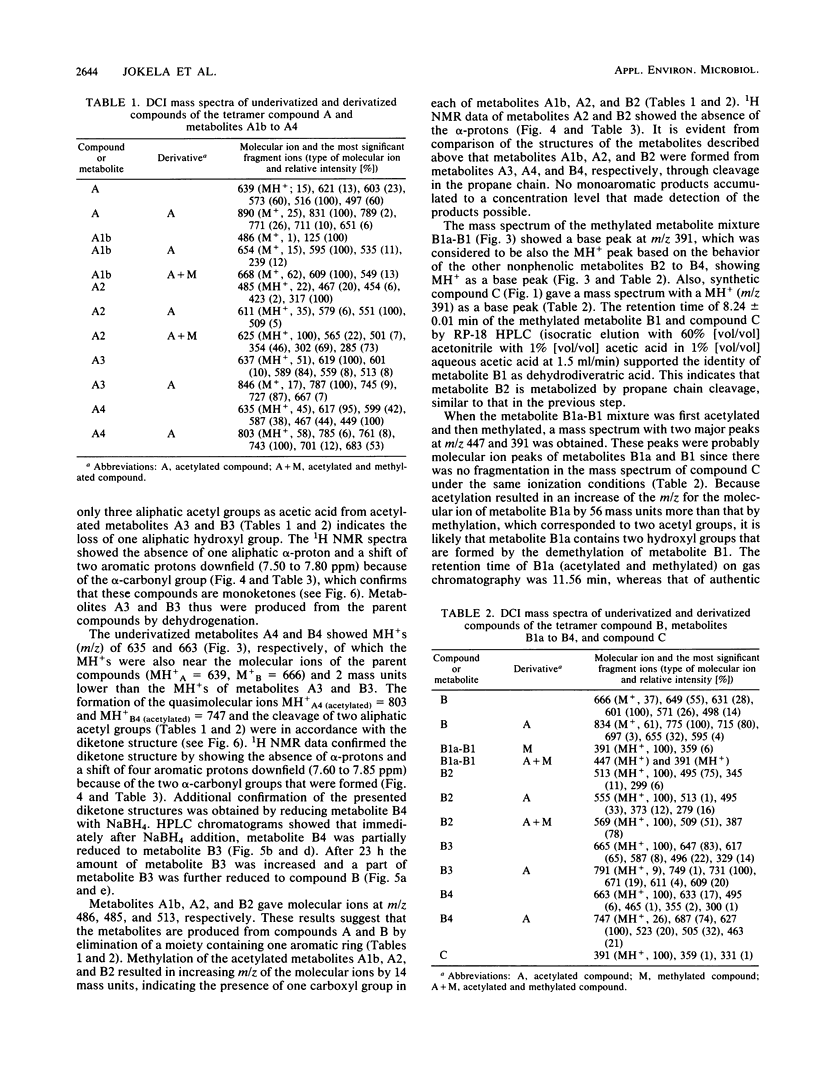
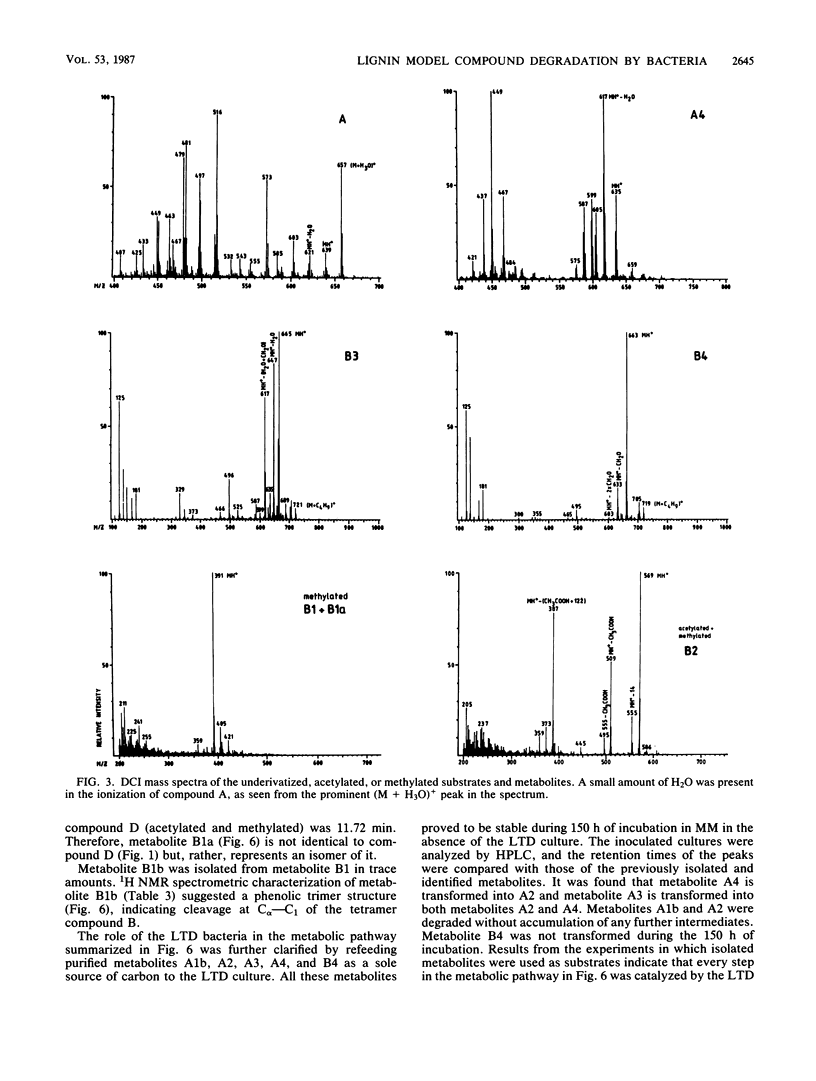
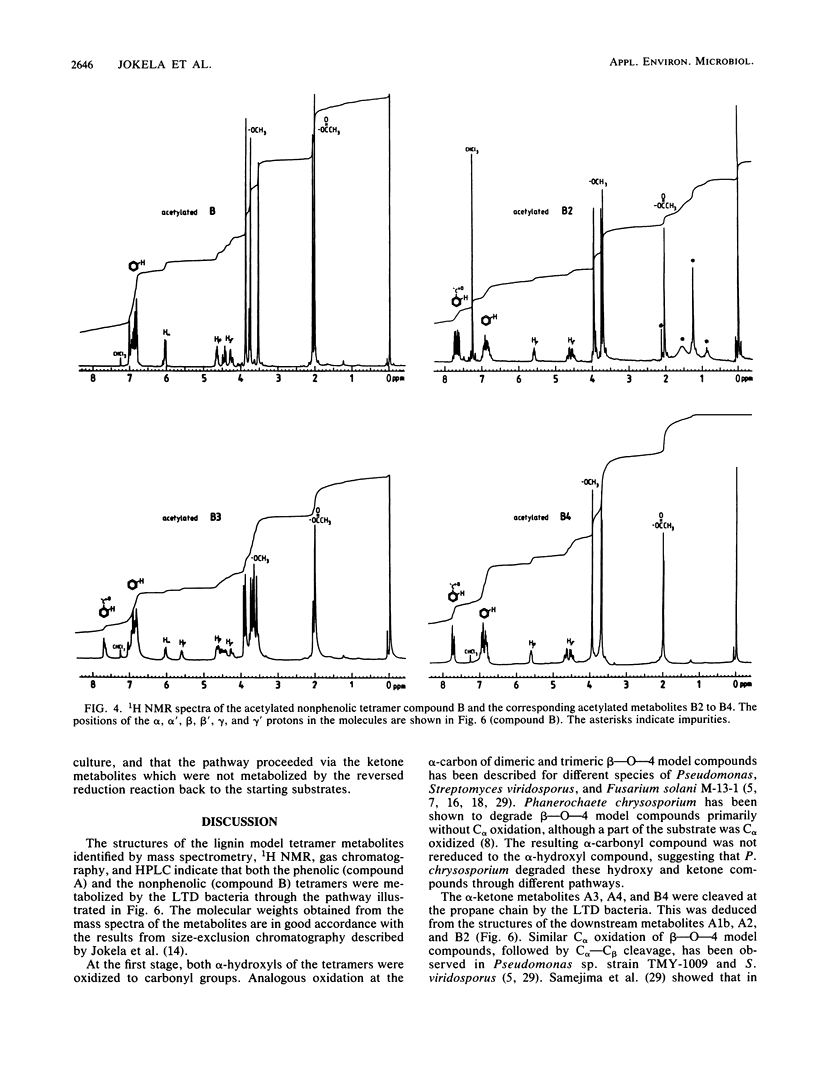
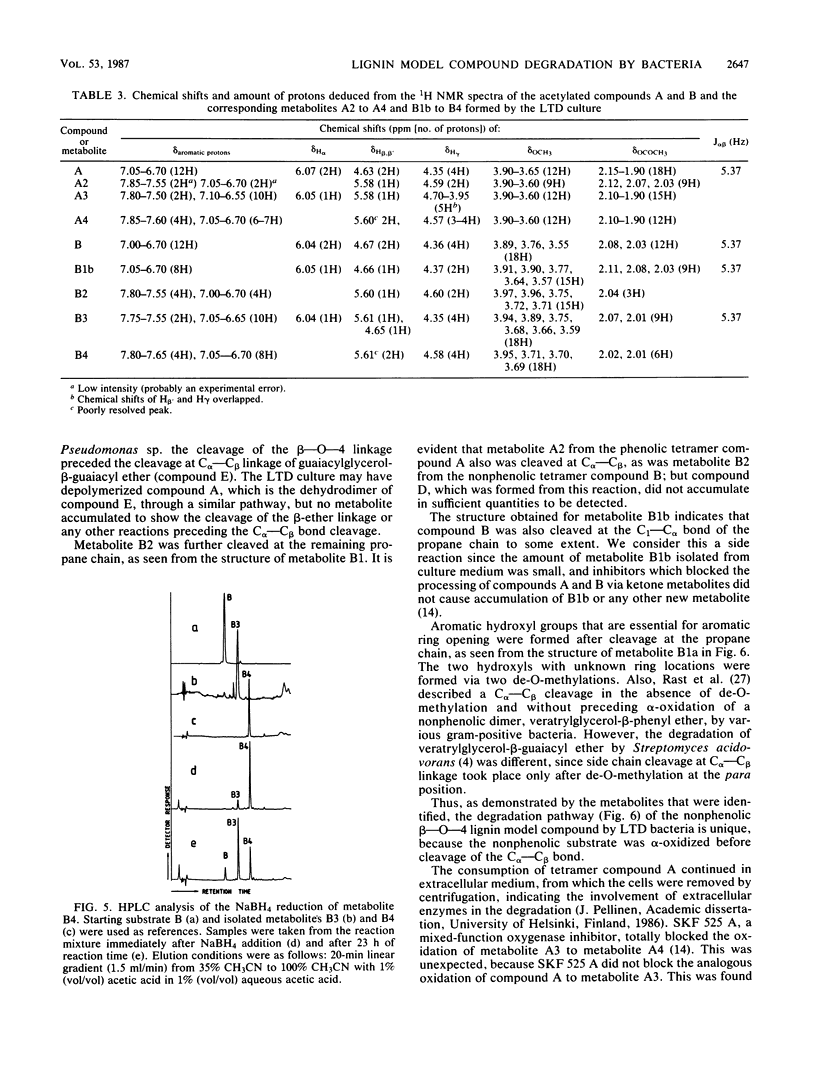
Abstract
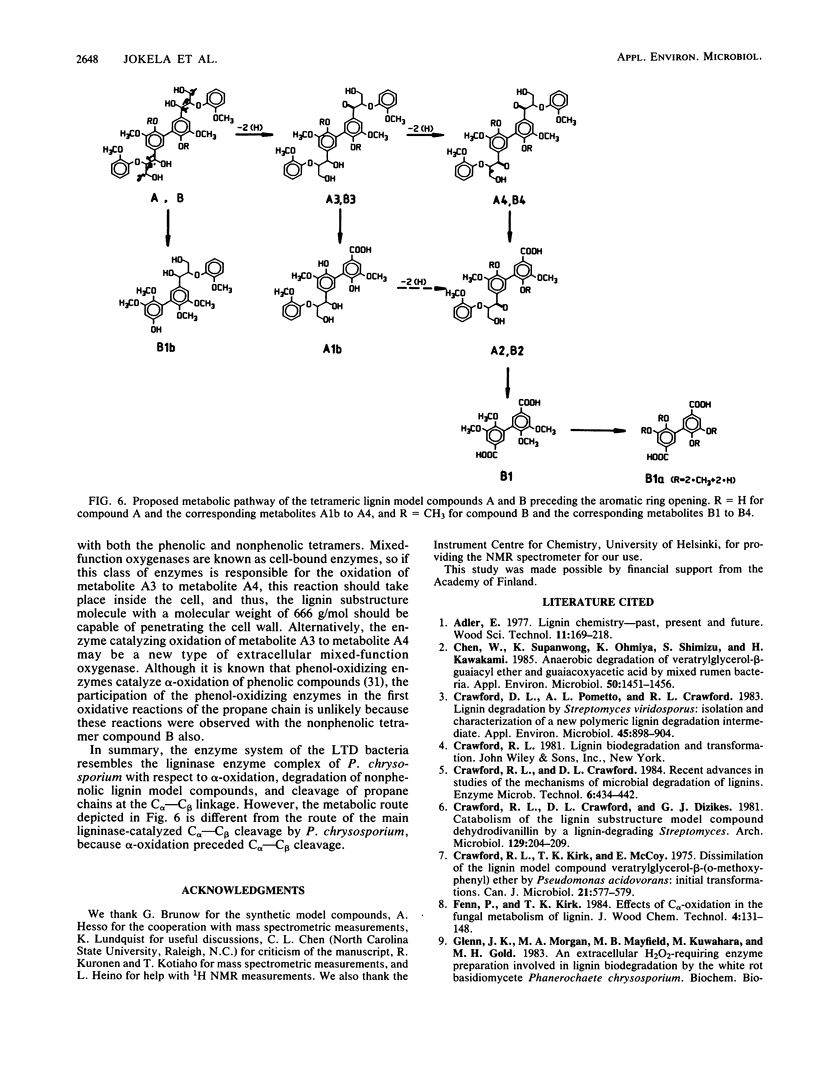
We investigated the metabolic route by which a lignin tetramer-degrading mixed bacterial culture degraded two tetrameric lignin model compounds containing β—O—4 and 5—5 biphenyl structures. The α-hydroxyl groups in the propane chain of both phenolic and nonphenolic tetramers were first oxidized symmetrically in two successive steps to give monoketones and diketones. These ketone metabolites were decomposed through Cα(=O)—Cβ cleavage, forming trimeric carboxyl acids which were further metabolized through another Cα(=O)—Cβ cleavage. Dehydrodiveratric acid, which resulted from the cleavage of the carbon bonds of the nonphenol tetramer, was demethylated twice. Four metabolites of the phenolic tetramer were purified and identified. All of these were stable compounds in sterile mineral medium, but were readily degraded by lignin