Abstract
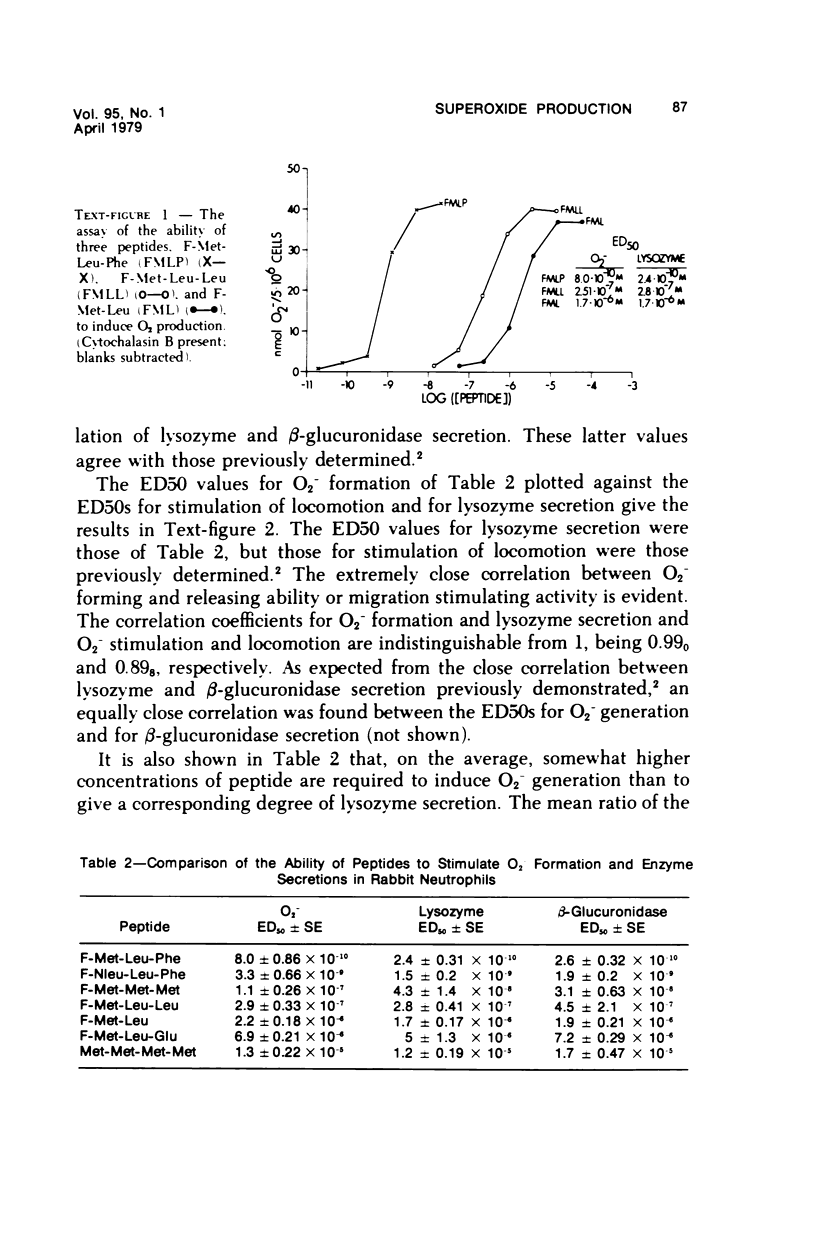
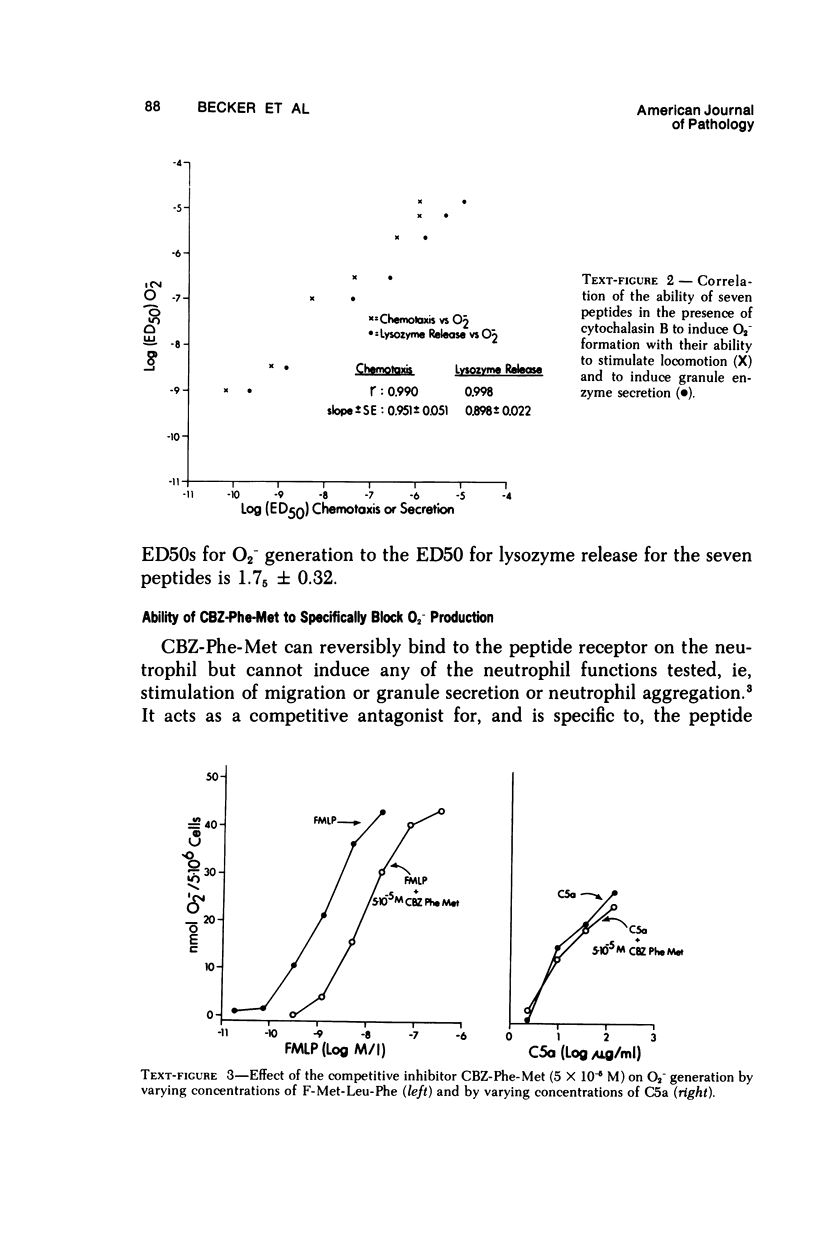
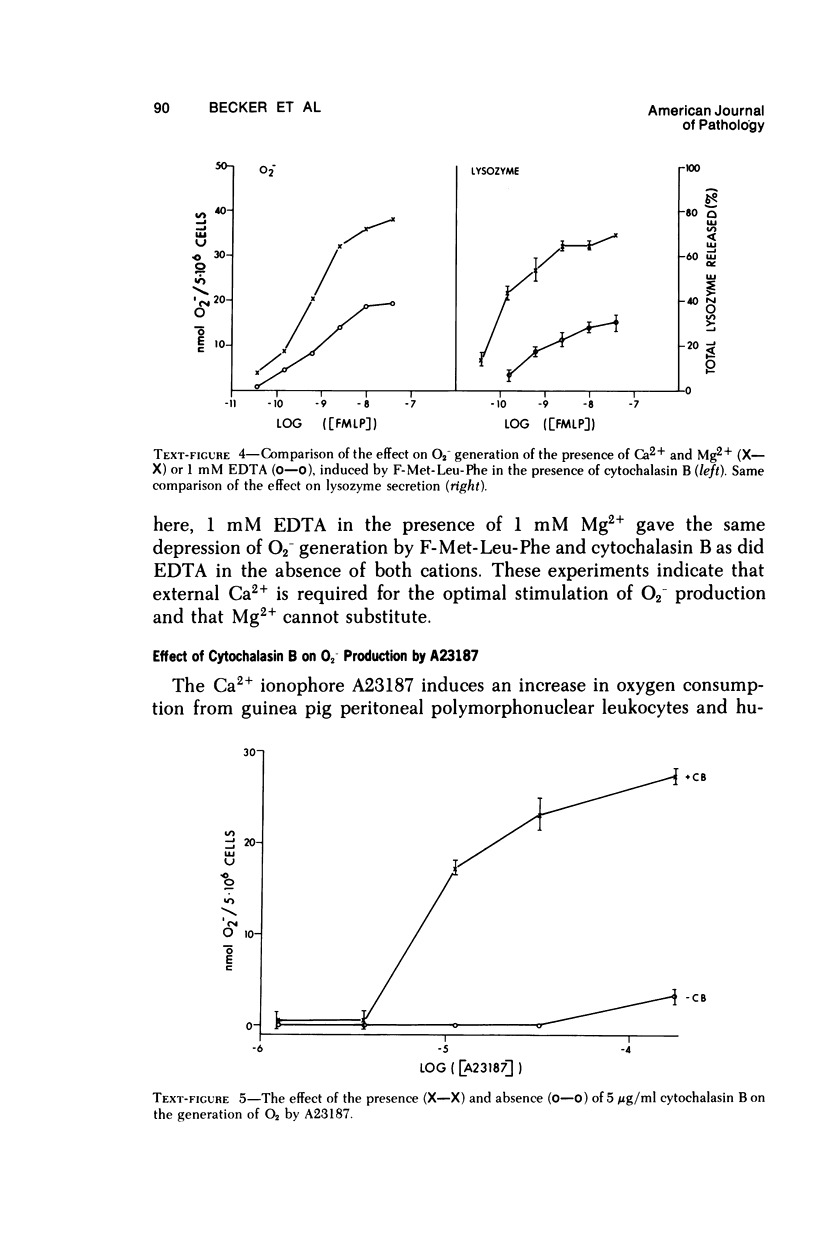
Synthetic formyl methionyl chemotactic peptides induce the various manifestations ofthe respiratory burst: increased 02 consumption, activation of the hexose mono-phosphate shunt, and increased production of superoxide (02-) and H202. They do soalone but to a much greater extent when in the presence of cytochalasin B. Superoxidegeneration by the chemotactic peptides in the presence of cytochalasin B shows thesame relationship of structure to activity as does the stimulation of chemokinesis andchemotaxis, granule enzyme secretion, and neutrophil aggregation by these sameagents. Carbobenzoxy-phenylalanyl-methionine, CBZ-Phe-Met, competitively inhibitsthe induced stimulation of locomotion, granule enzyme secretion, and neutrophilaggregation caused by the synthetic peptides. It also is a competitive inhibitor of O2- generation by the same peptides. The structure-activity and the competitive inhibitor studies lead to the conclusion that in polymorphonuclear leukocytes the chemotactic peptides induce superoxide formation and presumably the other manifestations of the respiratory burst by interacting with the same membrane receptor responsible for the stimulation of chemokinesis, chemotaxis, granule enzyme secretion, and neutrophil aggregation. The effectiveness of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, F-Met-Leu-Phe, in generating 02- is greatly reduced but not abolished by removing calcium from the external medium. The calcium ionophore A23187 induces 02- generation that requires external calcium and is greatly enhanced by cytochalasin B. From these findings we hypothesize that the proximate cause of the induction of 02- formation and other manifestations of the respiratory burst by the chemotactic peptides is the influx into the neutrophil of Ca2+ and/or possibly Na+ previously shown to be induced by the peptides.