Abstract
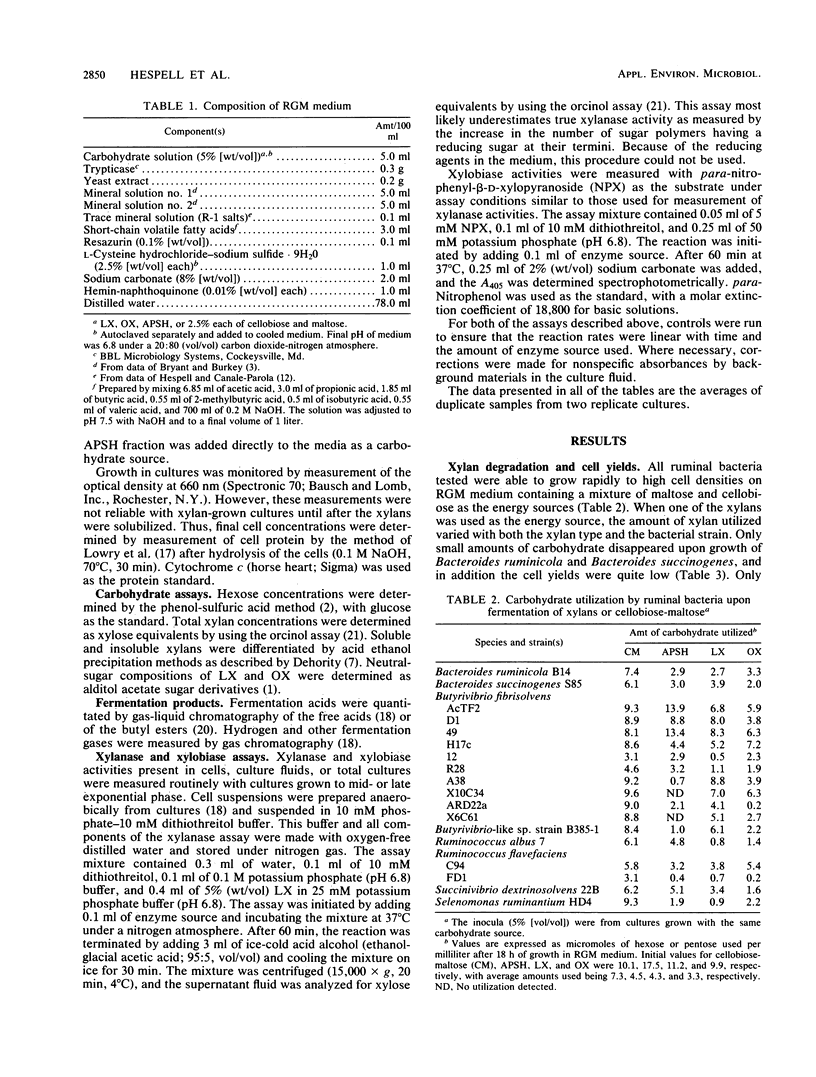
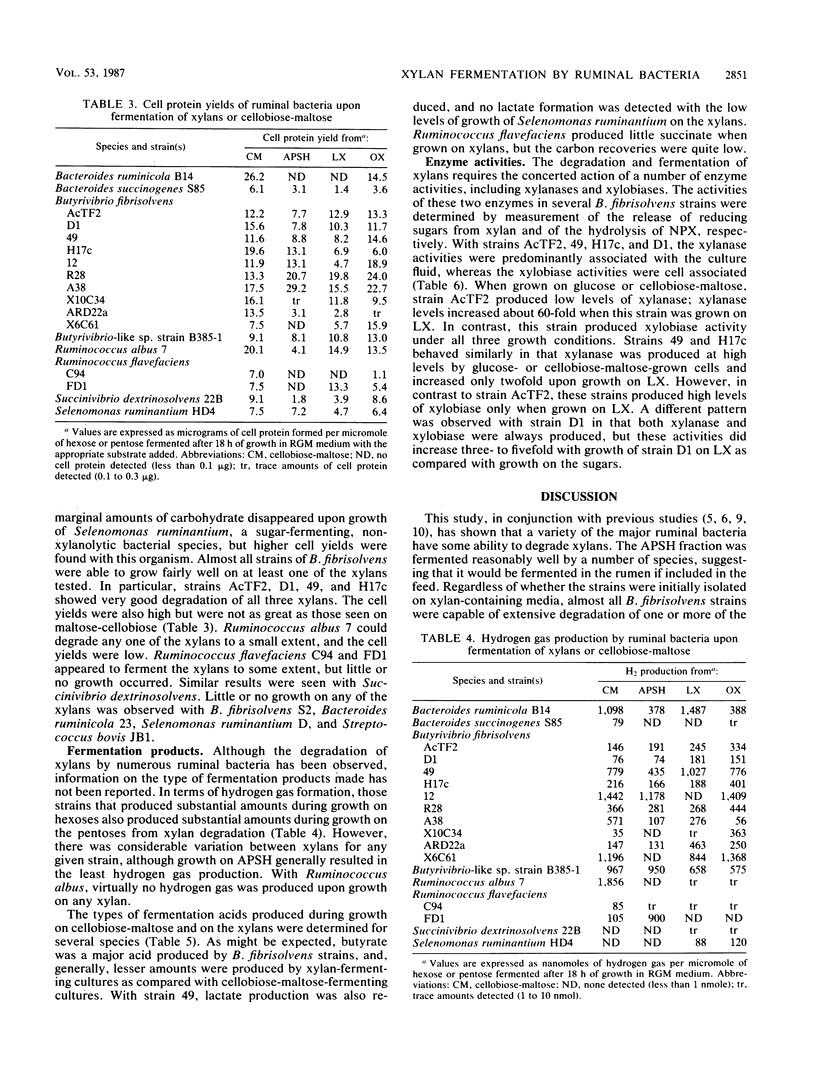
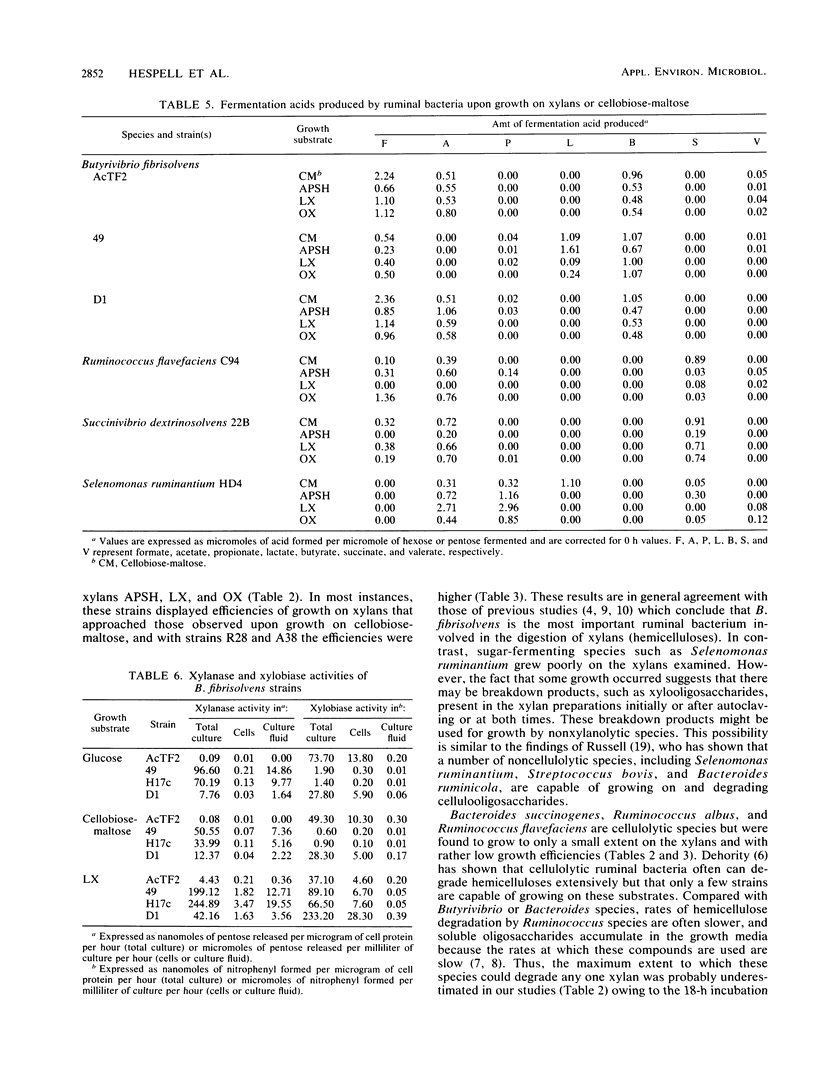
The ability of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens and other ruminal bacteria (6 species, 18 strains) to ferment a crude xylan from wheat straw or to ferment xylans from larchwood or oat spelts was studied. Liquid cultures were monitored for carbohydrate utilization, cell growth (protein), and fermentation acid production. B. fibrisolvens 49, H17c, AcTF2, and D1 grew almost as well on one or more of the xylans as they did on cellobiose-maltose. B. fibrisolvens 12, R28, A38, X10C34, ARD22a, and X6C61 exhibited moderate growth on xylans. Partial fermentation of xylans was observed with Bacteroides ruminicola B14, Bacteroides succinogenes S85, Ruminococcus albus 7, Ruminococcus flavefaciens C94 and FD1, and Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens 22B. All xylans tested appeared to have a small fraction of carbohydrate that supported low levels of growth of nonxylanolytic strains such as Selenomonas ruminantium HD4. Compared to growth on hexoses, the same array of fermentation acids was produced upon growth on xylans for most strains; however, reduced lactate levels were observed for B. fibrisolvens 49 and Selenomonas ruminantium HD4. Measurements of enzyme activities of B. fibrisolvens AcTF2, 