Abstract
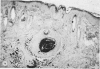
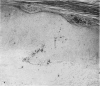
Experiments designed to identify the stimulus to transepidermal elimination (TE) are reported. An animal model has been used in which a charcoal suspension is injected intracutaneously and which mimics the process seen in human skin disease. Studied with antihistamines and indomethacin indicate that neither histamine nor prostaglandins are the initiating stimulus, although the latter substances may be responsible for the associated hyperplasia. Experiments using explants of previously injected skin suggest that physical disturbance of the skin may be implicated in the development of the TE response.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayoumi A. H., Gaskell S., Marks R. Development of a model for transepidermal elimination. Br J Dermatol. 1978 Dec;99(6):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1978.tb07054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bem J. L., Greaves M. W. Prostaglandin E1 effects on epidermal cell growth "in vitro". Arch Dermatol Forsch. 1974;251(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00561708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley-Phillips C. B., Paulli-Jorgensen H., Marks R. The effects of prostaglandins E1 and F2alpha on epidermal growth. Arch Dermatol Res. 1977 Jan 31;257(3):233–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00741838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaglstein W. H., Weinstein G. D. Prostaglandin and DNA synthesis in human skin: possible relationship to ultraviolet light effects. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Jun;64(6):386–389. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12512322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. J., Marks R. The effects of anti-prostaglandin agents on epidermal proliferation induced by dermal inflammation. Br J Dermatol. 1977 Oct;97(4):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb14247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürstenberger G., de Bravo M., Bertsch S., Marks F. The effect of indomethacin on cell proliferation induced by chemical and mechanical means in mouse epidermis in vivo. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;24(3):533–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe N. J., Stoughton R. B. Effects of topical prostaglandin E analogue on normal hairless mouse epidermal DNA synthesis. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Mar;68(3):134–137. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12492448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupulescu A. P. Cytologic and metabolic effects of prostaglandins on rat skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Mar;68(3):138–145. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12492460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malak J. A., Kurbvan A. K. "Catharsis": an excretory function of the epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Jun;84(6):516–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb02540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehregan A. H. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa: a review of the literature and report of 11 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1968 Apr;97(4):381–393. doi: 10.1001/archderm.97.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]