Abstract
Lysostaphin, a bacteriolytic enzyme, has been used to remove cell-adherent and extracellular Staphylococcus aureus from phagocyte-bacterial mixtures in vitro. Lysostaphin kills S. aureus more rapidly than penicillin, is not toxic for phagocytic cells and, when used for short periods at low concentrations, appears to enter neither human nor mouse mononuclear phagocytes. The use of lysostaphin provides the basis of a simple reliable direct in vitro assay for measuring the attachment and ingestion of S. aureus by phagocytic cells.
Full text
PDF

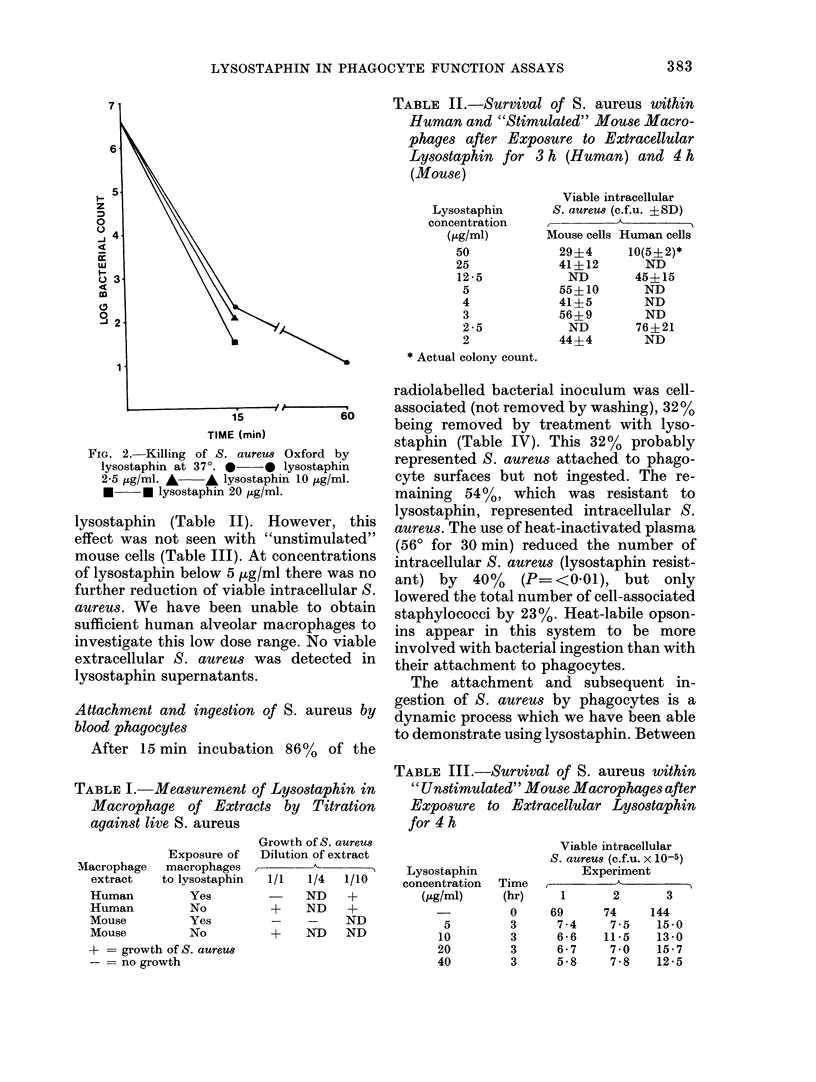
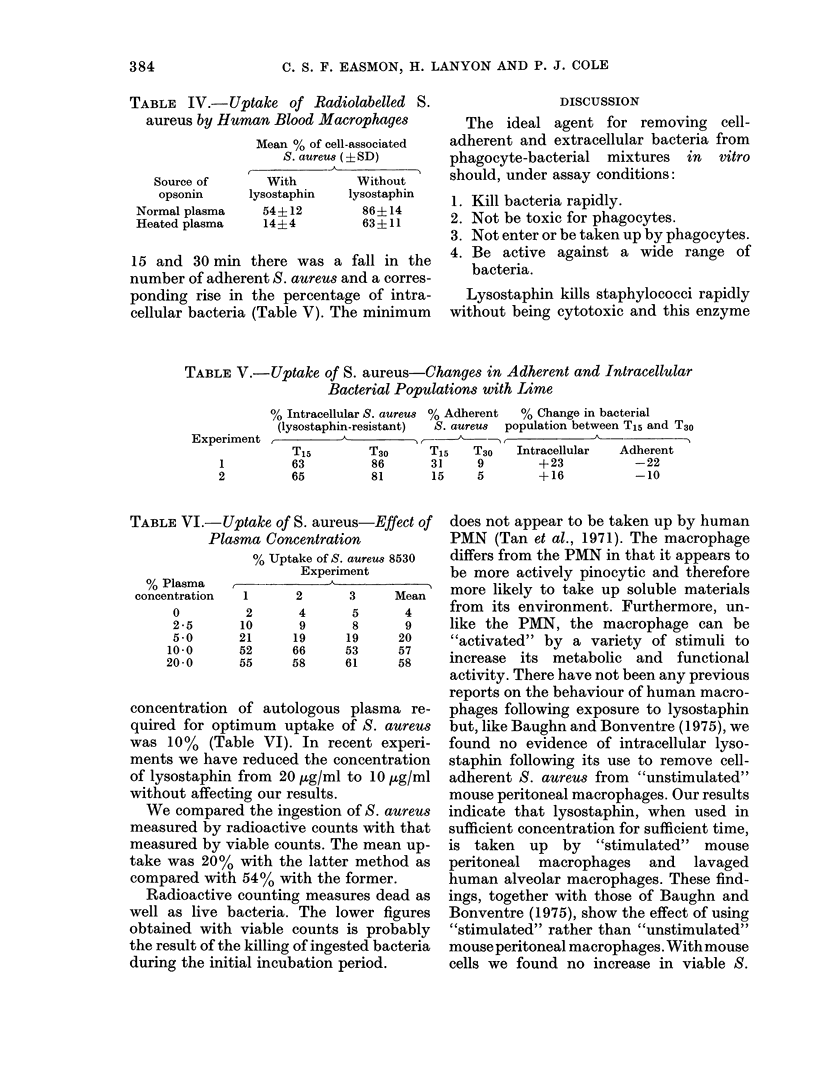

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughn R., Bonventre P. F. Phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by normal mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):346–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.346-352.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggar W. D. Phagocytosis in patients and carriers of chronic granulomatous disease. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):991–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91943-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P., Brostoff J. Intracellular killing of Listeria monocytogenes by activated macrophages (Mackaness system) is due to antibiotic. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):515–517. doi: 10.1038/256515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. S., Watanakunakorn C., Phair J. P. A modified assay of neutrophil function: use of lysostaphin to differentiate defective phagocytosis from impaired intracellular killing. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Aug;78(2):316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D. R., Finch H., Smith H. Penetration of penicillin into human phagocytes containing Neisseria gonorrhoeae: intracellular survival and growth at optimum concentrations of antibiotic. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Aug;96(2):353–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


