Abstract
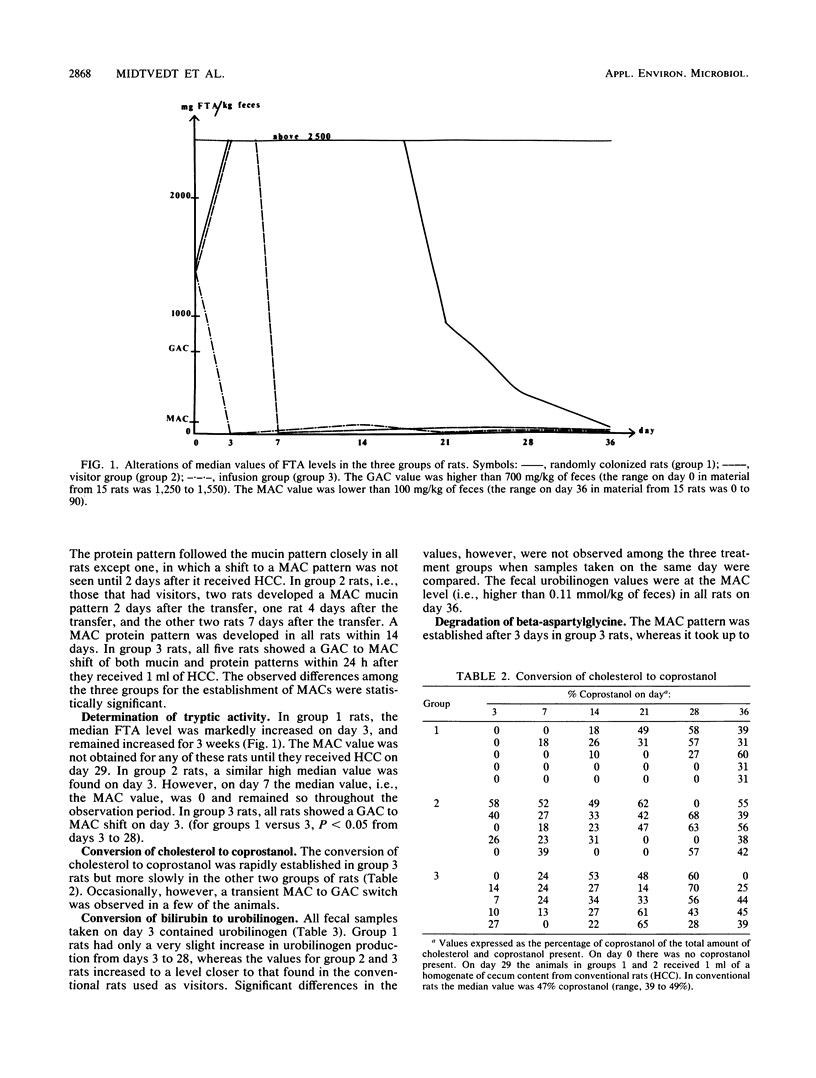
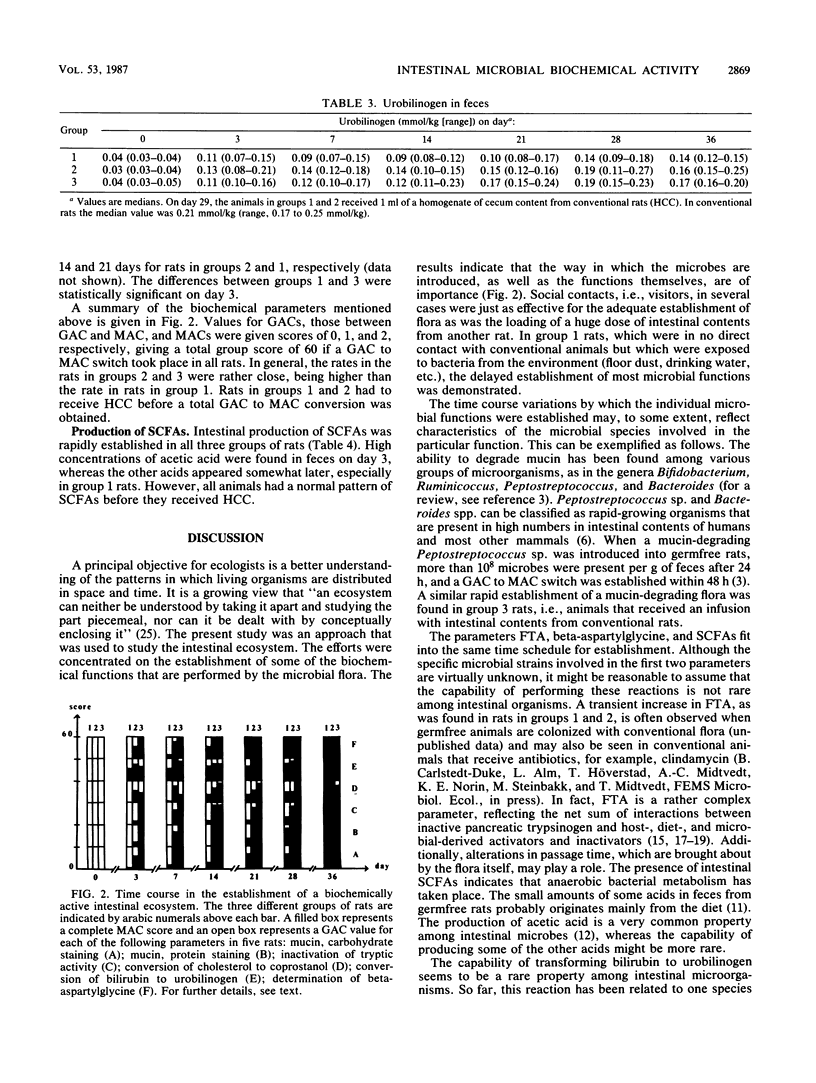
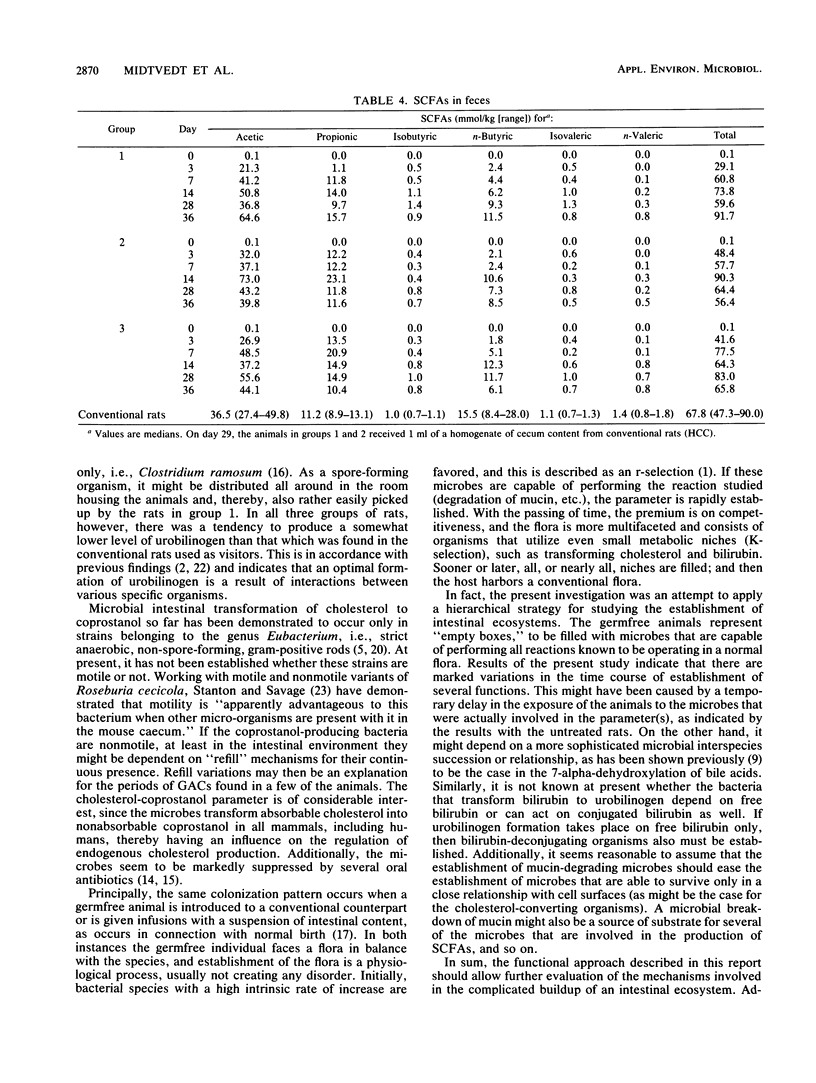
A time course study for the establishment of some biochemical microbial intestinal functions was undertaken in ex-germfree rats conventionalized, i.e., colonized with conventional flora, in three different ways: untreated (group 1); contact with visitor rats (group 2); inoculated with intestinal contents from conventional rats (group 3). The first two groups of rats were inoculated with the intestinal contents from conventional rats after being out of the germfree isolators for 4 weeks. The biochemical parameters studied were degradation of mucin, inactivation of tryptic activity, conversion of cholesterol to coprostanol and of bilirubin to urobilinogen, degradation of beta-aspartylglycine, and formation of short-chain fatty acids. The results showed that the way in which the microbes were introduced and the microbial biochemical functions themselves were of importance. In several cases, social contacts, i.e., contact with visitor rats, were just as effective for the functionally adequate establishment of microbial intestinal functions as was inoculation with intestinal contents from conventional rats. Some of the biochemical parameters studied were established after a few days, whereas the establishment of others was markedly delayed. When inoculated after 4 weeks, all rats in the first two groups were colonized with conventional flora within 1 week. The results indicate that the model system described is suitable when studying buildup mechanisms in intestinal ecosystem(s).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlstedt-Duke B., Gustafsson B. E., Midtvedt T. Clindamycin-induced alterations in intestinal microflora-associated characteristics in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Jan;20(1):92–98. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke B., Midtvedt T., Nord C. E., Gustafsson B. E. Isolation and characterization of a mucin-degrading strain of Peptostreptococcus from rat intestinal tract. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1986 Oct;94(5):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyssen H. J., Parmentier G. G., Compernolle F. C., De Pauw G., Piessens-Denef M. Biohydrogenation of sterols by Eubacterium ATCC 21,408--Nova species. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):411–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E. Lightweight stainless steel systems for rearing germfree animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 May 8;78:17–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb53092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B. E., Carlstedt-Duke B. Intestinal water-soluble mucins in germfree, exgermfree and conventional animals. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Oct;92(5):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B. E., Midtvedt T., Norman A. Metabolism of cholic acid in germfree animals after the establishment in the intestinal tract of deconjugating and 7 alpha-dehydroxylating bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(3):433–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høverstad T., Fausa O., Bjørneklett A., Bøhmer T. Short-chain fatty acids in the normal human feces. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 May;19(3):375–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høverstad T., Midtvedt T., Bøhmer T. Short-chain fatty acids in intestinal content of germfree mice monocontaminated with Escherichia coli or Clostridium difficile. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Apr;20(3):373–380. doi: 10.3109/00365528509091667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høverstad T., Midtvedt T. Short-chain fatty acids in germfree mice and rats. J Nutr. 1986 Sep;116(9):1772–1776. doi: 10.1093/jn/116.9.1772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Bjørneklett A., Carlstedt-Duke B., Gustafsson B. E., Høverstad T., Lingaas E., Norin K. E., Saxerholt H., Steinbakk M. The influence of antibiotics upon microflora-associated characteristics in man and mammals. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Carlstedt-Duke B., Høverstad T., Lingaas E., Norin E., Saxerholt H., Steinbakk M. Influence of peroral antibiotics upon the biotransformatory activity of the intestinal microflora in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;16(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1986.tb01300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Gustafsson B. E. Microbial conversion of bilirubin to urobilins in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Apr;89(2):57–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00152_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norin K. E., Gustafsson B. E., Lindblad B. S., Midtvedt T. The establishment of some microflora associated biochemical characteristics in feces from children during the first years of life. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Mar;74(2):207–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norin K. E., Gustafsson B. E., Midtvedt T. Strain differences in faecal tryptic activity of germ-free and conventional rats. Lab Anim. 1986 Jan;20(1):67–69. doi: 10.1258/002367786781062188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norin K. E., Midtvedt T., Gustafsson B. E. Influence of intestinal microflora on the tryptic activity during lactation in rats. Lab Anim. 1986 Jul;20(3):234–237. doi: 10.1258/002367786780865656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadzikowski M. R., Sperry J. F., Wilkins T. D. Cholesterol-reducing bacterium from human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):355–362. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.355-362.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxerholt H., Carlstedt-Duke B., Høverstad T., Lingaas E., Norin K. E., Steinbakk M., Midtvedt T. Influence of antibiotics on the faecal excretion of bile pigments in healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Oct;21(8):991–996. doi: 10.3109/00365528608996410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxerholt H., Midtvedt T., Gustafsson B. E. Deconjugation of bilirubin conjugates and urobilin formation by conventionalized germ-free rats. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1984 Oct;44(6):573–577. doi: 10.1080/00365518409083613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Savage D. C. Motility as a factor in bowel colonization by Roseburia cecicola, an obligately anaerobic bacterium from the mouse caecum. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jan;130(1):173–183. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling G. W., Groen G., Tuinte J. H., Koopman J. P., Kennis H. M. Biochemical effects on germ-free mice of association with several strains of anaerobic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):57–63. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


