Abstract
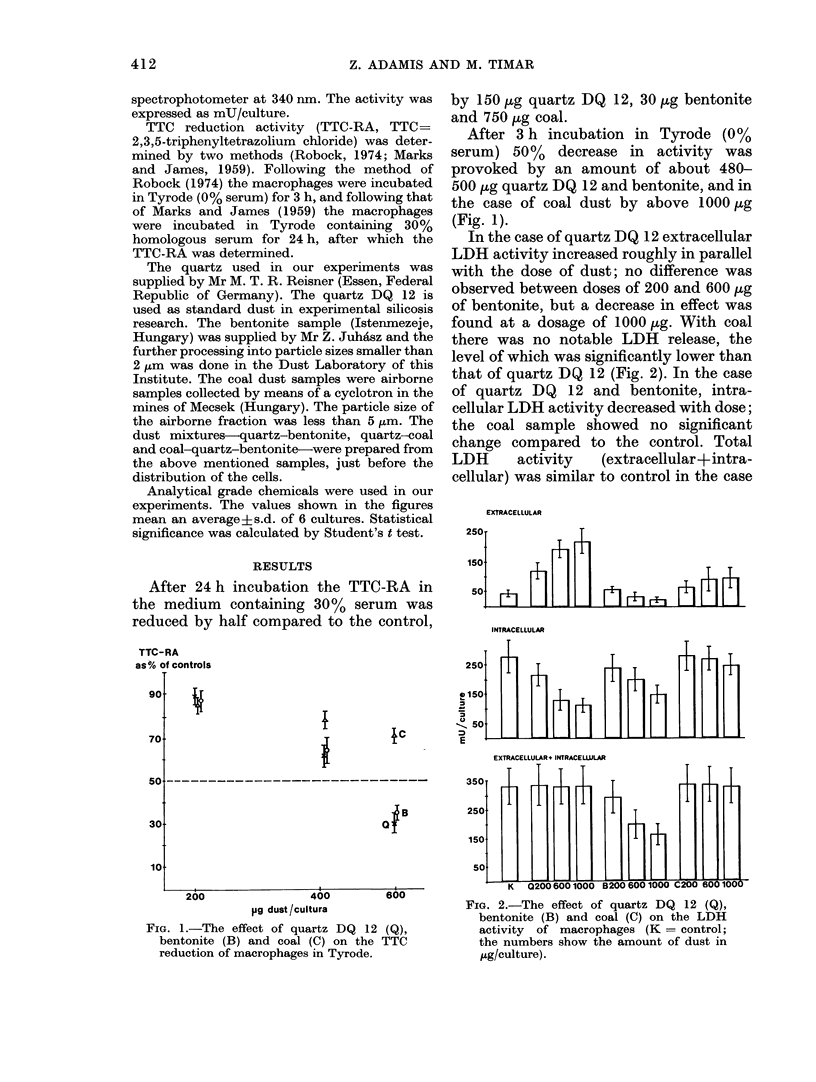
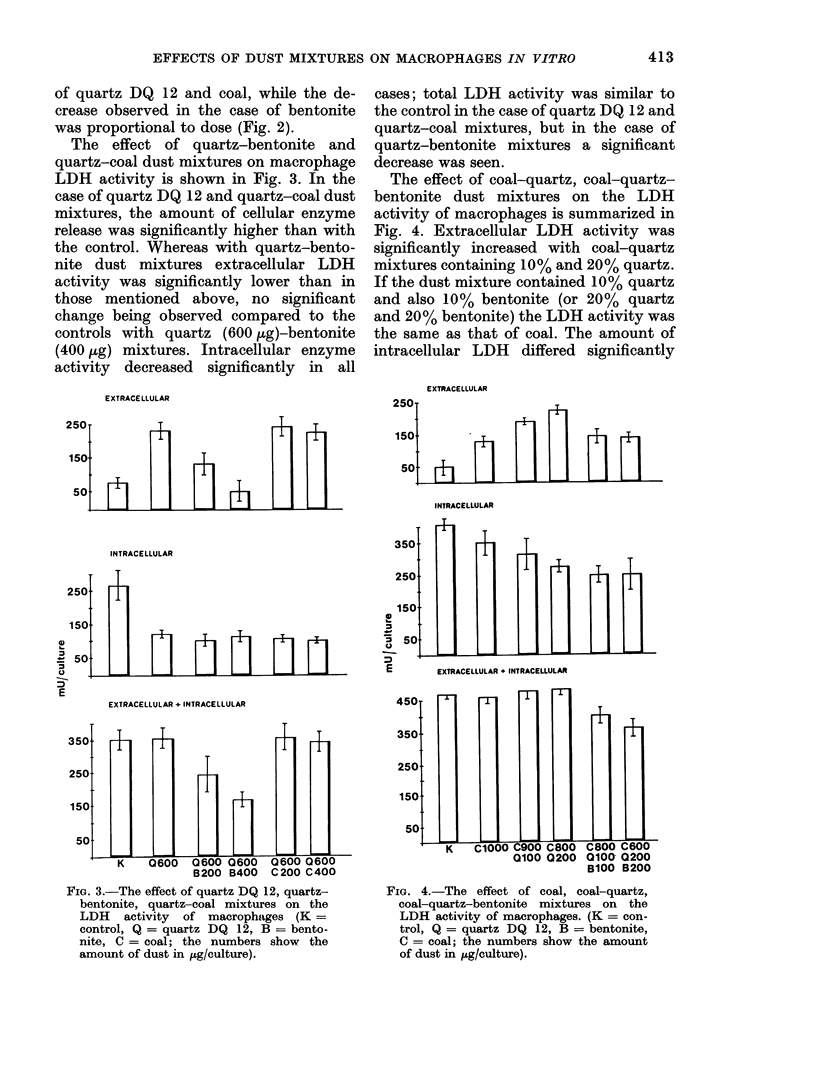
The effect of quartz, bentonite and coal dusts as well as the effect of the artificial mixture of these dusts on TTC reduction and extra-and intra-cellular lactate dehydrogenase activity in peritoneal rat macrophages was determined in vitro. The cell-membrane-damaging effect of quartz caused a significant extracellular release of lactate dehydrogenase. Bentonite caused no extracellular enzyme release, which leads us to believe that the biological effect of this dust is shown by decrease in intra-cellular lactate dehydrogenase activity. TTC reduction was inhibited equally by quartz and qentonite. In mixtures of quartz (60%)-bentonite (40%) dust the specific effect of quartz was inhibited by bentonite in vitro and also in vivo. We obtained the same results with coal-quartz-bentonite dust mixtures in vitro. Our experiments show that comparison of the biological effects of artificial dust mixtures and airborne dust samples is justified, and prove that performing various examinations simultaneously give fuller particulars on the probable biological effect of mineral dusts.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamis Z., Timár M. Effects of various mineral dusts on macrophages in vitro. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1976 Sep 6;37(4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00380113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E. G., Holt P. F., Manojlović N. Comparison of effects on macrophage cultures of glass fibre, glass powder, and chrysotile asbestos. Br J Ind Med. 1972 Jul;29(3):280–286. doi: 10.1136/oem.29.3.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., JAMES D. M. The measurement of dust toxicity in vitro. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(2):401–406. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., NAGELSCHMIDT G. Study of the toxicity of dust with use of the in vitro dehydrogenase technique. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1959 Nov;20:383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welscher H. D., Cruchaud A. The influence of various particles and 3', 5' cyclic adenosine monophosphate on release of lysosomal enzymes by mouse macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Dec;20(6):405–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


