Abstract
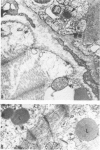
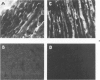
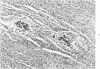
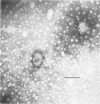
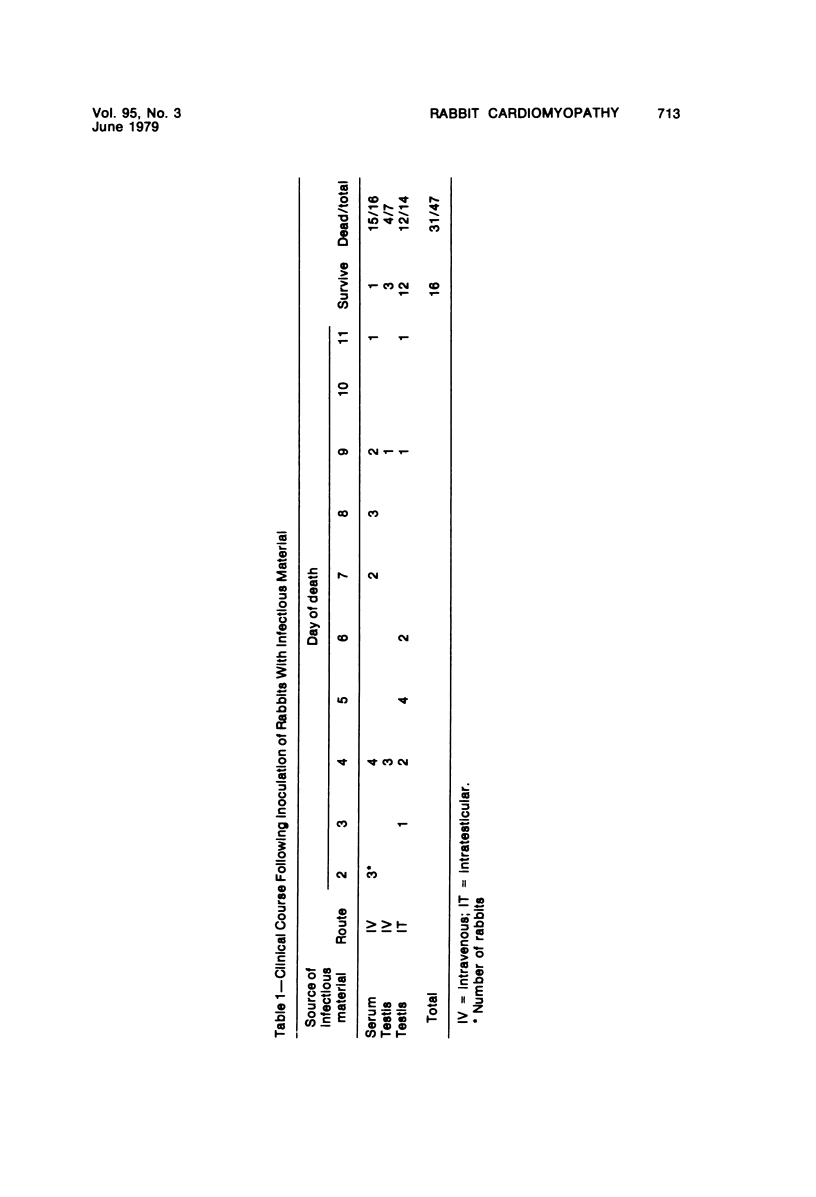
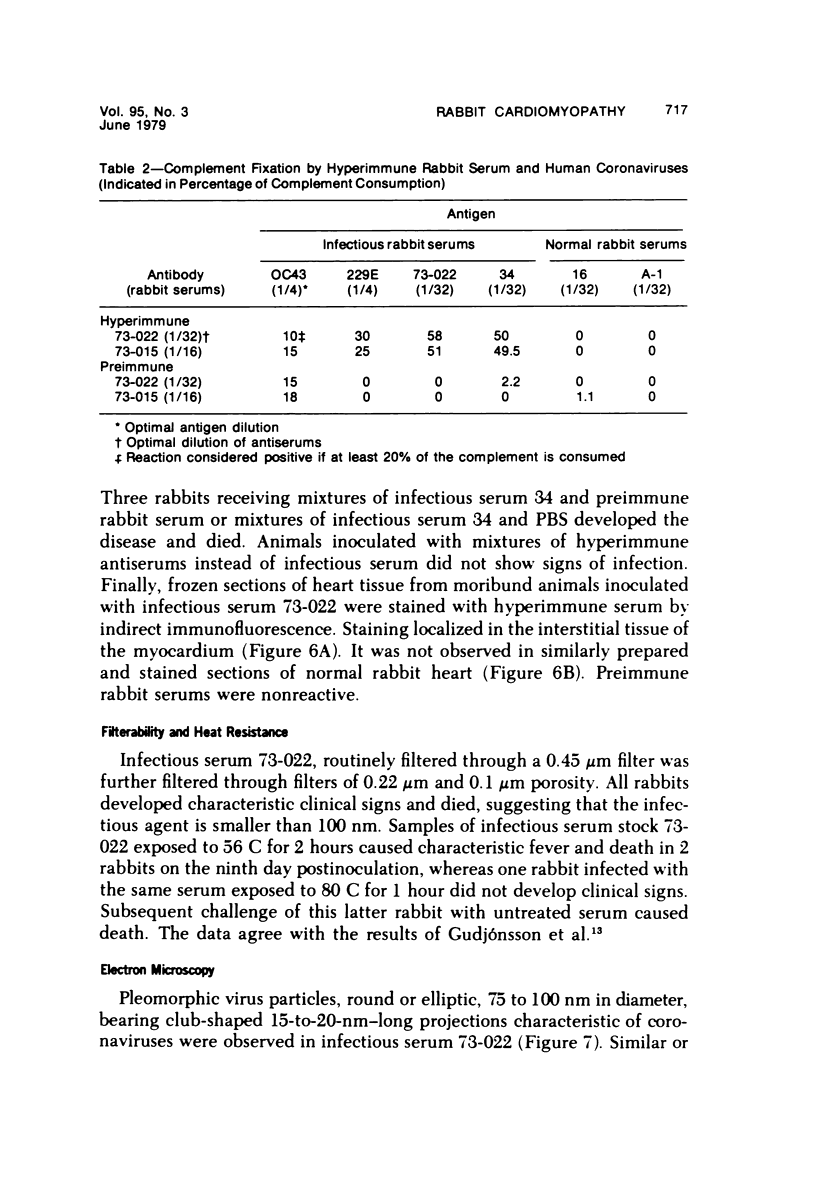
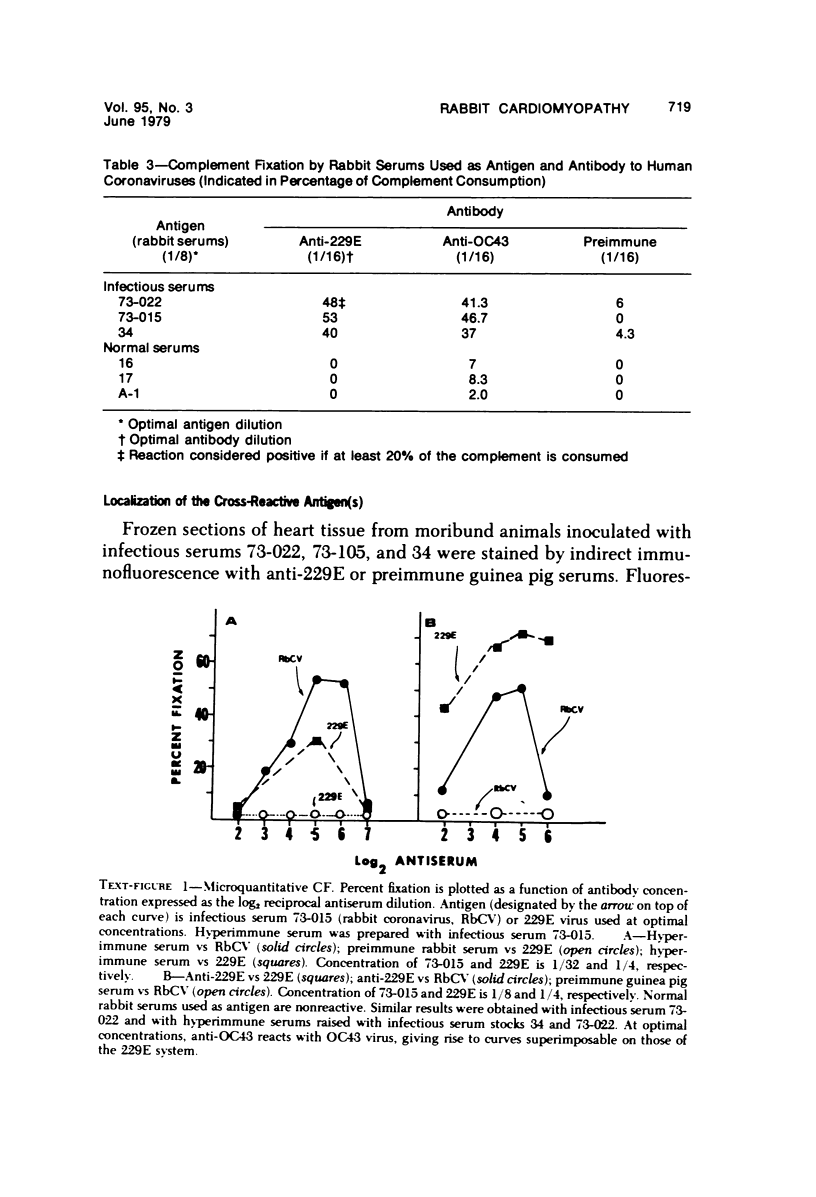
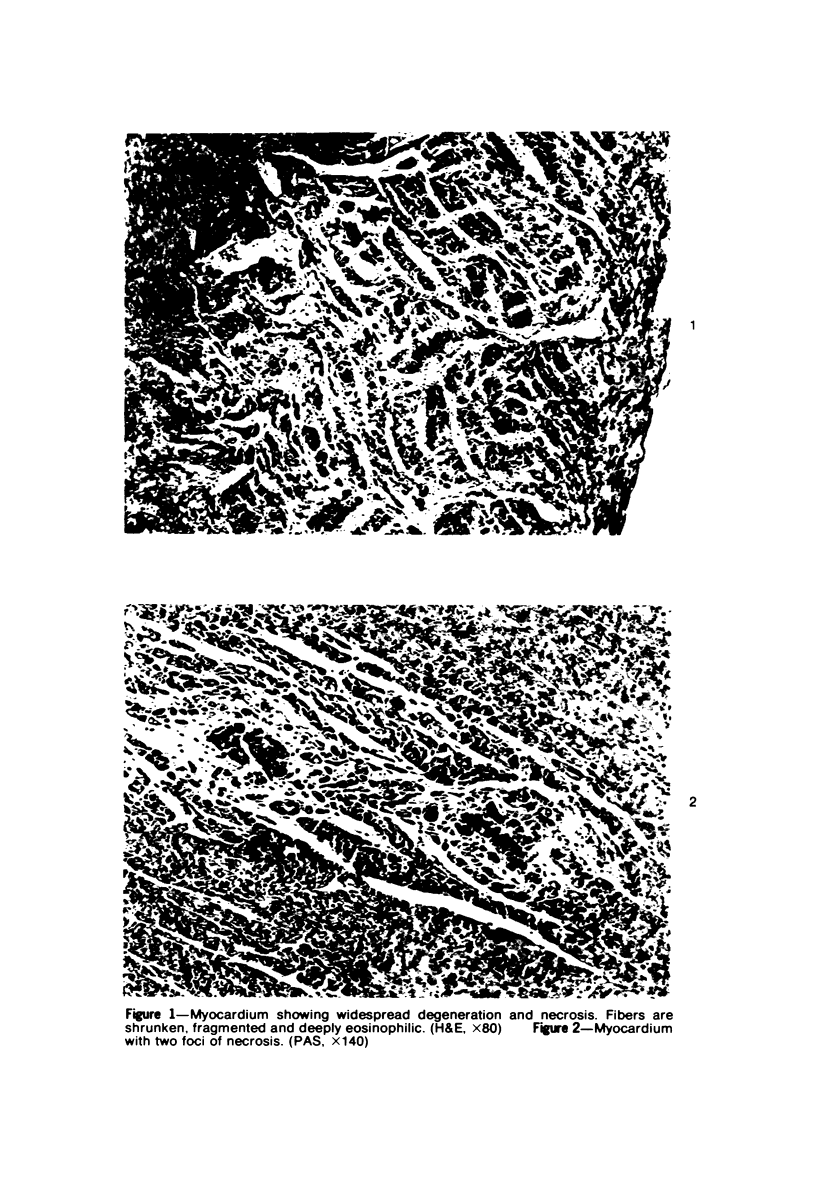
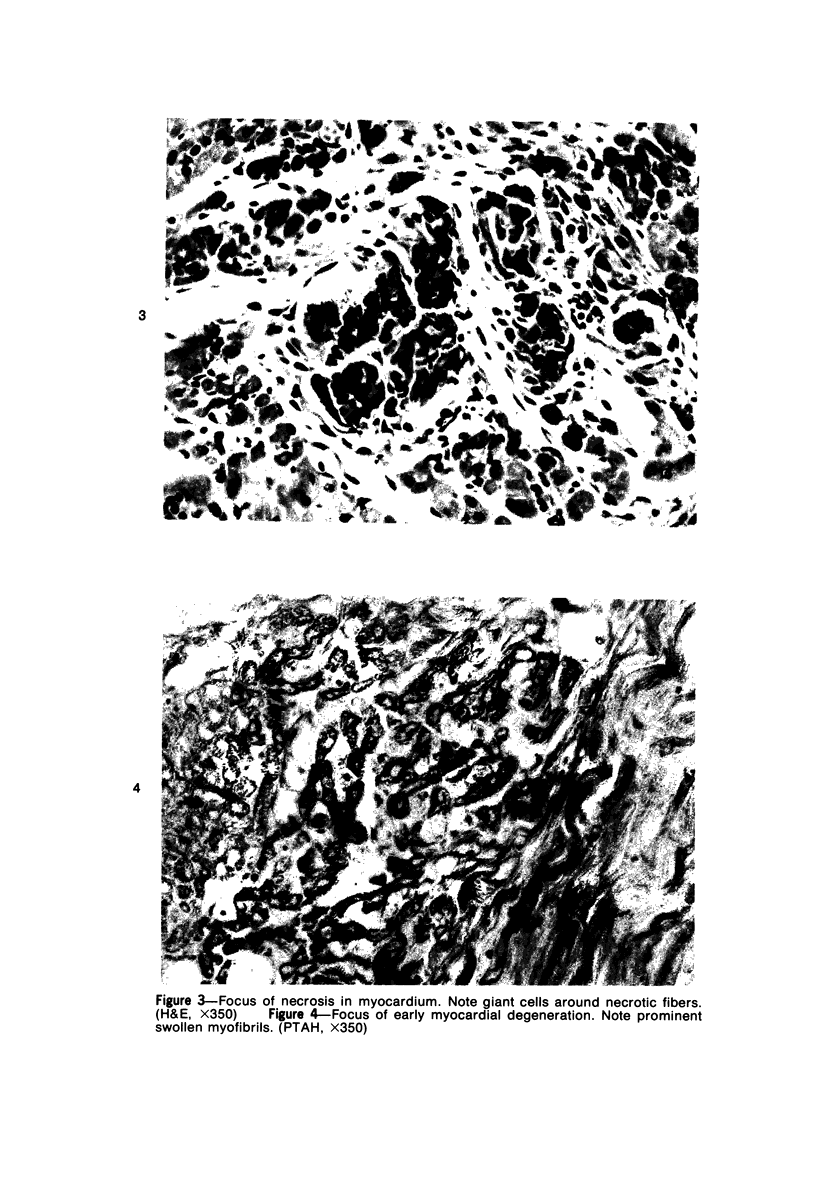
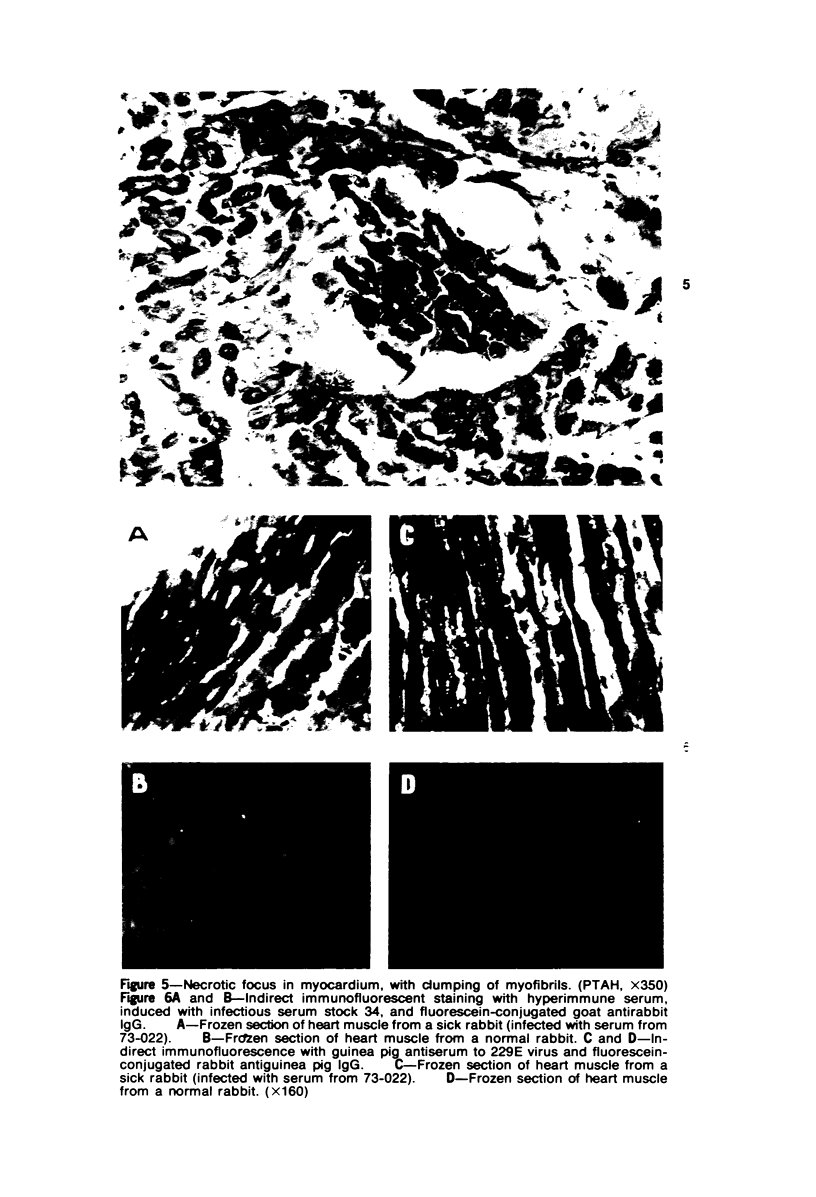
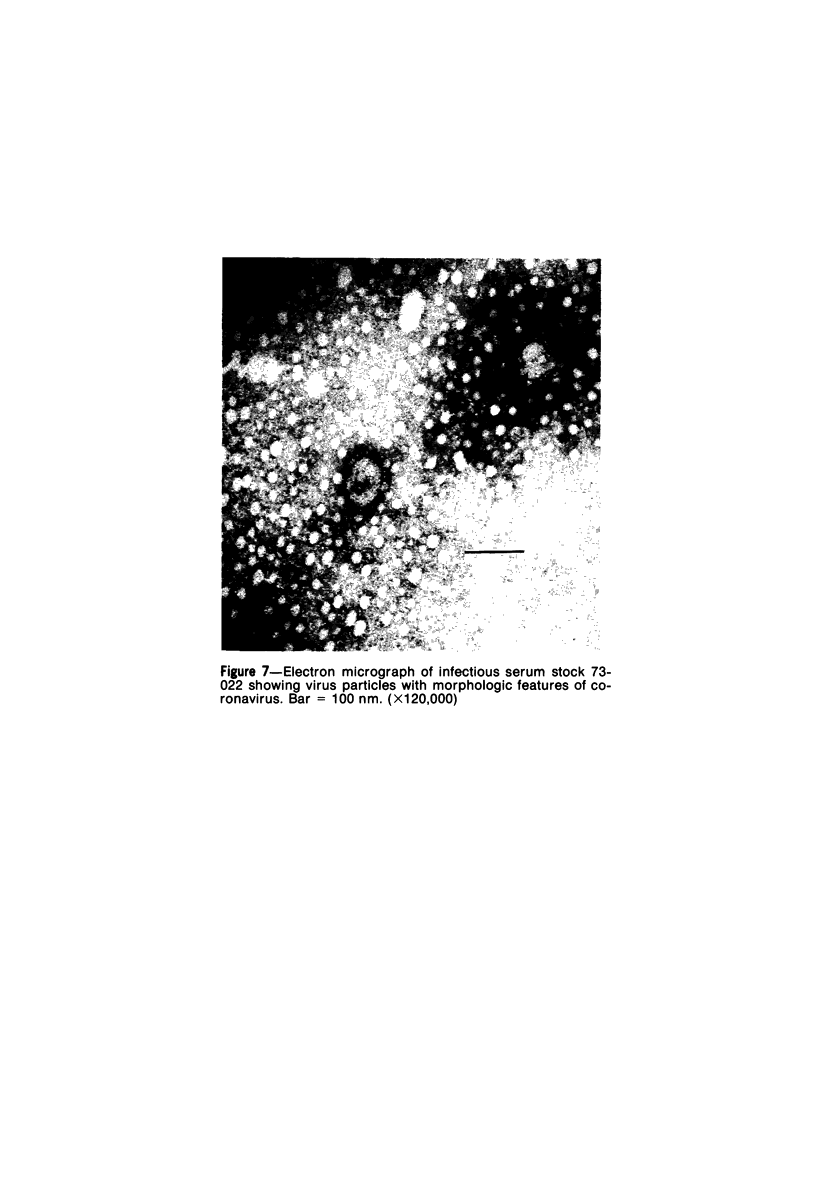
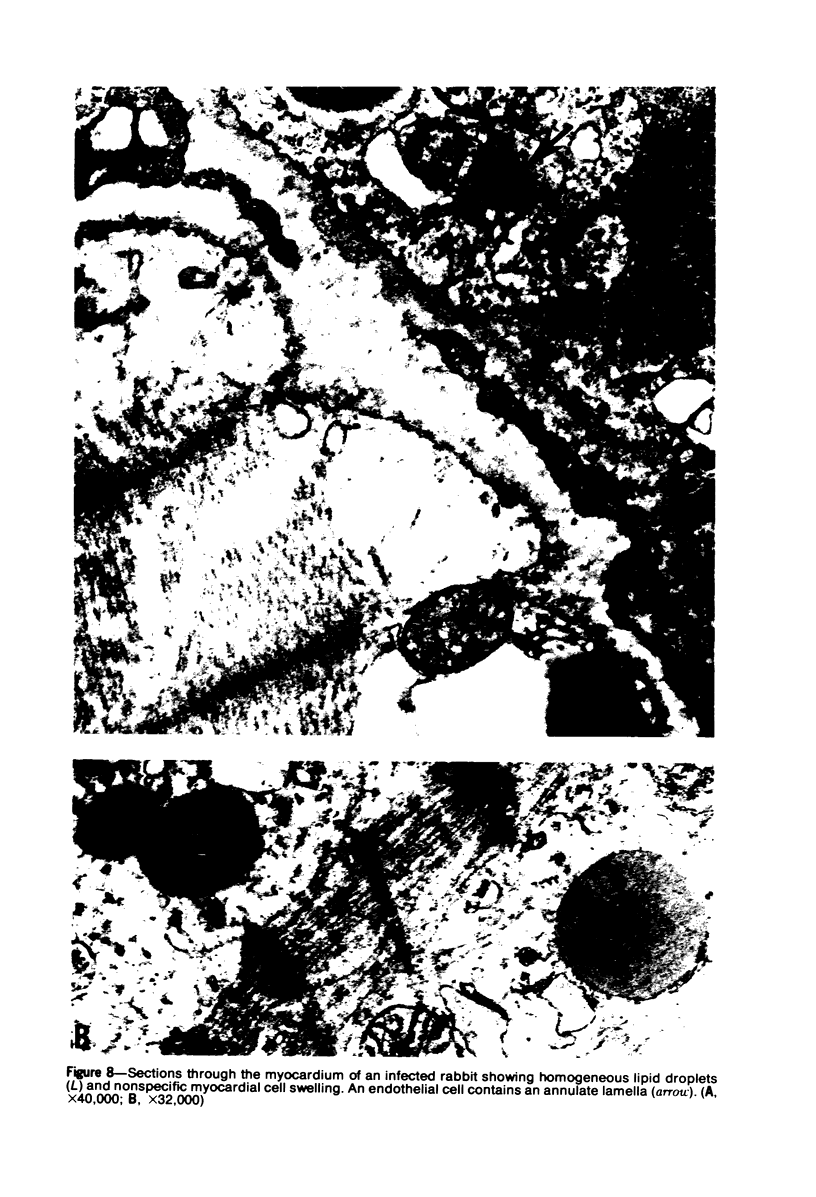
A new disease of rabbits is described. Following an acute febrile course, animals die or recover by the 11th day postinoculation. The characteristic pathologic finding is multifocal myocardial degeneration and necrosis. The disease can be transmitted by various routes with tissue filtrates or with infectious sera diluted to 10(-6) and passed through 0.1 micron filters. Virus particles with morphologic