Abstract
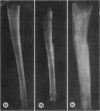
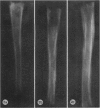
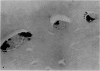
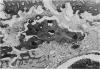
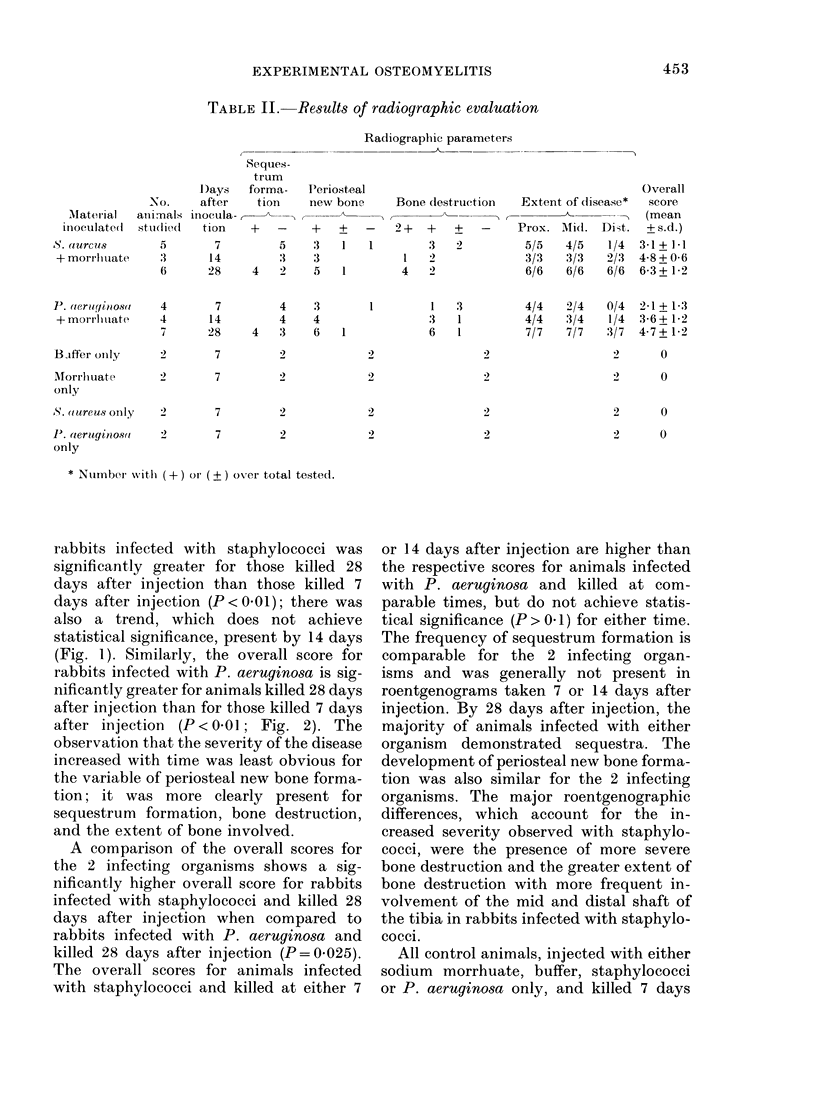
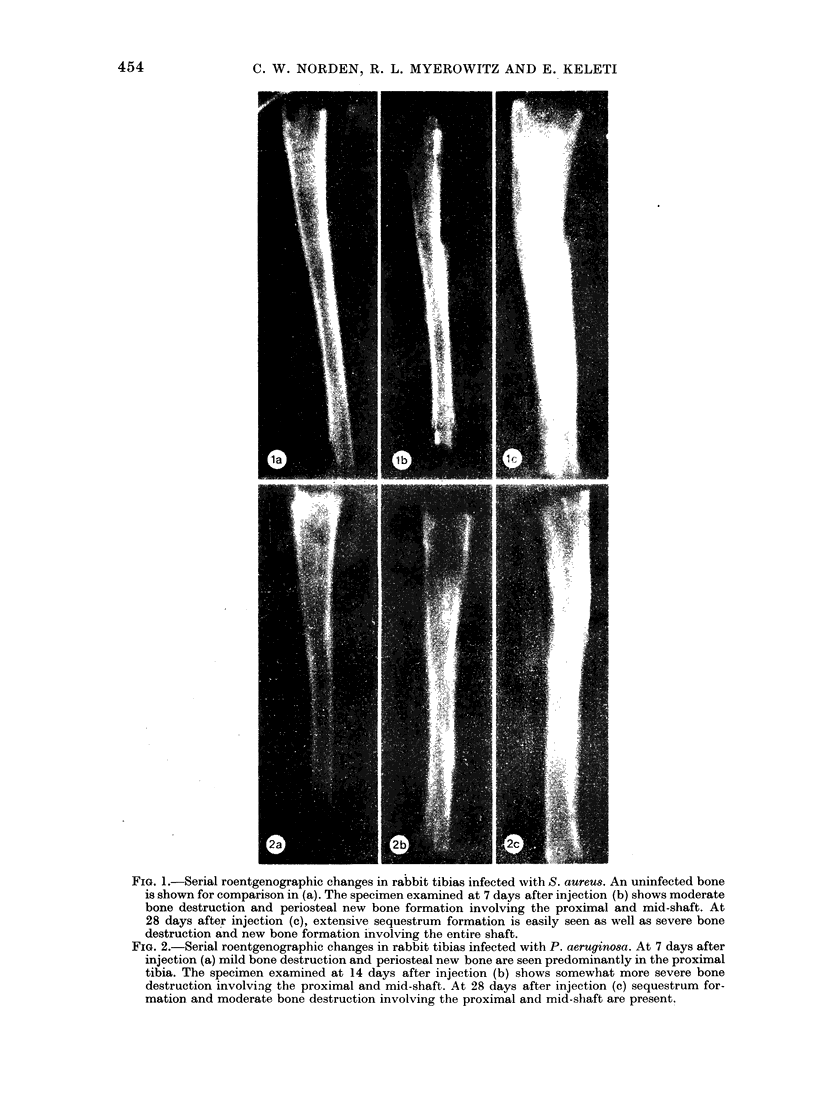
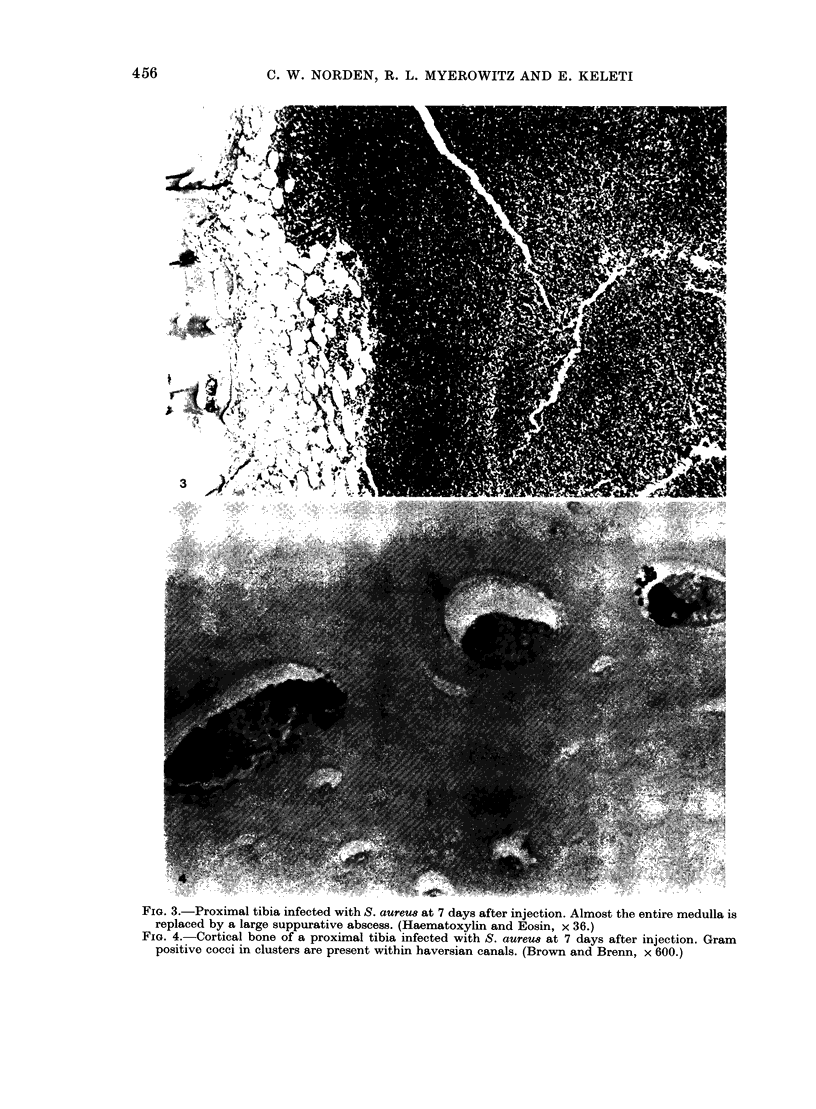
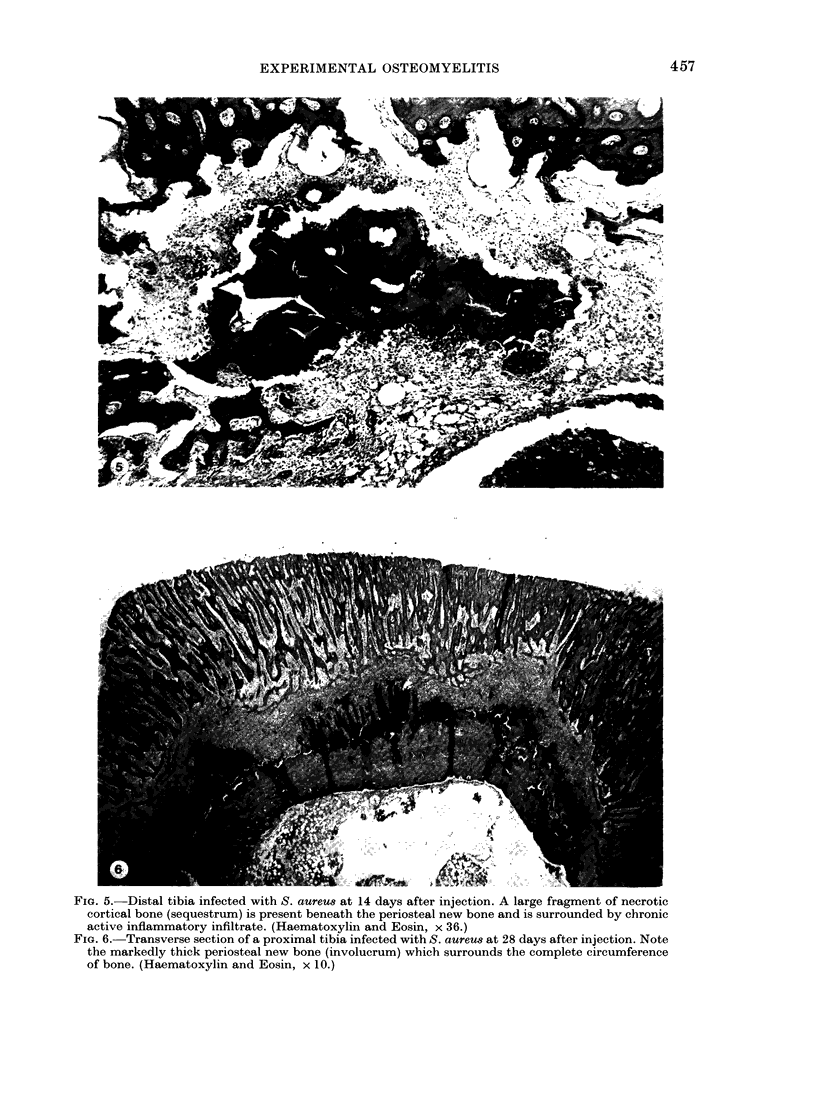
A previously-described experimental model of bacterial osteomyelitis was used to investigate systematically the sequential radiographic and histopathological changes in the tibias of rabbits infected with either Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The radiographic changes induced by both organisms were progressive, increasing in severity from the first to the fourth week after infection. The severity and extent of radiographic changes, especially that of bond destruction, were significantly greater for tibias infected with S. aureus. Histopathologically, staphylococcal disease was a severe, rapidly progressive purulent infection which led to extensive destruction of marrow and cortical bone, formation of sequestra, and frequent extraosseous extension. Disease due to P. aeruginosa was more indolent and less destructive, leading to earlier healing and no extraosseous extension. The sequential radiographic and pathological changes observed with this experimental model closely resemble those described in man and suggest that this model may be useful for future investigations of pathogenesis and therapy.
