Abstract
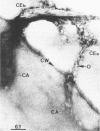
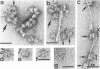
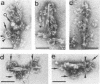
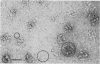
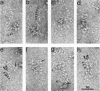
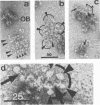
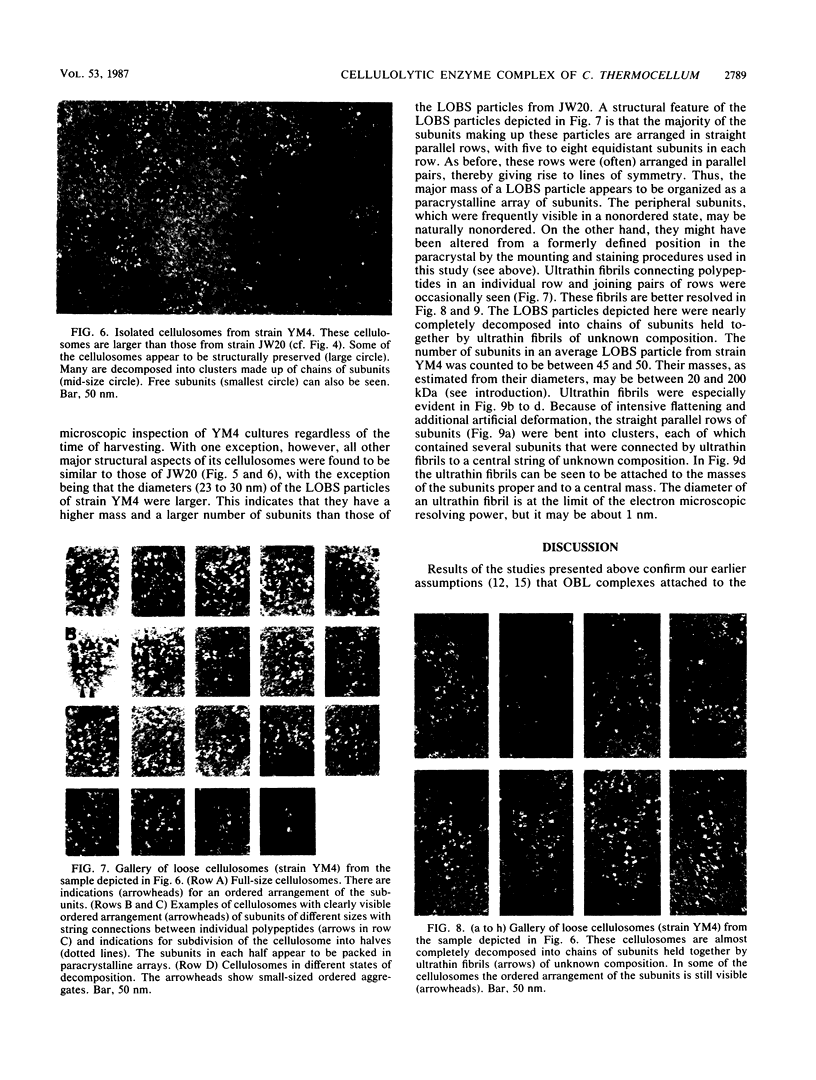
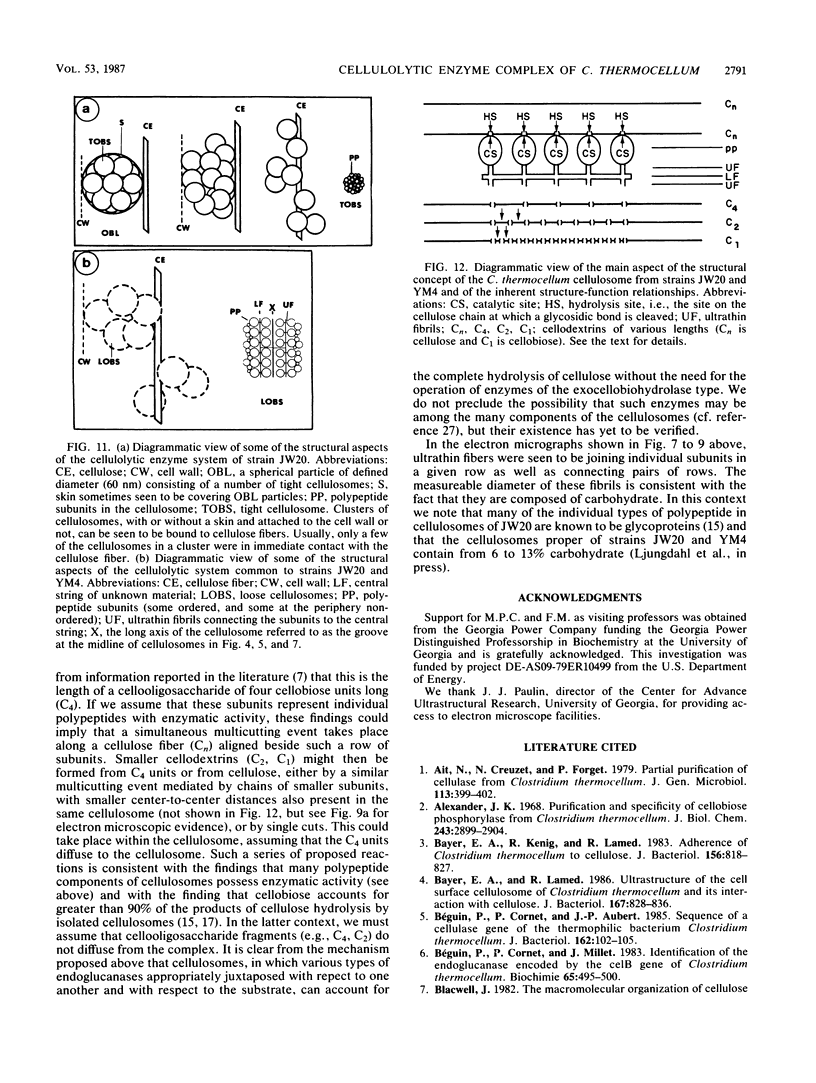
Clostridium thermocellum JW20 and YM4 both synthesize cellulolytic enzyme complexes, cellulosomes, when grown on medium containing cellulose. Electron microscopic studies showed that, in the early stages of growth of strain JW20, clusters of tightly packed cellulosomes, i.e., polycellulosomes, were located on the cell surface and were bound to cellulose. The polycellulosome was estimated to have a particle mass of 50 × 106 to 80 × 106 daltons (Da), while that of the cellulosome was estimated to be 2 × 106 to 2.5 × 106 Da and to contain about 35 polypeptides ranging from 20 to 200 kDa. The cellulosome produced by strain YM4 was found to be somewhat larger, with the estimated particle mass being 3.5 × 106 Da, and the number of polypeptides was counted to be 45 to 50, ranging from 20 to 200 kDa. In the early stages of cultivation, the cellulosomes from both species exist as tightly packed complexes (tight cellulosomes). These subsequently decompose to loosely packed complexes (loose cellulosomes) and ultimately to free polypeptides. Examination of the loose cellulosomal particles showed that they contain rows of equidistantly spaced, similarly sized polypeptide subunits, with an apparently identical orientation arranged parallel to the major axis of the cellulosome. It is postulated that on binding of a cellulose chain alongside such a row of subunits a simultaneous multicutting event occurs that leads to the release of cellooligosaccharides of four cellobiose units in length (C4). Rows of smaller-sized subunits with lower center-to-center distances, which are also present in the cellulosome, subsequently cleave the C4 fragments (or cellulose) to C2 (cellotetraose) or C1 (cellobiose). In this way the cellulosome can catalyze the complete hydrolysis of cellulose.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. K. Purification and specificity of cellobiose phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2899–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Kenig R., Lamed R. Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):818–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.818-827.