features characteristic of a coronavirus are present in infectious but not in normal rabbit serums. The antigen(s) in the infectious serums cross-reacts with the 229E and the OC43 strains of human coronavirus. Antigen cross-reacting with the 229E virus is detectable by immunofluorescent staining in frozen sections of heart tissue from sick but not from healthy animals. Animals surviving infection seroconvert to coronavirus specificity, as demonstrated by the presence in convalescent serums of antibody capable of reacting with the 339E virus. Susceptibility to infection has not been demonstrated in mice, hamsters, or guinea pigs, and the virus was not adapted for growth in tissue culture. It is uncertain whether the agent is a natural pathogen of rabbits or a coronavirus contaminant from another species, possibly human. The name rabbit infectious cardiomyopathy is suggested for this disease.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binn L. N., Eddy G. A., Lazar E. C., Helms J., Murnane T. Viruses recovered from laboratory dogs with respiratory disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):140–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody N. I., Walker J. G., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. Interaction of antigenic competition and suppression of antibody formation by passive antibody on the immune response. J Exp Med. 1967 Jul 1;126(1):81–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Rowe W. P. Mouse hepatitis, reo-3, and the Theiler viruses. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Feb;20:67–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennestad K. L., Skovgaard Jensen H. J., Moller S., Weis Bentzon M. Pleural effusion disease in rabbits, clinical and post mortem observations. