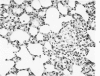
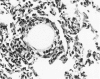
Abstract
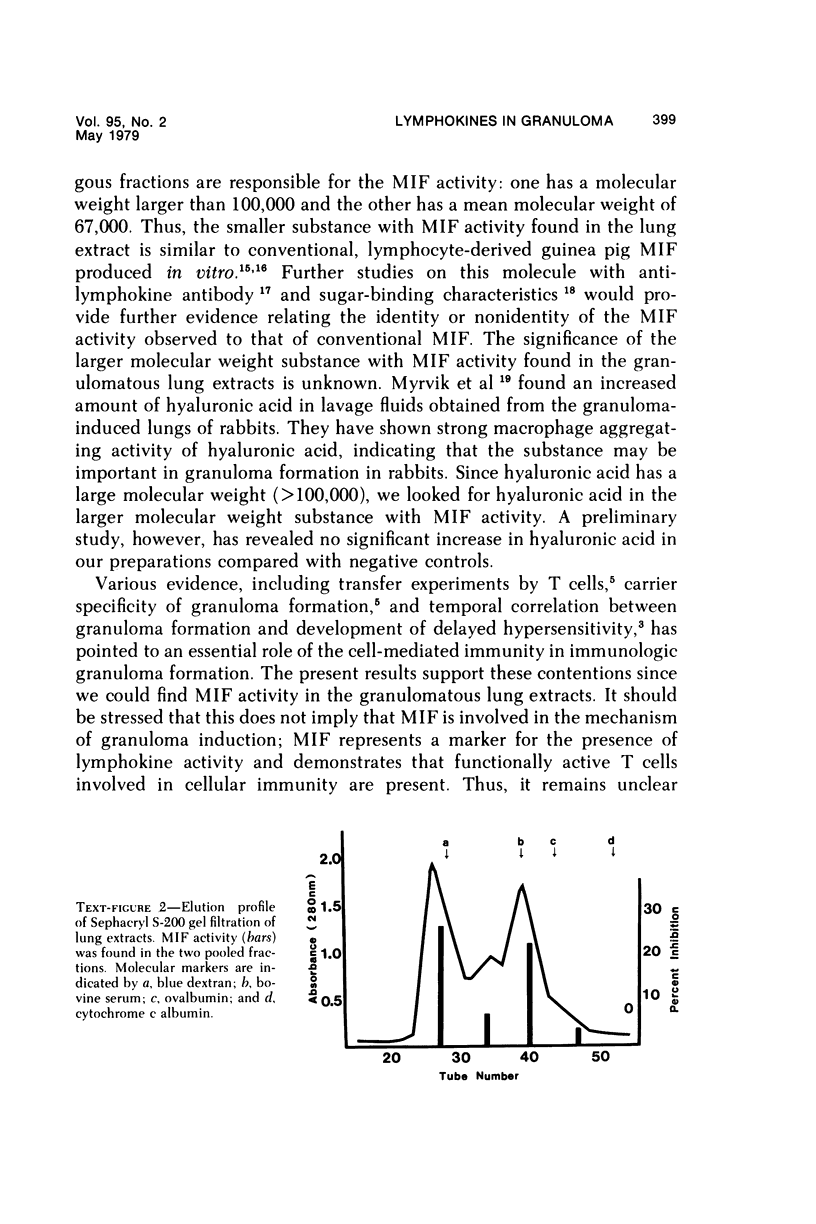
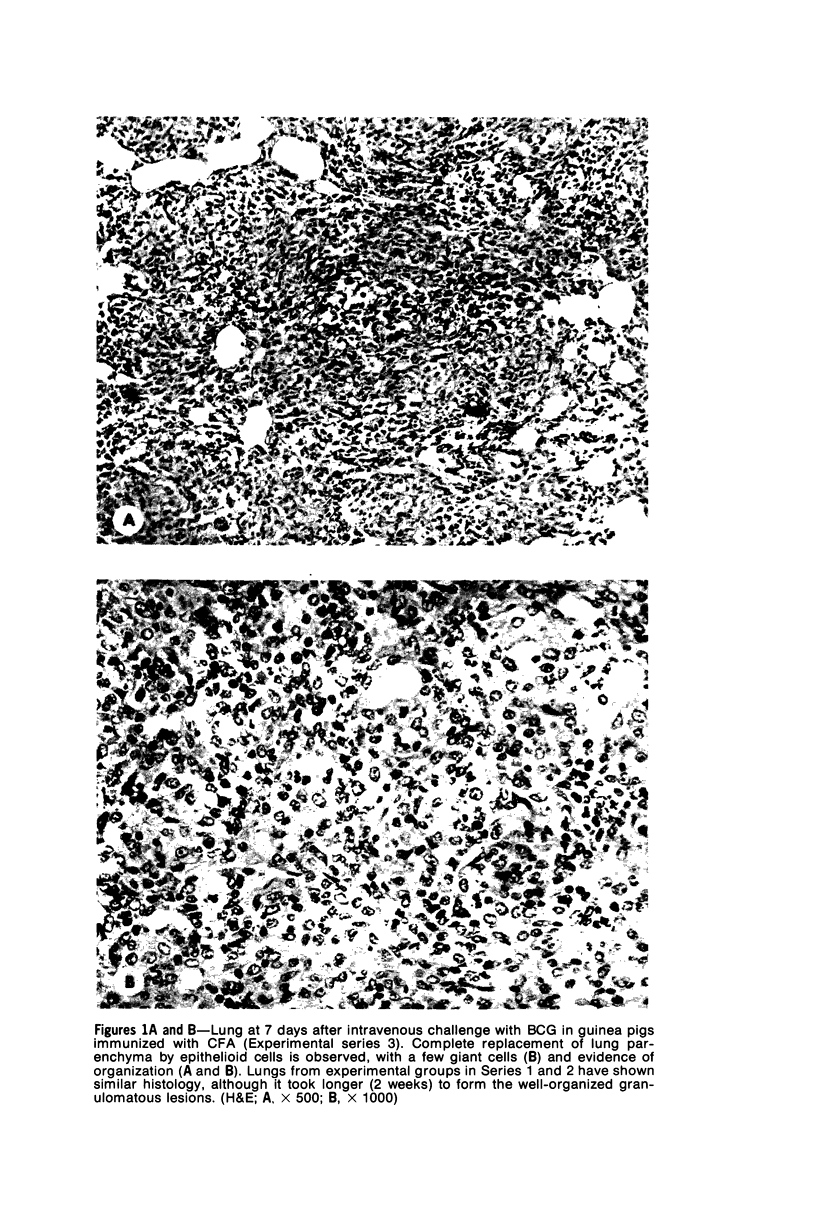
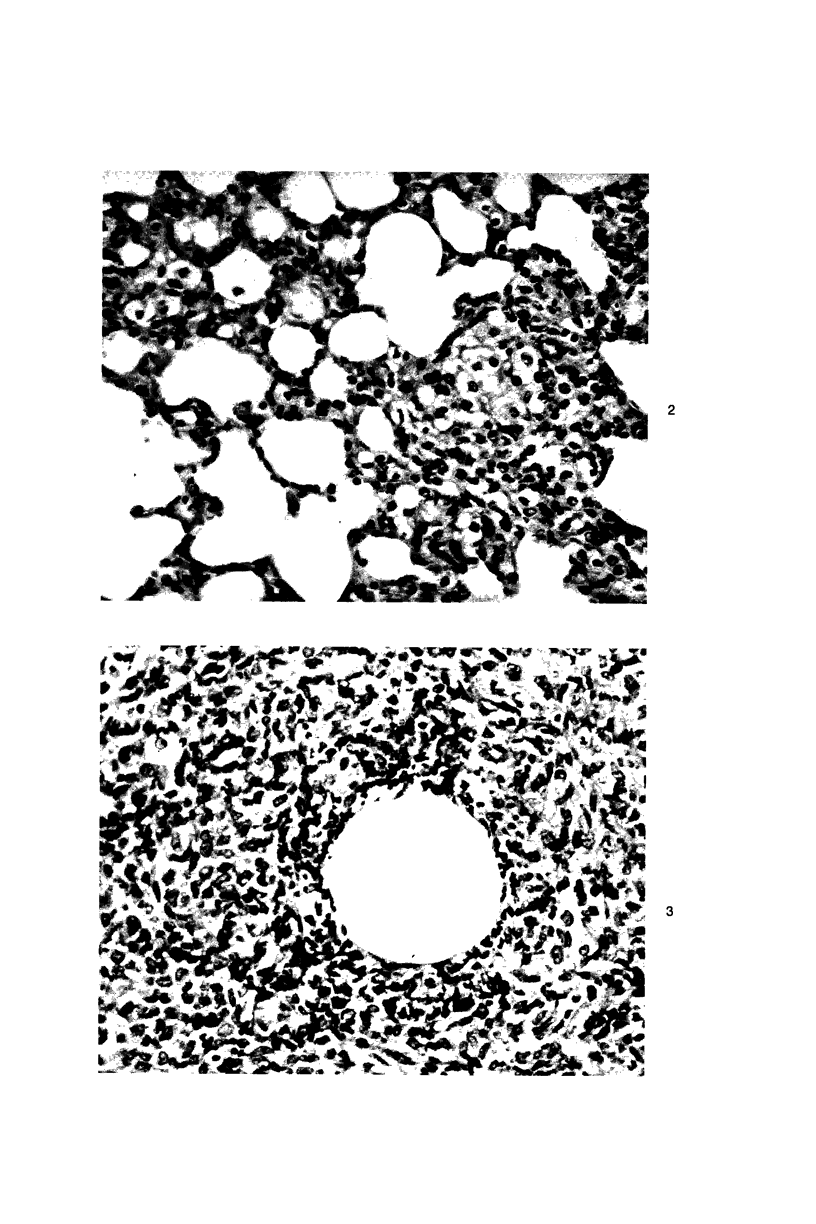
Granulomatous reactions were immunologically induced in guinea pigs by several procedures, including intravenous injections of Bacille Calmette Gúerin (BCG) into animals immunized with complete Freund's Adjuvant and an intravenous injection of agarose beads linked to a specific antigen (dinitrophenylated bovine serum albumin) into immune animals. The tissue extracts obtained from lungs at various stages of granuloma formation were examined for macrophage migration inhibition (MIF) activity. The activity was found in a high incidence during the early stages of the granulomatous response. In contrast, MIF activity could be detected only rarely in granulomatous spleens and not in granulomatous livers. Chemotactic factor activity and mitogenic factor activity were only sporadically detectable. The MIF activity was associated with fractions showing chemical heterogeneity. One fraction was physicochemically indistinguishable from conventional lymphocyte-derived MIF; the other was a substance of large molecular weight. These results demonstrate the presence of biologically active mediators in immune granulomas, which may be related to early events involved in the induction or enhancement of such reactions.
