Abstract
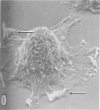
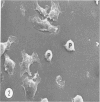
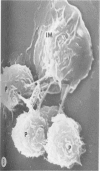
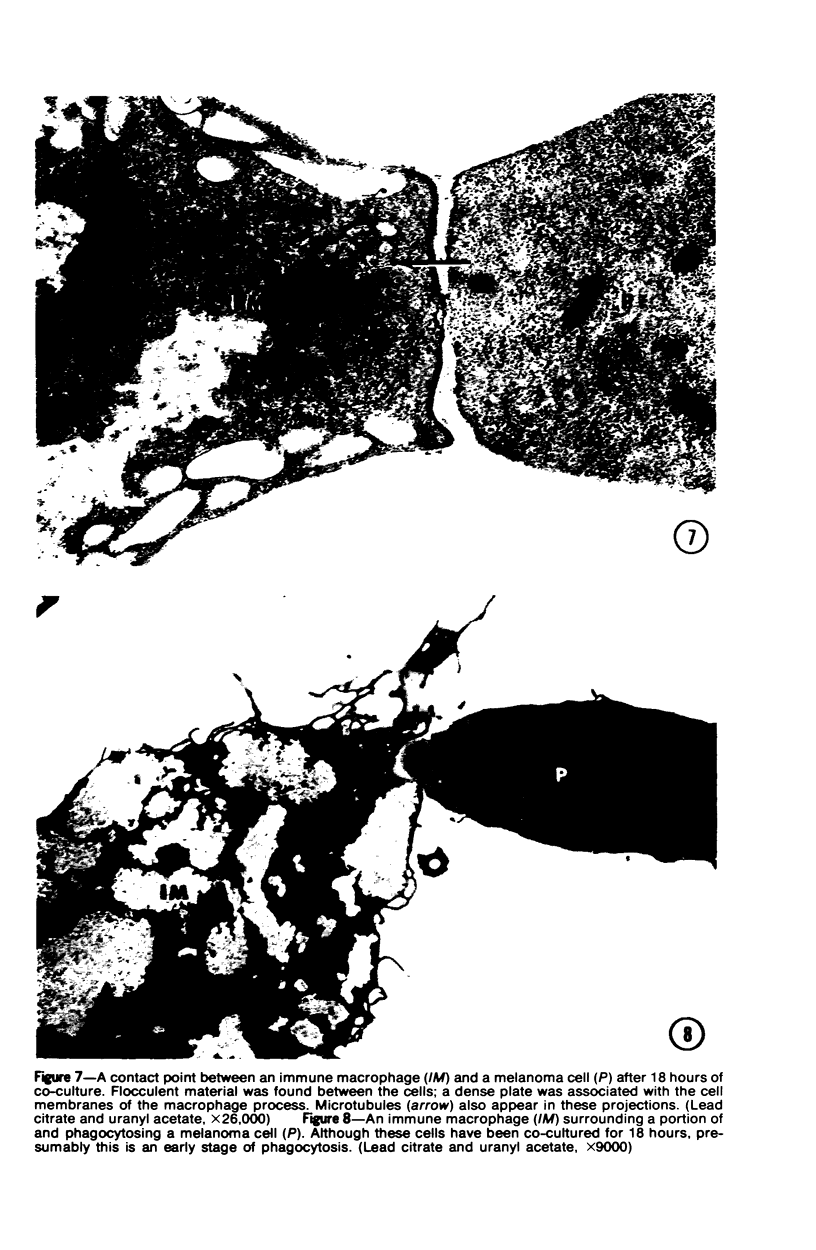
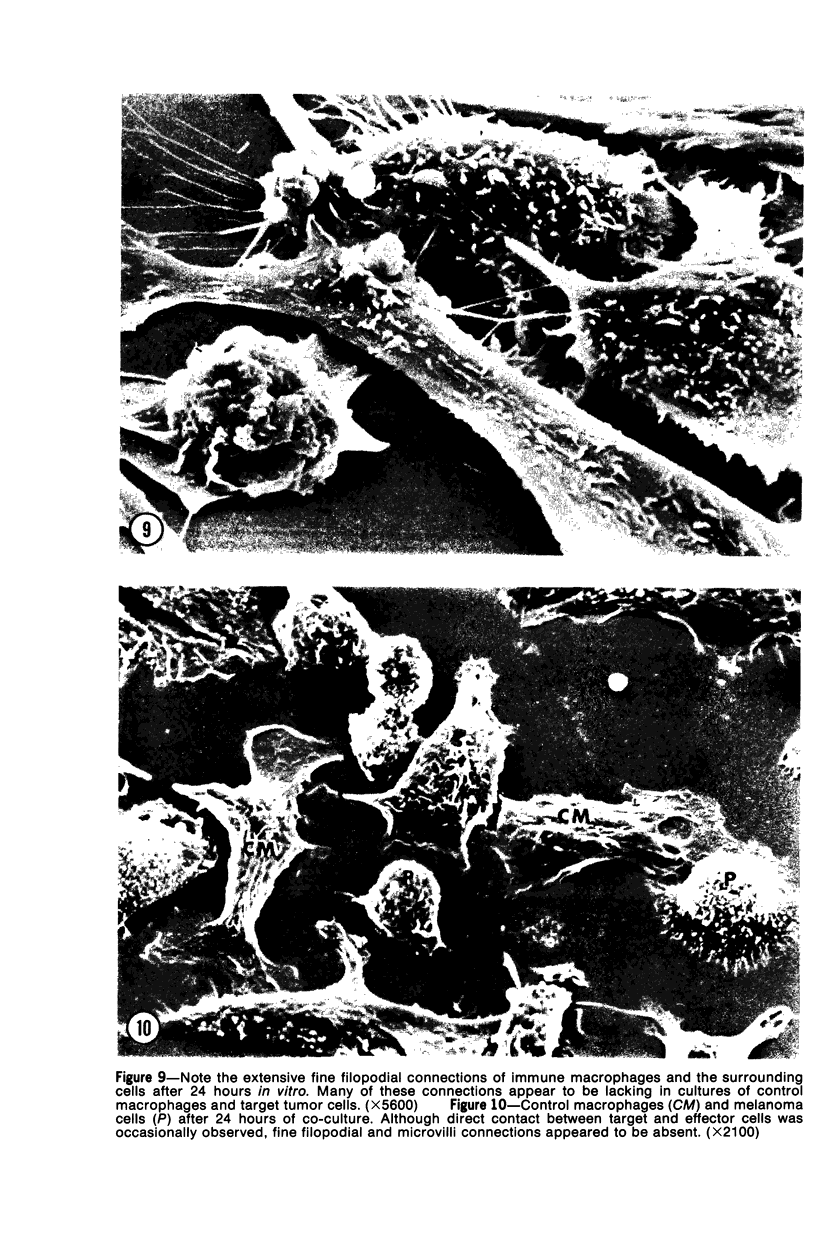
Thioglycolate-induces peritoneal macrophages from melanoma-bearing mice (immune macrophages) or from control mice (control macrophages) were cultured with syngeneic melanoma cells (P51) to determine the surface characteristics of the effector cells during interaction and destruction of the target cells. After a short culture period (3 hours), immune macrophages had extensive connections via filopodia and ruffled membranes to the surfaces of the melanoma cells; control macrophages did not exhibit the same behavior. A dense region in the cytoplasm immediately beneath the macrophage plasmalemma was observed at the point of contact with the target tumor cell. With longer periods of culture (24 hours), effector cells began phagocytosis of the target cells; immune macrophages, however, had more fine filopodial connections and were more cytostatic than were controls. These observations indicate that one of the initial mechanisms of tumor cell destruction was contact-induced lysis, with phagocytosis playing a minor part.
