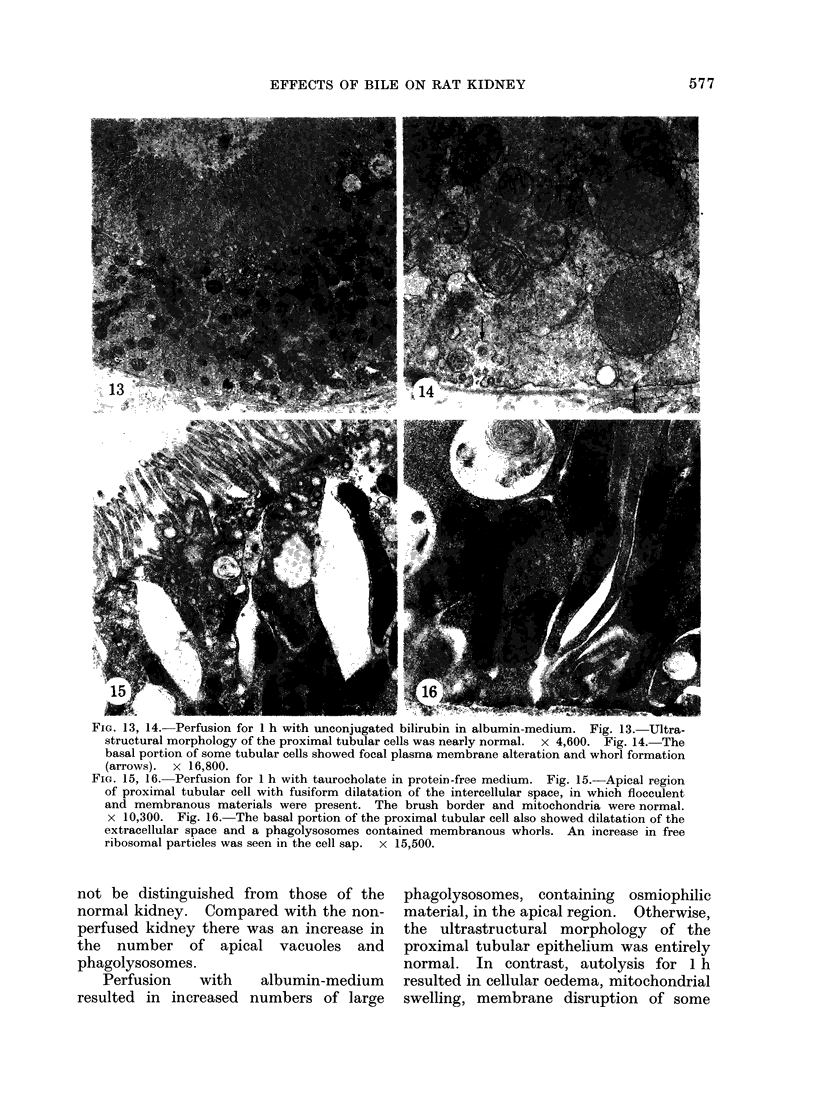
The effects of bilirubin and bile acids on the ultrastructure of proximal renal tubules have been studied using an isolated rat kidney preparation, perfused with a protein-free dextran medium. Control kidneys perfused for 1 h had a normal glomerular filtration rate and effective renal plasma flow; the ultrastructure of proximal tubular cells was well preserved, with normal mitochondria, nuclear and plasma membranes, and microvilli of the brush border. When conjugated bilirubin, prepared from human hepatic bile, was added to the perfusion medium (5-0-7-5 mg/100 ml), marked alterations were observed in some cells, particularly with regard to the mitochondria and plasma membranes. These changes were greatly diminished by the inclusion of bovine albumin in the medium, indicating that the unbound fraction was primarily responsible for the tubular damage. The addition of taurocholate (450 muM), taurochenodeoxycholate (550 muM) or taurolithocholate (250 muM, bound to albumin) also produced plasma membrane changes, but only slight abnormalities were seen in the mitochondria and other structures. These ultrastructural observations support the concept that the elevated plasma levels of conjugated bilirubin and to a lesser extent bile acids are related to the renal failure associated with obstructive jaundice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M. A., Billing B. H. Effect of acid-base changes on renal clearance of bile pigments. Clin Sci. 1966 Jun;30(3):543–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Lowenstein L. M. The effect of bile acids and renal ischemia on renal function. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Apr;71(4):686–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M., Stirling G. A., Dawson J. L. Further study into obstructive jaundice and ischaemic renal damage. Br Med J. 1969 Apr 26;2(5651):229–231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5651.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. S., Eastwood M. A., MacLean N. Bile acids in the rat: studies in experimental occlusion of the bile duct. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):83–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowger M. L., Igo R. P., Labbe R. F. The mechanism of bilirubin toxicity studied with purified respiratory enzyme and tissue culture systems. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2763–2770. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON J. L. JAUNDICE AND ANOXIC RENAL DAMAGE: PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF MANNITOL. Br Med J. 1964 Mar 28;1(5386):810–811. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5386.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON J. L., STIRLING G. A. PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF MANNITOL ON ANOXIC JAUNDICED KIDNEYS; A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY. Arch Pathol. 1964 Sep;78:254–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON J. L. THE INCIDENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE RENAL FAILURE IN OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE. Br J Surg. 1965 Sep;52:663–665. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800520906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., De Wolf-Peeters C., Desmet V. Histochemical changes in rat kidney after bile duct obstruction. Beitr Pathol. 