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Lamed R. Ultrastructure of the cell surface cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum and its interaction with cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.828-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguin P., Cornet P., Millet J. Identification of the endoglucanase encoded by the celB gene of Clostridium thermocellum. Biochimie. 1983 Aug-Sep;65(8-9):495–500. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(83)80131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P., Cornet P., Aubert J. P. Sequence of a cellulase gene of the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):102–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.102-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan M. P., Hon-Nami K., Hon-Nami H., Ljungdahl L. G., Paulin J. J., Rigsby W. E. The cellulolytic enzyme complex of Clostridium thermocellum is very large. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):904–909. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sakajoh M., Halliwell G., Madia A., Demain A. L. Saccharification of Complex Cellulosic Substrates by the Cellulase System from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1125-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Setter E., Bayer E. A. Characterization of a cellulose-binding, cellulase-containing complex in Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.828-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBEE R. H. The characteristics of Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1954 Apr;67(4):505–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.4.505-506.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J. D., Bayer R. The limits of the ledger in public health promotion. Hastings Cent Rep. 1985 Dec;15(6):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase (1,4-beta-D-glucan glucanohydrolase) from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):341–350. doi: 10.1042/bj1990341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petre J., Longin R., Millet J. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochimie. 1981 Jul;63(7):629–639. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth K., Alexander J. K. Purification and properties of beta-1,4-oligoglucan:orthophosphate glucosyltransferase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):457–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]