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Dechatelet L. R., McCall C. E. Independent stimulation of motility and the oxidative metabolic burst of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):172–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Showell H. J., Henson P. M., Hsu L. S. The ability of chemotactic factors to induce lysosomal enzyme release. I. The characteristics of the release, the importance of surfaces and the relation of enzyme release to chemotactic responsiveness. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. Some interrelations of neutrophil chemotaxis, lysosomal enzyme secretion, and phagocytosis as revealed by synthetic peptides. Am J Pathol. 1976 Nov;85(2):385–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Talley V., Showell H. J., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Activation of the rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte membrane "Na+, K+"-ATPase by chemotactic factor. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):329–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. The relationship of the chemotactic behavior of the complement-derived factors, C3a, C5a, and C567, and a bacterial chemotactic factor to their ability to activate the proesterase 1 of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):376–387. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Stimulation of human neutrophil leukocyte aerobic glucose metabolism by purified chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI107594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Influence of divalent cations upon complement-mediated enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch G. E., Gardner D. E., Menzel D. B. Chemiluminescence of phagocytic cells caused by N-formylmethionyl peptides. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):182–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Stimulation of human neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates. Secretion of granule constituents and increased oxidation of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI108152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson D., DeChatelet L. R., Spitznagel J. K., Wang P. Comparison of NADH and NADPH oxidase activities in granules isolated from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes with a fluorometric assay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):282–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI108639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Changes in ionic movements across rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes during lysosomal enzyme release. Possible ionic basis for lysosomal enzyme release. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):635–649. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Transport of sodium, potassium, and calcium across rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Effect of chemotactic factor. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):428–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro neutrophil responses to chemotactic factors by a competitive antagonist. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Cramer R., Dri P., Fant L., Basford R. E., Rossi F. NADPH oxidizing activity in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes: localization in azurophilic granules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):830–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J. A. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. Relationship to superoxide anion formation and cellular catabolism of H2O2: studies with normal and cytochalasin B-treated cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1266–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI108886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I., Becker E. L. The effects of extracellular K+, Na+ and Ca++ on lysosomal enzyme secretion from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):804–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Mandell B., Mehta J., Sullivan T., Simchowitz L. Dissociation of the neutrophill functions of exocytosis and chemotaxis. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Aug;92(2):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabucchi G., Romeo D. The dissociation of exocytosis and respiratory stimulation in leucocytes by ionophores. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):209–213. doi: 10.1042/bj1560209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