Full text
PDF



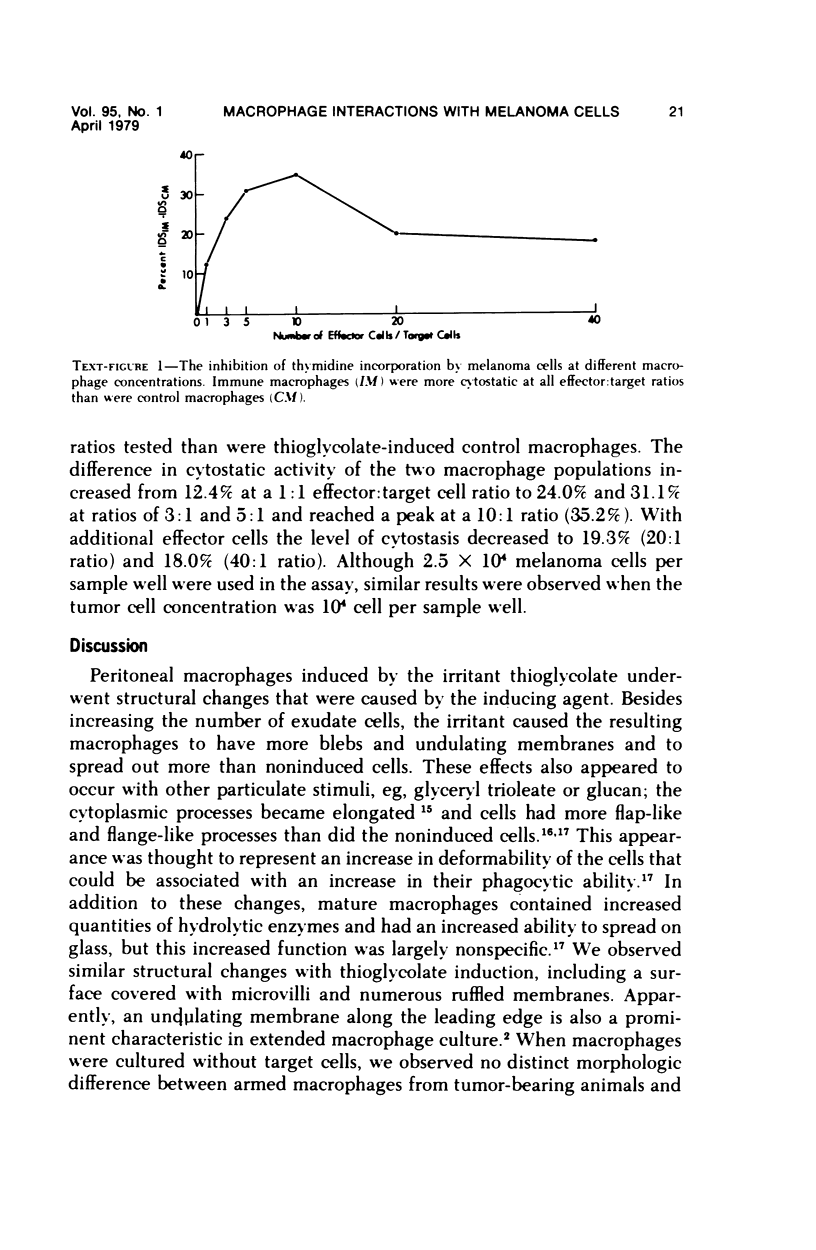



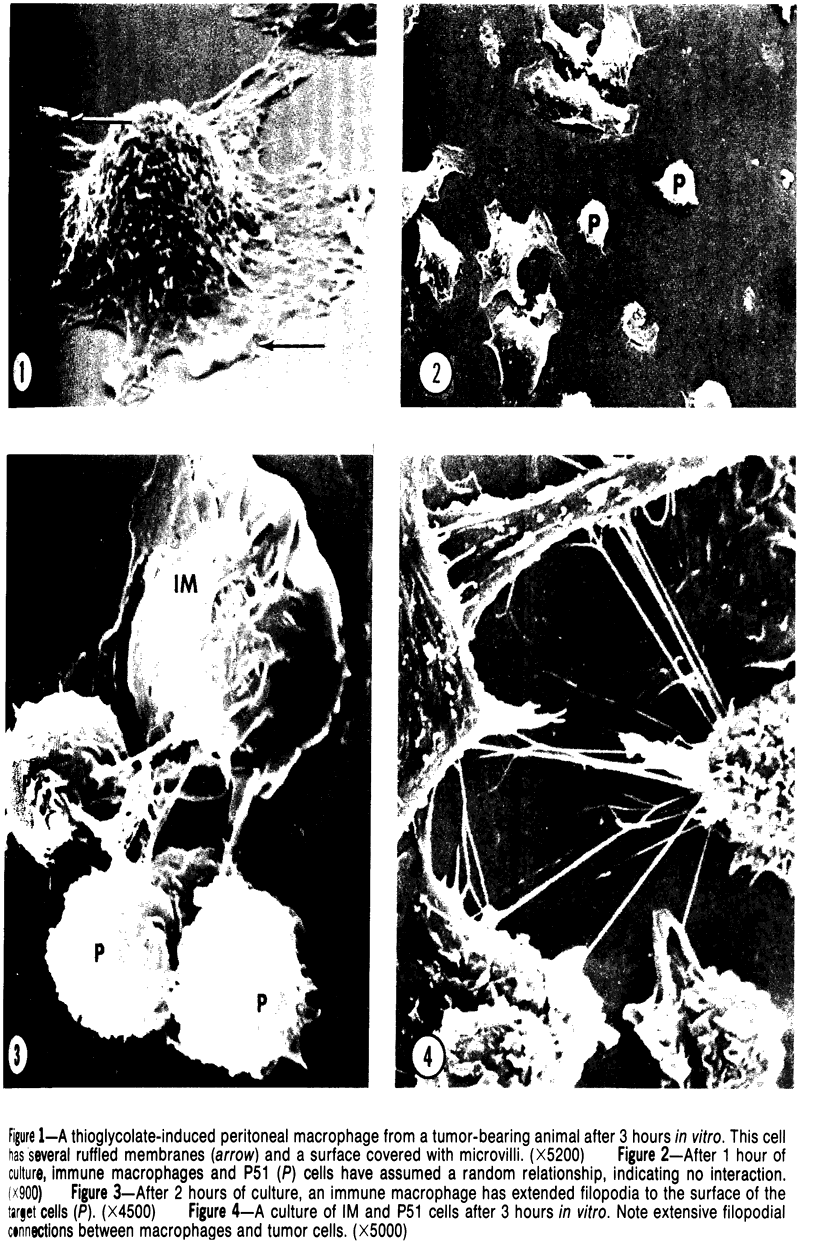
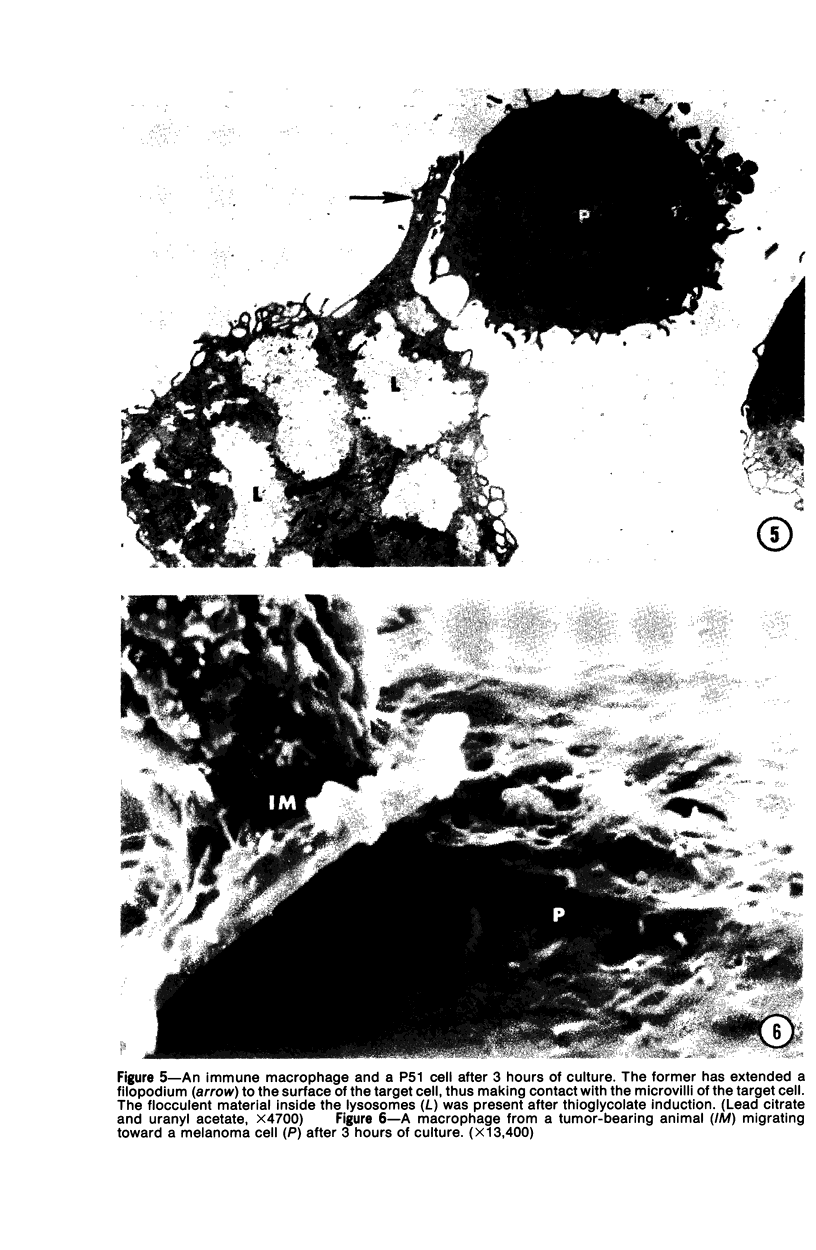
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. P. A new technique for separation of coverglass substrate from epoxy-embedded specimens for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Nov;37(3):370–377. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Cooperation of immune lymphoid cells with macrophages in tumour immunity. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):620–622. doi: 10.1038/228620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Role of macrophages in tumour immunity. II. Involvement of a macrophage cytophilic factor during syngeneic tumour growth inhibition. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):627–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Weiser R. S. Homograft target cells: contact destruction in vitro by immune macrophages. Science. 1966 Jan 7;151(3706):97–99. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3706.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HU F., LESNEY P. F. THE ISOLATION AND CYTOLOGY OF TWO PIGMENT CELL STRAINS FROM B-16 MOUSE MELANOMAS. Cancer Res. 1964 Oct;24:1634–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill J. S., Fett J. W. Possible evidence for antibody-dependent macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity directed against murine adenocarcinoma cells in vivo. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1992–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes J. W. The structure of fish skin. I. General organization. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;149(2):147–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00222270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Schipper H., Fischer H. Macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity against allogeneic target cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P., Pinto J., Hanifin J. M. Surface morphology of human mononuclear phagocytes during maturation and phagocytosis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Aug;48(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasztor L. M., Hu F., McNulty W. P., Jr 5-Bromodeoxyuridine-tolerant melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Yale J Biol Med. 1973 Dec;46(5):397–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion F., Fray A., Halpern B. A cytochemical study of the in vitro interaction between normal and activated mouse peritoneal macrophages and tumor cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jan;54(1):95–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Eisen H. N. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulins to Fc receptors of mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1520–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]