Abstract
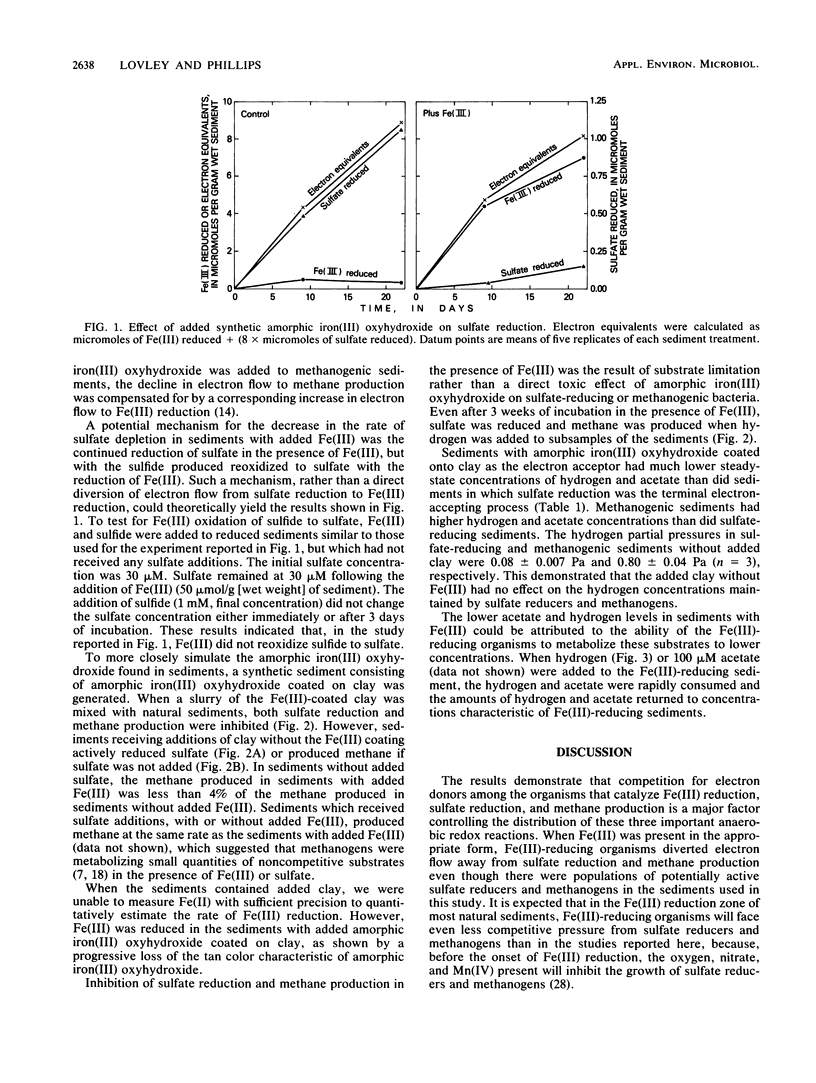
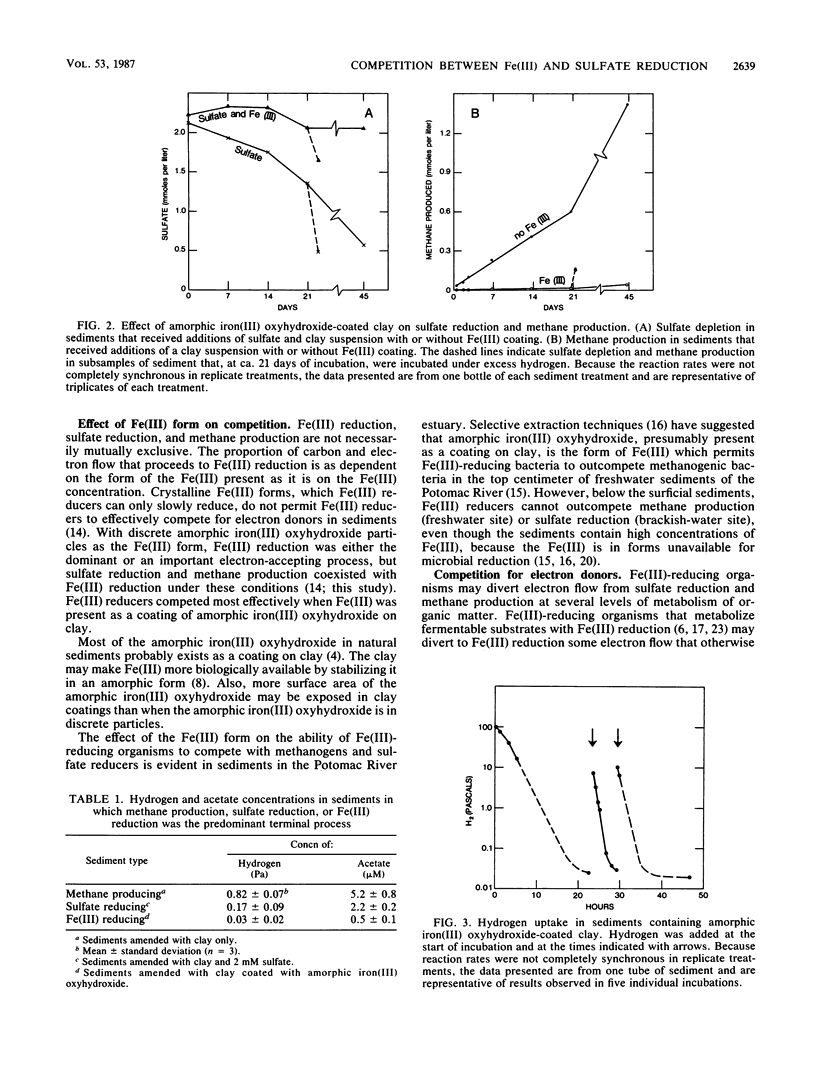
Mechanisms for inhibition of sulfate reduction and methane production in the zone of Fe(III) reduction in sediments were investigated. Addition of amorphic iron(III) oxyhydroxide to sediments in which sulfate reduction was the predominant terminal electron-accepting process inhibited sulfate reduction 86 to 100%. The decrease in electron flow to sulfate reduction was accompanied by a corresponding increase in electron flow to Fe(III) reduction. In a similar manner, Fe(III) additions also inhibited methane production in sulfate-depleted sediments. The inhibition of sulfate reduction and methane production was the result of substrate limitation, because the sediments retained the potential for sulfate reduction and methane production in the presence of excess hydrogen and acetate. Sediments in which Fe(III) reduction was the predominant terminal electron-accepting process had much lower concentrations of hydrogen and acetate than sediments in which sulfate reduction or methane production was the predominant terminal process. The low concentrations of hydrogen and acetate in the Fe(III)-reducing sediments were the result of metabolism by Fe(III)-reducing organisms of hydrogen and acetate at concentrations lower than sulfate reducers or methanogens could metabolize them. The results indicate that when Fe(III) is in a form that Fe(III)-reducing organisms can readily reduce, Fe(III)-reducing organisms can inhibit sulfate reduction and methane production by outcompeting sulfate reducers and methanogens for electron donors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lovley D. R., Dwyer D. F., Klug M. J. Kinetic analysis of competition between sulfate reducers and methanogens for hydrogen in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1373–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1373-1379.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Intermediary metabolism of organic matter in the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):552–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.552-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Sulfate reducers can outcompete methanogens at freshwater sulfate concentrations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):187–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.187-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. Minimum threshold for hydrogen metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1530–1531. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1530-1531.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Availability of ferric iron for microbial reduction in bottom sediments of the freshwater tidal potomac river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):751–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.751-757.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):683–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.683-689.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Rapid assay for microbially reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1536–1540. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1536-1540.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Effect of sulfate on carbon and electron flow during microbial methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.275-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