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudjónsson H., Newman B., Turner T. B. Demonstration of a virus-like agent contaminating material containing the Stockholm substrain of the Nichols pathogenic Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Dec;46(6):435–440. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudjónsson H., Newman B., Turner T. B. Screening out a virus-like agent from the testicular suspension of the Nichols pathogenic T. pallidum with observations on certain characteristics of the agent. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):102–107. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudjónsson H., Skog E. Fever after inoculation of rabbits with Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Aug;46(4):318–322. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.4.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa D. T. Relationships among measles, canine distemper and rinderpest viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:160–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen B. B. Spontaneous deaths among rabbits inoculated with Treponema pallidum less than 2 weeks before. Abnormal susceptibility in apparently normal laboratory rabbits indicated by serological tests for human syphilis. Z Versuchstierkd. 1968;10(1):46–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Hierholzer J. C., Dowdle W. R. Purification and further characterization of an "IBV-like" virus (coronavirus). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):457–463. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye H. S., Yarbrough W. B., Reed C. J., Harrison A. K. Antigenic relationship between human coronavirus strain OC 43 and hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus strain 67N of swine: antibody responses in human and animal sera. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):201–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R. L., Townes A. S. Partial dissociation of rheumatoid synovial fluid cryoprotein: micro-complement fixation by IgG- or IgG and IgM-containing fractions and denatured calf thymus DNA. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1499–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Kapikian A. Z., Hardison K. A., Hartley J. W., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among the coronaviruses of man and between human and animal coronaviruses. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1109–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C. Morphologic and physical characteristics of feline infectious peritonitis virus and its growth in autochthonous peritoneal cell cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1976 May;37(5):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stair E. L., Rhodes M. B., White R. G., Mebus C. A. Neonatal calf diarrhea: purification and electron microscopy of a coronavirus-like agent. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Jun;33(6):1147–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafler S. W., Setlow P., Levine L. Serological relatedness of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):18–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.18-23.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M. Morphology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus of pigs. A possible member of coronaviruses. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01253886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia S. S., Cunningham C. H. Antigenic characterization of infectious bronchitis virus. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]