Abstract
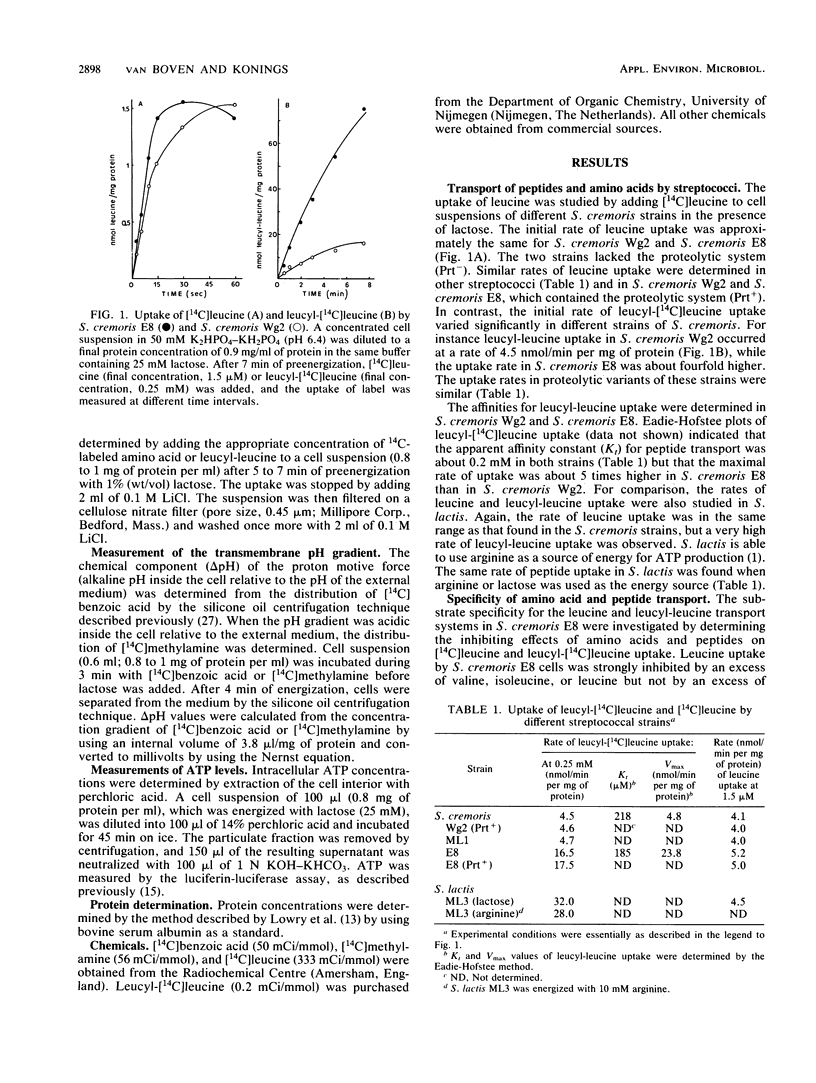
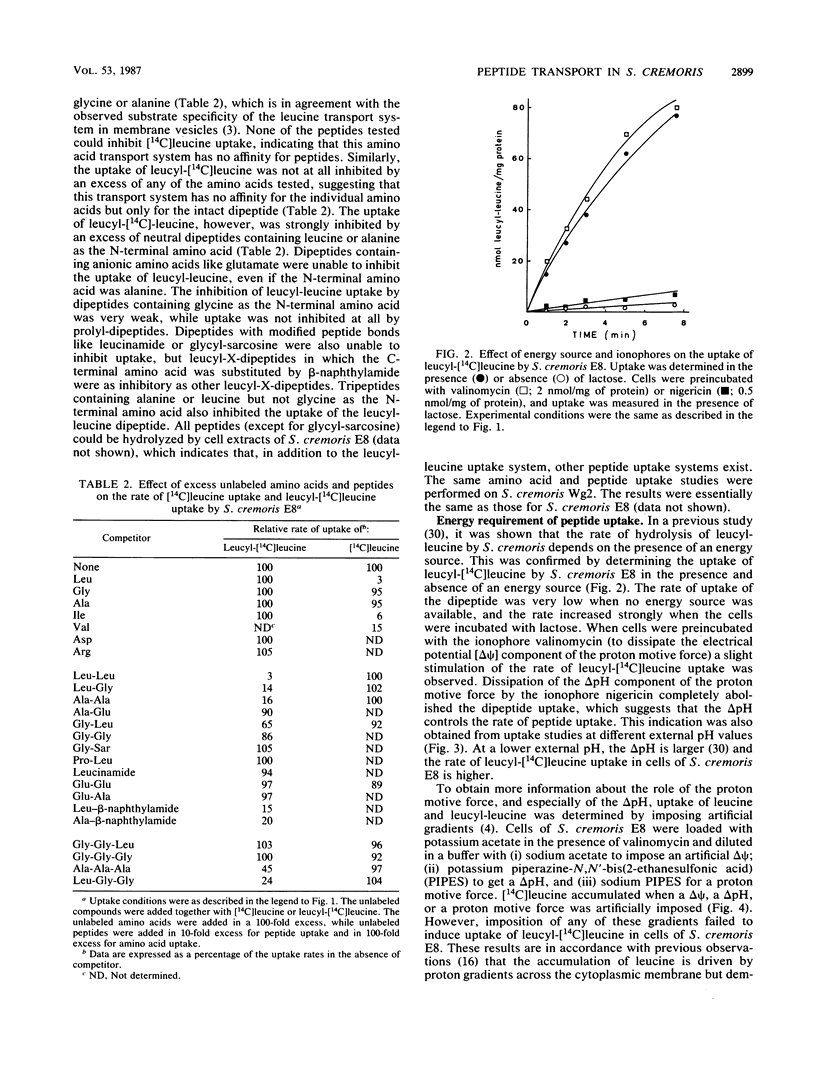
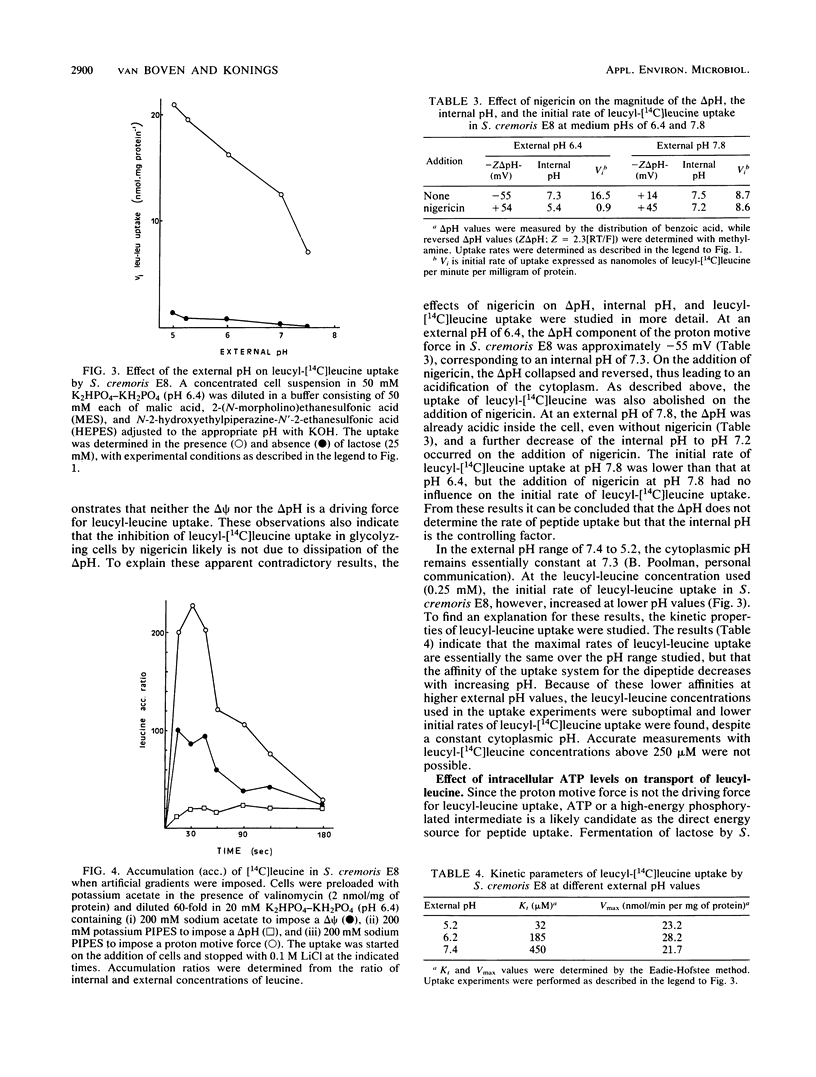
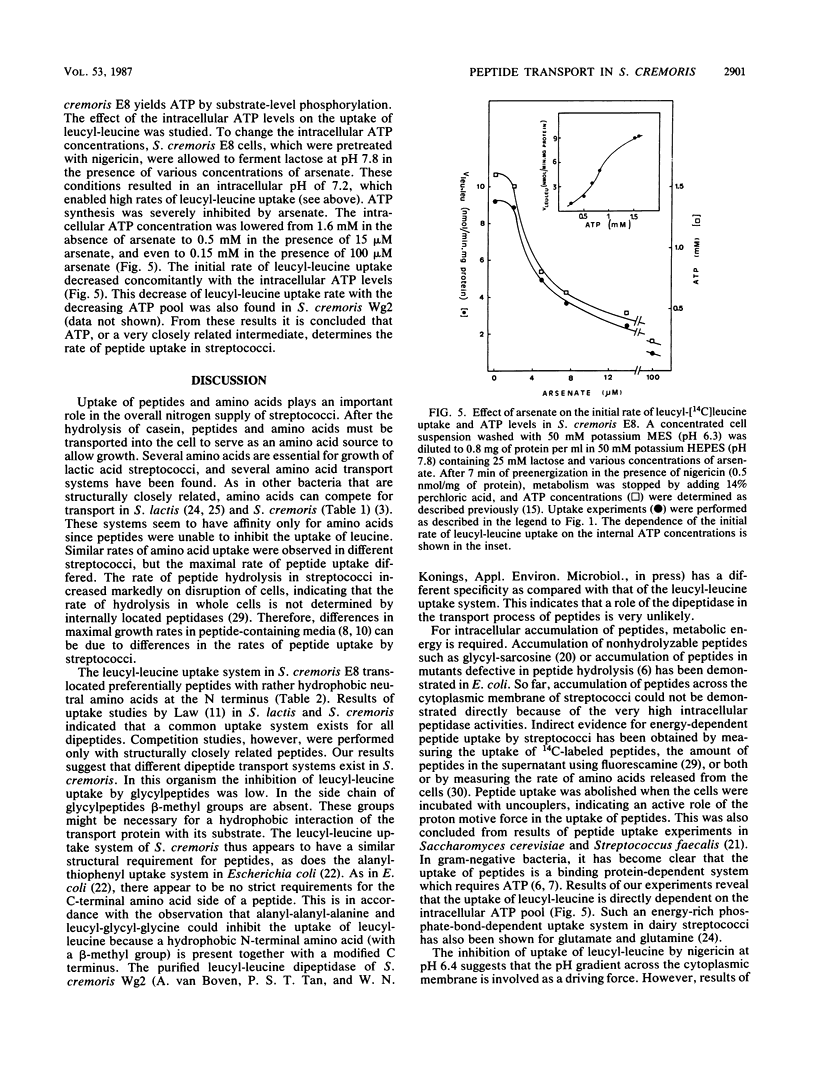
The uptake of amino acids and peptides by Streptococcus cremoris is mediated by different highly specific transport systems. The leucine transport system has a high affinity only for leucine, isoleucine, and valine and no affinity for leucyl-peptides. The transport system for leucyl-leucine is strongly inhibited by several dipeptides with hydrophobic, neutral, N-terminal amino acids but not by leucine. The leucyl-leucine transport system has a high affinity for dipeptides containing β-methyl groups in the side chain; the C terminus of the dipeptide affects the affinity to a much lower extent. Leucyl-leucine transport in whole cells was studied as a function of the internal pH at different external pH values in the presence and absence of nigericin. The internal pH was shown to be an important controlling factor in leucyl-leucine uptake, but the ΔpH was not involved as a driving force. At increasing external pH values, the affinity of the transport system for leucyl-leucine decreased. Uptake of leucyl-leucine was also studied in the presence of arsenate, which inhibited ATP synthesis by substrate-level phosphorylation. The rate of leucyl-leucine transport appeared to be dependent on the intracellular ATP concentrations. These results indicate that the energy for the leucyl-leucine transport is directly supplied by ATP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crow V. L., Thomas T. D. Arginine metabolism in lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1024–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1024-1032.