49, H17c, and D1 indicated that the xylobiase activities were cell associated and that the xylanase activities were predominantly associated with the culture fluid. The pattern of expression of these enzymes varied both between strains and between the carbon sources on which the strains were grown.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen J. A., Dehority B. A. Degradation and utilization of hemicellulose from intact forages by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):362–368. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.362-368.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEHORITY B. A. DEGRADATION AND UTILIZATION OF ISOLATED HEMICELLULOSE BY PURE CULTURES OF CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1515-1520.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Hemicellulose degradation by rumen bacteria. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1819–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Mechanism of isolated hemicellulose and xylan degradation by cellulolytic rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 May;16(5):781–786. doi: 10.1128/am.16.5.781-786.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Rate of isolated hemicellulose degradation and utilization by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):987–993. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.987-993.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD B. H. Hydrolysis of the soluble pentosans of wheat flour and Rhodymenia pa'mata by ruminal micro-organisms. Biochem J. 1957 Dec;67(4):643–651. doi: 10.1042/bj0670643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD B. H., JONES G., PURDOM M. R. The pentosanases of some rumen bacteria. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:173–180. doi: 10.1042/bj0740173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerley M. S., Fahey G. C., Jr, Berger L. L., Merchen N. R., Gould J. M. Effects of alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment of wheat straw on site and extent of digestion in sheep. J Anim Sci. 1986 Sep;63(3):868–878. doi: 10.2527/jas1986.633868x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. Fermentation of cellodextrins by cellulolytic and noncellulolytic rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):572–576. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.572-576.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Muirhead P. A. Quantitative method for the gas chromatographic analysis of short-chain monocarboxylic and dicarboxylic acids in fermentation media. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):374–381. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.374-381.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