tetramer-degrading bacteria along the same pathway as the phenol tetramer. No monoaromatic metabolites accumulated. All metabolites were identified by mass and proton magnetic resonance spectrometry. The metabolic route by which the mixed bacterial culture degraded tetrameric lignin model compounds was different from the route of the main ligninase-catalyzed Cα—Cβ cleavage by Phanerochaete chrysosporium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W., Supanwong K., Ohmiya K., Shimizu S., Kawakami H. Anaerobic degradation of veratrylglycerol-beta-guaiacyl ether and guaiacoxyacetic acid by mixed rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1451-1456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., Pometto A. L., Crawford R. L. Lignin Degradation by Streptomyces viridosporus: Isolation and Characterization of a New Polymeric Lignin Degradation Intermediate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):898–904. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.898-904.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., Kirk T. K., McCoy E. Dissimilation of the lignin model compound veratrylglycerol-beta-(o-methoxyphenyl) ether by Pseudomonas acidovorans: initial transformations. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):577–579. doi: 10.1139/m75-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Morgan M. A., Mayfield M. B., Kuwahara M., Gold M. H. An extracellular H2O2-requiring enzyme preparation involved in lignin biodegradation by the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. H., Enoki A., Morgan M. A., Mayfield M. B., Tanaka H. Degradation of the gamma-Carboxyl-Containing Diarylpropane Lignin Model Compound 3-(4'-Ethoxy-3'-Methoxyphenyl)-2-(4''-Methoxyphenyl)Propionic Acid by the Basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):597–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.597-600.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Umezawa T., Higuchi T. Arylglycerol-gamma-Formyl Ester as an Aromatic Ring Cleavage Product of Nonphenolic beta-O-4 Lignin Substructure Model Compounds Degraded by Coriolus versicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1505–1508. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1505-1508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Tien M., Kersten P. J., Mozuch M. D., Kalyanaraman B. Ligninase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Mechanism of its degradation of the non-phenolic arylglycerol beta-aryl ether substructure of lignin. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):279–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2360279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odier E., Janin G., Monties B. Poplar lignin decomposition by gram-negative aerobic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.337-341.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odier E., Rolando C. Catabolism of arylglycerol-beta-aryl ethers lignin model compounds by Pseudomonas cepacia 122. Biochimie. 1985 Feb;67(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-Degrading Enzyme from the Hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