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Kodde J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Neutral amino acid transport by membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris is subject to regulation by internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2748-2754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Transport of branched-chain amino acids in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5193–5200. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5193-5200.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Location of Peptidases Outside and Inside the Membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.177-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gibson M. M. Peptide transport in bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:365–377. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Powell L. M., Higgins C. F. Peptide transport in Salmonella typhimurium: molecular cloning and characterization of the oligopeptide permease genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):101–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00326543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolstad J., Law B. A. Comparative peptide specificity of cell wall, membrane and intracellular peptidases of group N streptococci. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 May;58(5):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A., Kolstad J. Proteolytic systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):225–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00399500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A. Peptide utilization by group N streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Mar;105(1):113–118. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W., Bell G. Direct determination of the properties of peptide transport systems in Escherichia coli, using a fluorescent-labeling procedure. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):447–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.447-455.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. Peptide transport in bacteria: methods, mutants and energy coupling. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):794–798. doi: 10.1042/bst0110794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D., Gilvarg C. Spectrophotometric determination of affinities of peptides for their transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):943–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.943-948.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of the glutamate-glutamine transport system by intracellular pH in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2272–2276. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2272-2276.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Konings W. N. Kinetic properties of a phosphate-bond-driven glutamate-glutamine transport system in Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2755–2761. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2755-2761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Hillier A. J., Lees G. J. The nature of the stimulation of the growth of Streptococcus lactis by yeast extract. J Dairy Res. 1975 Feb;42(1):123–138. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900015156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Brink B., Konings W. N. Electrochemical proton gradient and lactate concentration gradient in Streptococcus cremoris cells grown in batch culture. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.682-686.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boven A., Konings W. N. Energetics of Leucyl-Leucine Hydrolysis in Streptococcus cremoris Wg(2). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):95–100. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.95-100.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


