Abstract
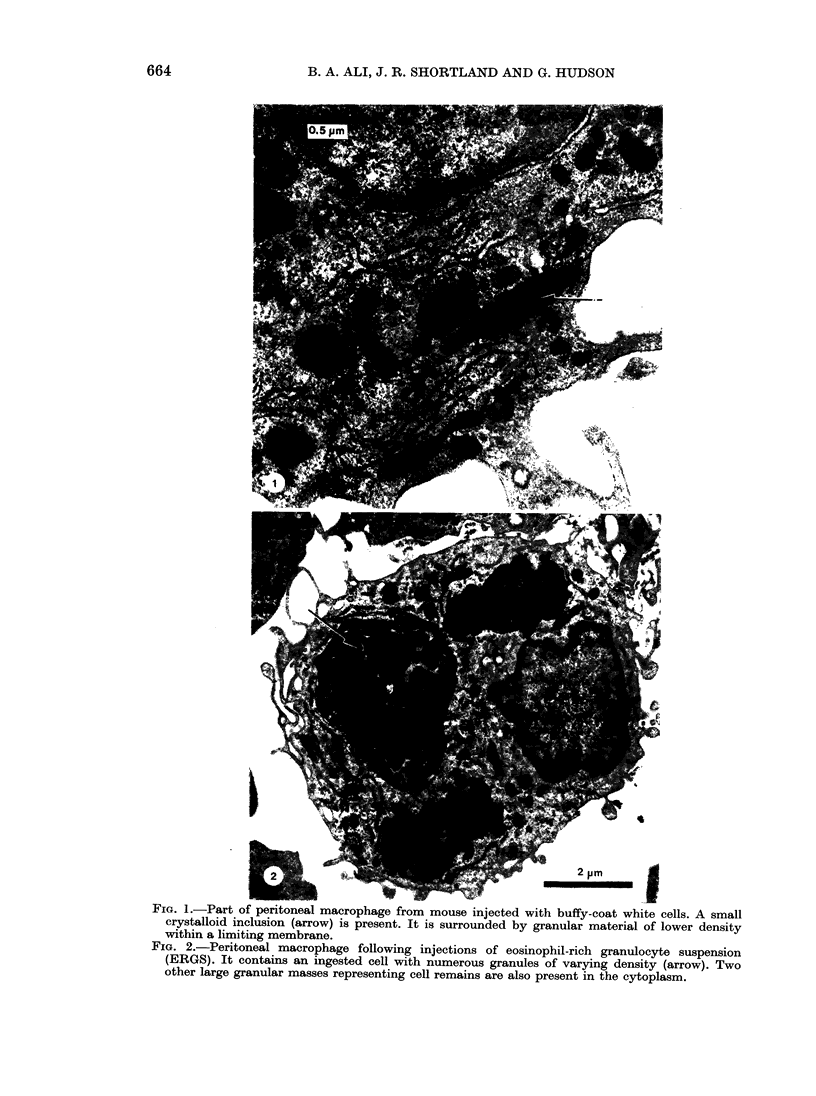
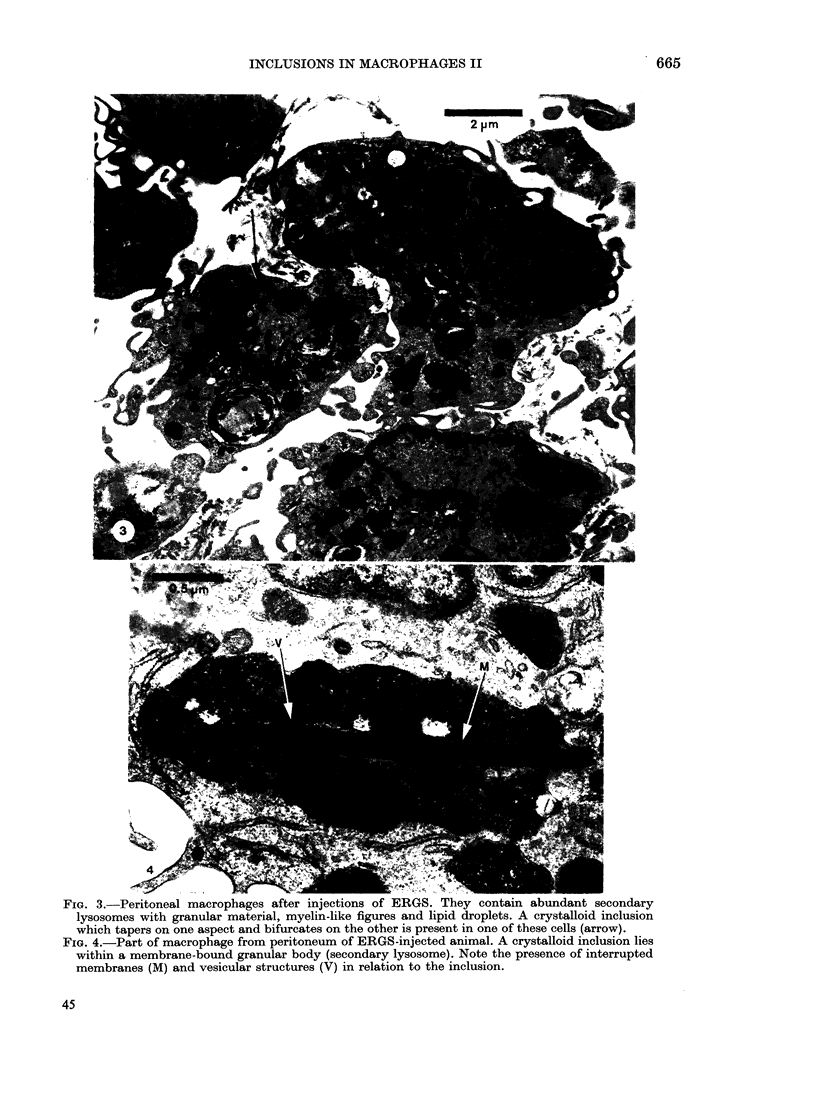
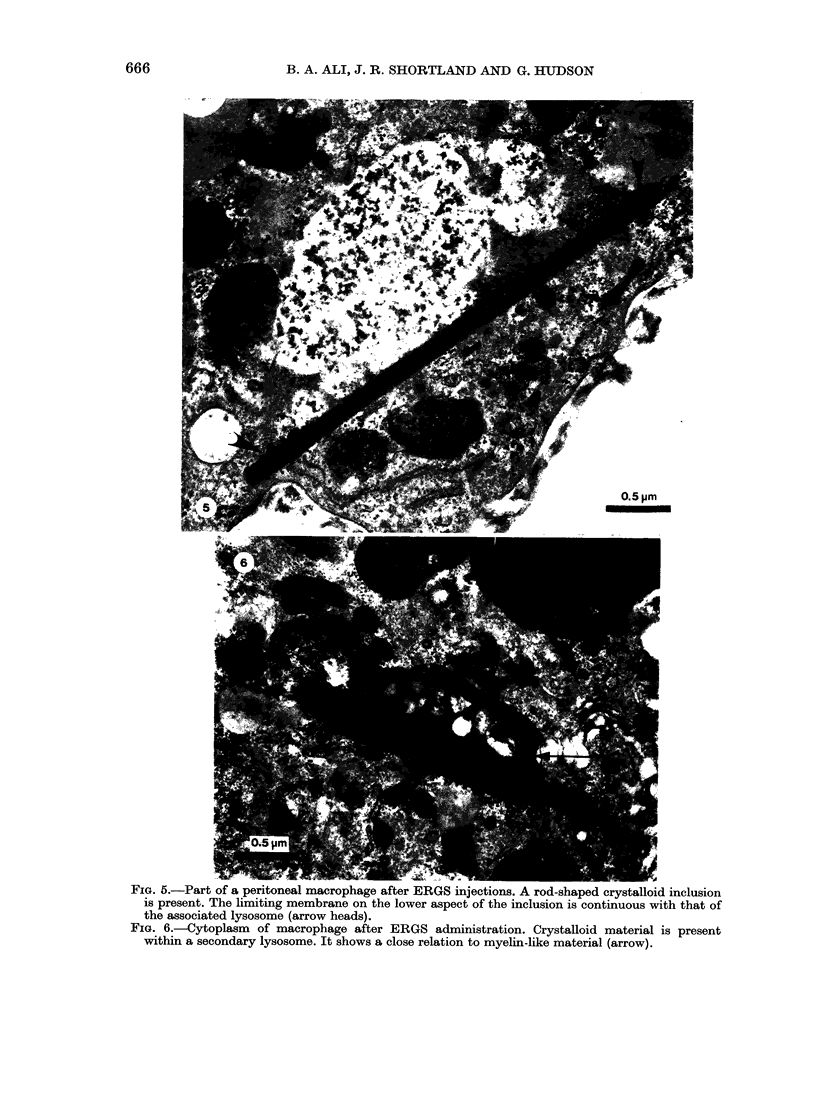
Peritoneal macrophages were studied by light and electron microscopy in normal adult mice 24 h after 3 daily injections of preparations of leucocytes and platelets. Crystalloid inclusions, similar to those seen in bone marrow macrophages of normal adult mice and in man, were occasionally observed in peritoneal macrophages after administration buffy-coat white cells but not after platelets. They were much more frequently seen following the ingestion of eosinophil-rich granulocytes and were almost always associated with secondary lysosomes. Energy-dispersive analysis of X-ray provided further evidence that both crystalloid inclusions and lysosomes originated from the injected granulocytes. These observations suggest that crystalloid inclusions in marrow macrophages are derived from granulocyte breakdown and that in this respect eosinophil granulocytes are of prime importance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER G. T., BLACKWOOD A. FORMATION OF CHARCOT-LEYDEN CRYSTALS IN HUMAN EOSINOPHILS AND BASOPHILS AND STUDY OF THE COMPOSITION OF ISOLATED CRYSTALS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:173–180. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali B. A., Shortland J. R., Hudson G. Origin of crystalloid inclusions in macrophages I: studies of peritoneal macrophages after erythrocyte ingestion. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Dec;62(6):655–661. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUDDECKE E., ESSELLIER A. F., MARTI H. R. Uber die chemische Natur der Charcot-Leydenschen Kristalle. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1956 Sep 25;305(4-6):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. Crystalloid material in macrophages of mouse bone marrow. Acta Anat (Basel) 1968;71(1):100–107. doi: 10.1159/000143176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G., Shortland J. R. Crystalloid material in marrow macrophages of specific pathogen-free mice. Acta Anat (Basel) 1974;87(3):404–408. doi: 10.1159/000144188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. Variations in the amount of crystalloid material in marrow macrophages in mice of different body weights. Acta Anat (Basel) 1969;73(1):136–141. doi: 10.1159/000143290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake E. S., Wright M. J. The fine structure of lung macrophages from rhesus and squirrel monkeys, with special reference to the large numbers of mitochondria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Sep;114(3):581–592. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matulionis D. H., Traurig H. H. In situ response of lung macrophages and hydrolase activities to cigarette smoke. Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(3):314–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Forbes I. M. Charcot-Leyden crystals in human bone marrow. Pathology. 1972 Oct;4(4):279–294. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSH R. A. The genesis of the Charcot-Leyden crystal in the eosinophilic leukocyte of man. Am J Pathol. 1959 Nov-Dec;35:1091–1103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Whest G. M., Nishimura E. T. Age-related variations of paracrystalline inclusions in central reticular cells of mouse bone marrow. Exp Mol Pathol. 1979 Apr;30(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(79)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyngier F. R., Brockbank A. Electron microscopy of the lung in experimental Toxocara canis infection. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1974 Jun;68(2):229–233. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1974.11686940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Hashimi W. Charcot-Leyden crystals. Formation from primate and lack of formation from nonprimate eosinophils. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):311–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]