Full text
PDF


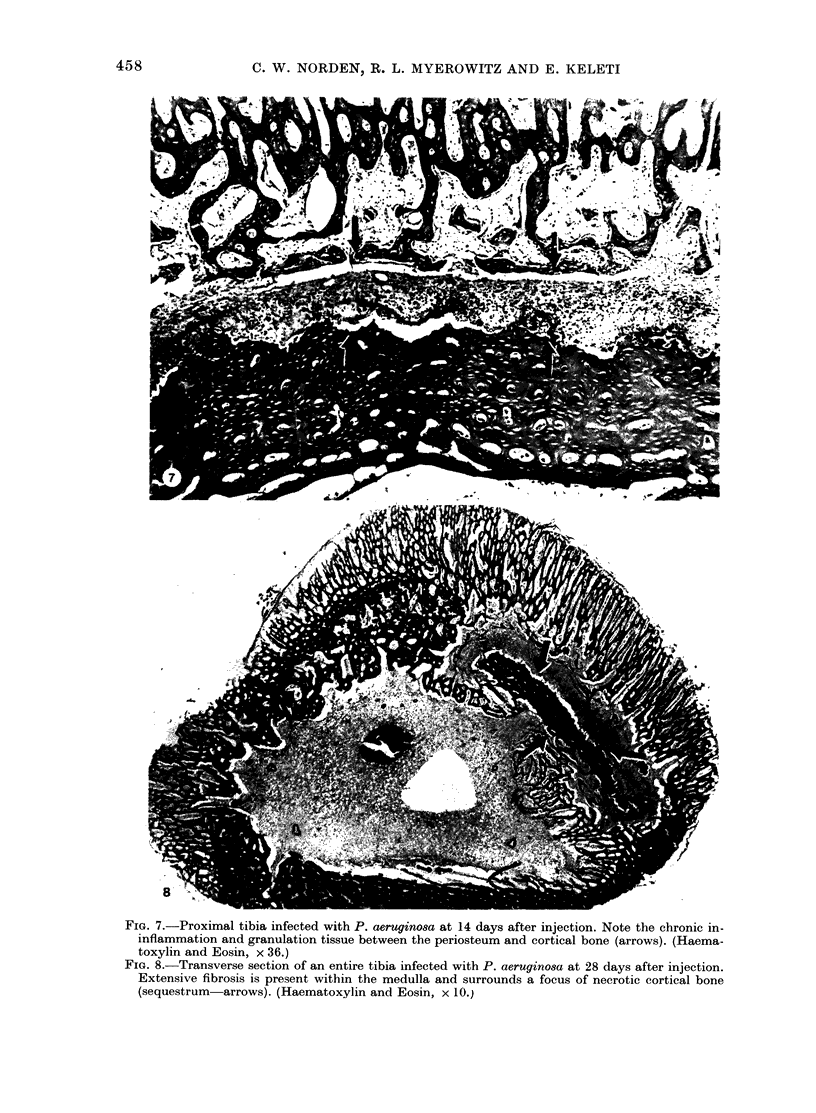


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crane L. R., Kapdi C. C., Wolfe J. N., Silberberg B. K., Lerner A. M. Xeroradiographic, bacteriologic, and pathologic studies in experimental staphylococcus osteomyelitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):303–314. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader J. T., Guckian J. C., Glass D. L., Reinarz J. A. Therapy with hyperbaric oxygen for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1978 Sep;138(3):312–318. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. I. A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):410–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. II. Therapeutic trials and measurement of antibiotic levels in bone. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):565–571. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. IV. Therapeutic trials with rifampin alone and in combination with gentamicin, sisomicin, and cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):493–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. V. Therapeutic trials with oxacillin and sisomicin alone and in combination. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):155–160. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Keleti E. Experimental osteomyelitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):71–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. B. The value of prophylactic penicillin in experimental osteomyelitis. J Surg Res. 1966 Oct;6(10):446–450. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(66)80026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wingerden G. I., Lolans V., Jackson G. G. Experimental pseudomonas osteomyelitis: treatment with sisomicin and carbenicillin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Oct;56(7):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]