Full text
PDF



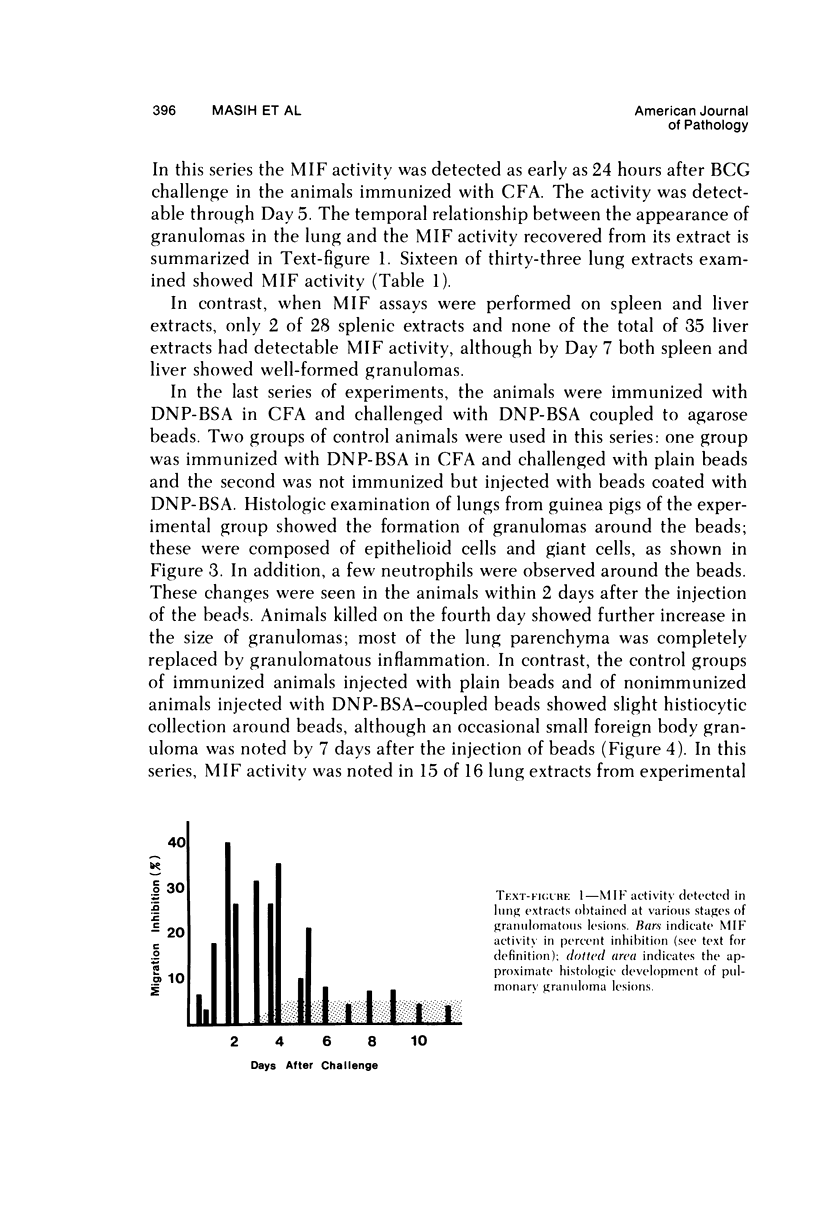







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsden A., Ewan V., Yoshida T., Cohen S. Studies on cellular receptors for lymphokines. I. Interaction of chemotactic factors with monosaccharides. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):542–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. In vitro approaches to the mechanism of cell-mediated immune reactions. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:101–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Granulomatous inflammations. Prog Allergy. 1978;24:183–267. doi: 10.1159/000401230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Pelley R. P., Warren K. S. Spontaneous modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity in schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1437–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S., Pelley R. P. The secretion of migration inhibitory factor by intact schistosome egg granulomas maintained in vitro. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):224–226. doi: 10.1038/246224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasdon E. J., Schlossman S. F. An experimental model of pulmonary arterial granulomatous inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jun;71(3):365–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J., Yoshida T., Cohen S. Quantitative aspects of the migration inhibition reaction. Immunol Commun. 1973;2(3):287–296. doi: 10.3109/08820137309022800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonozaki H., Papermaster V., Yoshida T., Cohen S. Desensitization: effects on cutaneous and peritoneal manifestations of delayed hypersensitivity in relation to lymphokine production. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1657–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Benacerraf B. Immunologic events in experimental hypersensitivity granulomas. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jun;71(3):349–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Bigazzi P., Cohen S. Biologic and antigenic similarity of virus-induced migration inhibition factor to conventional, lymphocyte-derived migration inhibition factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1641–1644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Cohen S., Bigazzi P. E., Kurasuji T., Amsden A. Inflammatory mediators in culture filtrates of Escherichia coli. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):389–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Janeway C. A., Jr, Paul W. E. Activity of migration inhibitory factor in the absence of antigen. J Immunol. 1972 Aug;109(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]