Abstract
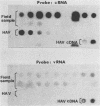
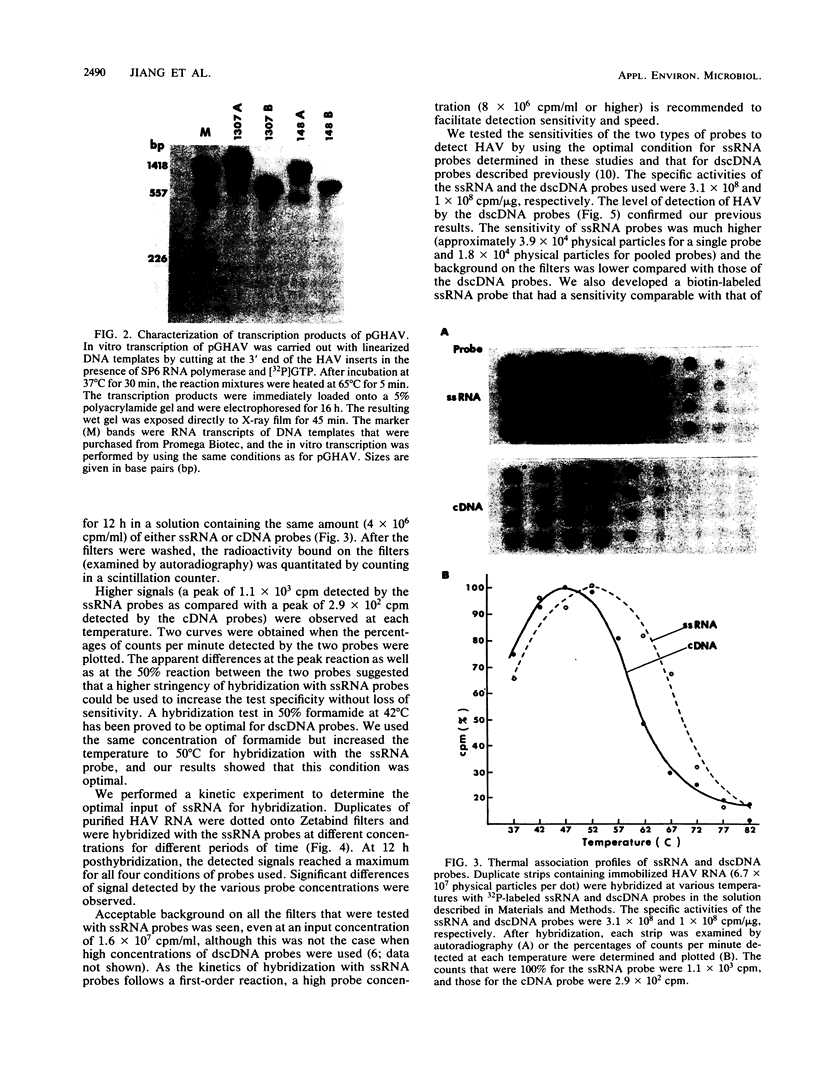
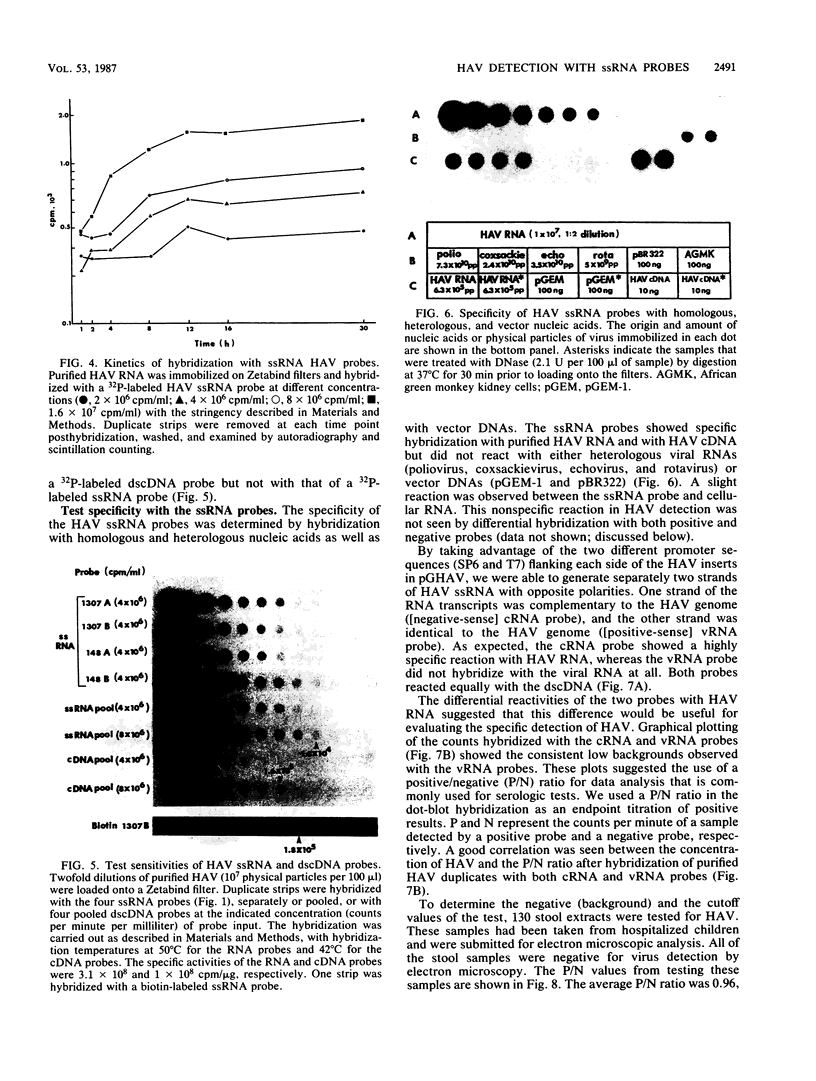
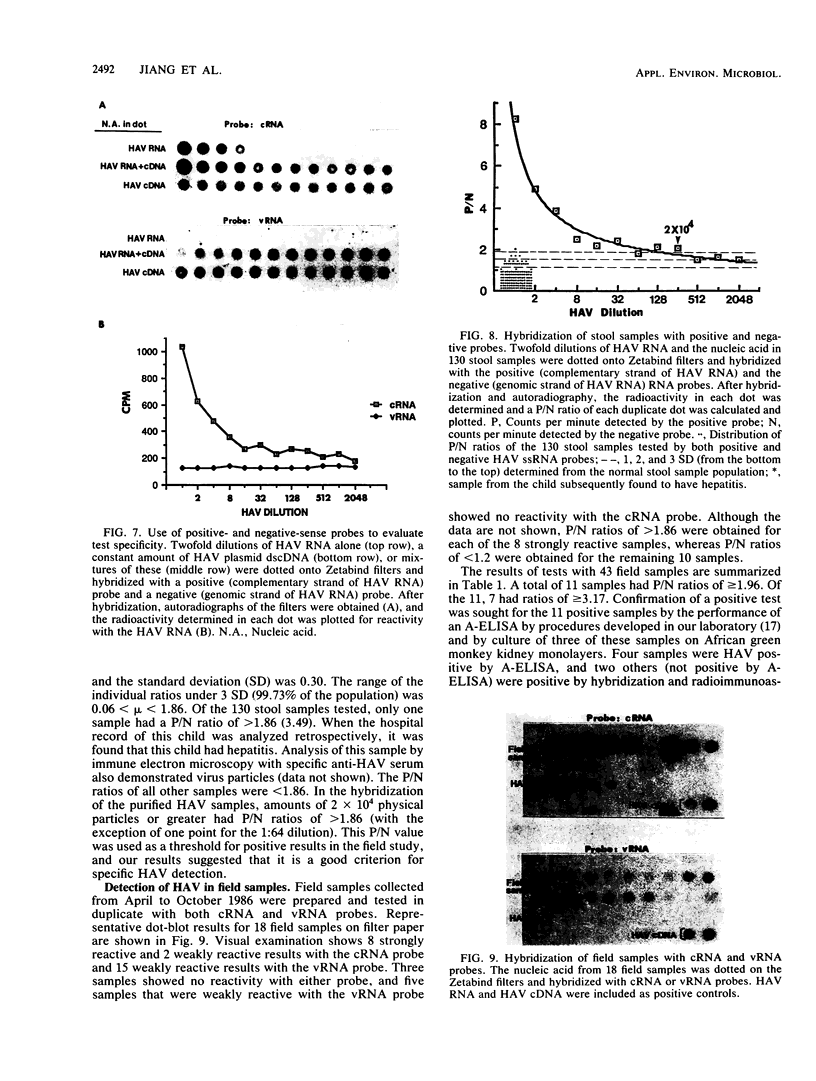
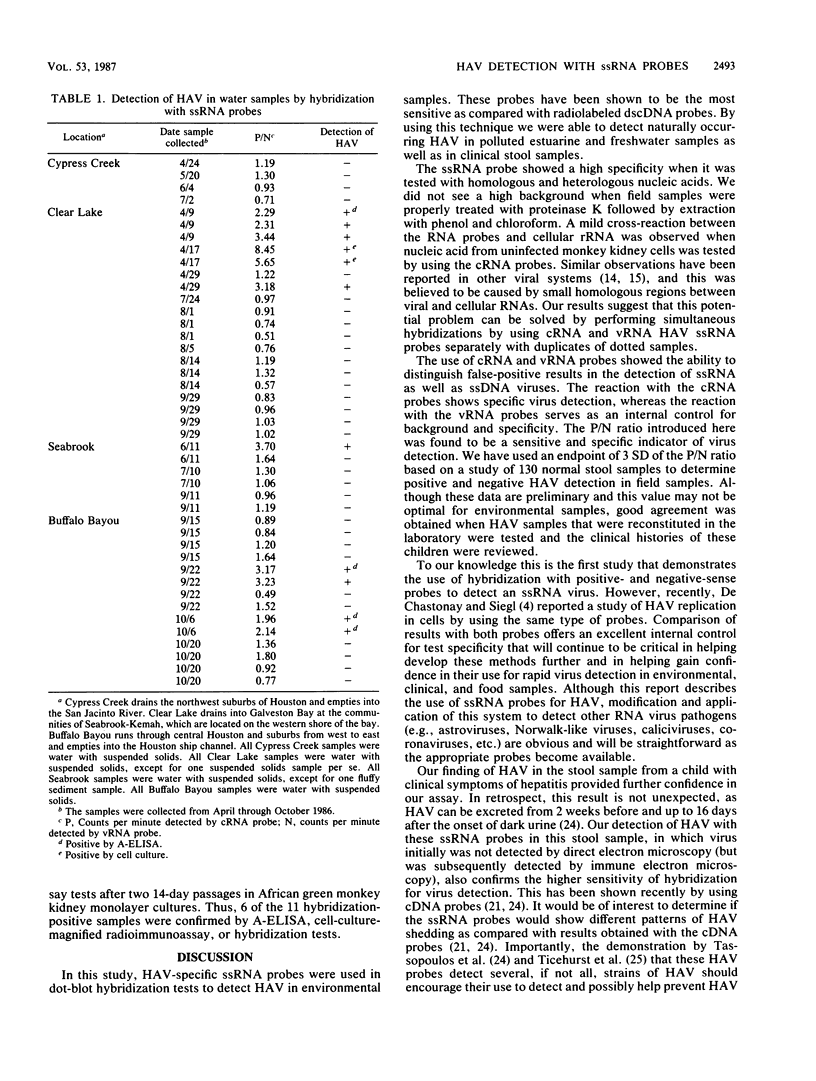
An improved method of dot-blot hybridization to detect hepatitis A virus (HAV) was developed with single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) probes. Radioactive and nonradioactive ssRNA probes were generated by in vitro transcription of HAV templates inserted into the plasmid pGEM-1. 32P-labeled ssRNA probes were at least eightfold more sensitive than the 32P-labeled double-stranded cDNA counterparts, whereas biotin-labeled ssRNA probes showed a sensitivity comparable with that of the 32P-labeled double-stranded cDNA counterparts. Hybridization of HAV with the ssRNA probes at high stringency revealed specific reactions with a high signal-to-noise ratio. The differential hybridization reactions seen with probes of positive and negative sense (compared with HAV genomic RNA) were used to detect HAV in clinical and field samples. A positive/negative ratio was introduced as an indicator that permitted a semiquantitative expression of a positive HAV reaction. Good agreement of this indicator was observed with normal stool samples and with HAV-seeded samples. By using this system, HAV was detected in estuarine and freshwater samples collected from a sewage-polluted bayou in Houston and a saltwater tributary of Galveston Bay.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Charache P., Staal S., Wright P., Forman M., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. The vector homology problem in diagnostic nucleic acid hybridization of clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.16-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Ticehurst J. R., Miele T. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Sequence analysis of hepatitis A virus cDNA coding for capsid proteins and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahling D. R., Wright B. A. Recovery of viruses from water by a modified flocculation procedure for second-step concentration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1326–1331. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1326-1331.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Chastonay J., Siegl G. Replicative events in hepatitis A virus-infected MRC-5 cells. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegutis P. S., Keirnan E., Burnett L., Nightingale B. N., Cossart Y. E. False-positive results with hepatitis B virus DNA dot-hybridization in hepatitis B surface antigen-negative specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):797–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.797-799.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of rotaviruses by nucleic acid hybridization with cloned DNA of simian rotavirus SA11 genes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):293–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Lopez J., Muchinik G., Velasco G., Stenback W. A., Estes M. K. RNA electropherotypes of human rotaviruses from North and South America. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(2):321–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Mason B. B., Crawford S., Cohen J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the simian rotavirus gene 6 that codes for the major inner capsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Estes M. K., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Detection of hepatitis A virus in seeded estuarine samples by hybridization with cDNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.711-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Norval M. Nucleic acid probes in diagnosis of viral diseases of man. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1985;83(1-2):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01310960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 24;313(17):1059–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510243131706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. D., Loutit M. W., Austin F. J. A method for detecting human enteroviruses in aquatic sediments. J Virol Methods. 1985 Feb;10(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. Poliovirus genome RNA hybridizes specifically to higher eukaryotic rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6797–6816. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. RNA virus genomes hybridize to cellular rRNAs and to each other. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):917–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.917-921.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P., Gealt M. A. Isolation of indigenous wastewater bacterial strains capable of mobilizing plasmid pBR325. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):904–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.904-909.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasser A. M., Metcalf T. G. An A-ELISA to detect hepatitis A virus in estuarine samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1192–1195. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1192-1195.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. C., Waghmare S. V., Lakhe S. B. Detection of viruses in drinking water by concentration on magnetic iron oxide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):421–426. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.421-426.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V., Matz B., Wiegand H., Polack A., Corsten B., Neumann-Haefelin D. Nucleic acid hybridization for detection of herpes viruses in clinical specimens. J Med Virol. 1986 Jul;19(3):277–286. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjogren M. H., Tanno H., Fay O., Sileoni S., Cohen B. D., Burke D. S., Feighny R. J. Hepatitis A virus in stool during clinical relapse. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Feb;106(2):221–226. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Hickey A. R. Effects of humic and fulvic acids on poliovirus concentration from water by microporous filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):259–264. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.259-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassopoulos N. C., Papaevangelou G. J., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H. Fecal excretion of Greek strains of hepatitis A virus in patients with hepatitis A and in experimentally infected chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):231–237. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Chestnut T., Tassopoulos N. C., Popper H., Purcell R. H. Detection of hepatitis A virus by extraction of viral RNA and molecular hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1822–1829. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1822-1829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]