1972;145(4):315–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Schmid R. Experimental bilirubin encephalopathy. The mode of entry of bilirubin-14C into the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):678–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERNSTER L., ZETTERSTROM R. Bilirubin, an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria. Nature. 1956 Dec 15;178(4546):1335–1337. doi: 10.1038/1781335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greim H., Trülzsch D., Czygan P., Rudick J., Hutterer F., Schaffner F., Popper H. Mechanism of cholestasis. 6. Bile acids in human livers with or without biliary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):846–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie S. O., Bratlid D. The protective effect of albumin on bilirubin toxicity on human fibroblasts. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Aug;26(1):37–41. doi: 10.3109/00365517009049211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyai K., Price V. M., Fisher M. M. Bile acid metabolism in mammals. Ultrastructural studies on the intrahepatic cholestasis induced by lithocholic and chenodeoxycholic acids in the rat. Lab Invest. 1971 Apr;24(4):292–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. G., Cowger M. L., King T. E. Effects of bilirubin on mitochondrial reactions. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6403–6414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J. M., Ross B. D., Krebs H. A. Metabolic activities of the isolated perfused rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):852–862. doi: 10.1042/bj1030852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. H. Bile acids, liver injury, and liver disease. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):606–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradisi F., Graziano L. Mitochondrial swelling induced by unconjugated bilirubin in vitro. Experientia. 1973 Nov 15;29(11):1376–1377. doi: 10.1007/BF01922829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. W., Dunnicliff M. A., Billing B. H. Red cell survival in experimental cholestatic cholestatic jaundice. Br J Haematol. 1968 Nov;15(5):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. D., Epstein F. H., Leaf A. Sodium reabsorption in the perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1973 Nov;225(5):1165–1171. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.5.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. P., Hofmann A. F. Separation of bilirubin and its conjugates by thin layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Dec;35(2):517–519. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., GLASSER J. E., LACK L. RENAL EXCRETION OF BILE ACIDS: TAUROCHOLIC, GLYCOCHOLIC, AND COLIC ACIDS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:964–970. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. D., ELLIOTT D. W., ZOLLINGER R. M. The effect of hypotension in obstructive jaundice. Arch Surg. 1960 Aug;81:334–340. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1960.01300020162022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Renal failure in obstructive jaundice--pathogenic factors. Postgrad Med J. 1975 Aug;51(598):512–514. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.51.598.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]