Abstract
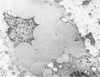
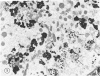
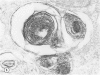
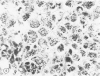
Rare cases of hemochromatosis have been reported in patients who underwent prolonged oral iron therapy for hemolytic anemia or prolonged self-treatment with iron pills. A proportionately large segment of the South African Bantu tribe, who ingest large quantities of an alcoholic beverage brewed in iron pots, are found to have the disease. Reports of health fadists developing hemochromatosis due to excessive dietary iron intake, however, are extremely rare. This report presents clinical considerations and pathologic findings in a compulsive health fadist who consumed large numbers of vitamins containing iron. Clinical findings included the development and progression of cirrhosis of the liver, bronzing of the skin, and diabetes mellitus, all consistent with a diagnosis of hemochromatosis. Light microscopy of liver biopsies taken late in the course of the disease revealed a massive buildup of iron in the hepatocytes, less in the Kupffer cells, and sparse deposition in the epithelial cells of the bile duct. Minimal periportal fibrosis was noted. Electron microscopy showed numerous pleomorphic siderosomes with varying degrees of crystallization and ferritin attached at uniform intervals to the membranes of residual bodies. Abundant free ferritin was observed in most cells. The aggregated and membrane-associated ferritin was verified by non-dispersive x-ray analysis. An additional finding, noted only by electron microscopy, was the presence of many fat-storing cells of Ito, which are thought to be involved in the onset of fibrosis.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arborgh B. A., Glaumann H., Ericsson J. L. Studies on iron loading of rat liver lysosomes. Effects on the liver and distribution and fate of iron. Lab Invest. 1974 May;30(5):664–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN E. B., Jr, DUBACH R., SMITH D. E., REYNAFARJE C., MOORE C. V. Studies in iron transportation and metabolism. X. Long-term iron overload in dogs. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Dec;50(6):862–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcerzak S. P., Mintz D. H., Westerman M. P. Diabetes mellitus and idiopathic hemochromatosis. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Jan;255:53–62. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196801000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. L., Marshall W. C. Iron distribution in the liver of patients with thalassaemia major. Lancet. 1967 May 13;1(7498):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91543-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dymock I. W., Cassar J., Pyke D. A., Oakley W. G., Williams R. Observations on the pathogenesis, complications and treatment of diabetes in 115 cases of haemochromatosis. Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLBERG L., SMITH J. P. Iron overloading and hepatic vulnerability. Am J Pathol. 1960 Feb;36:125–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Shibasaki S. Electron microscopic study on the hepatic sinusoidal wall and the fat-storing cells in the normal human liver. Arch Histol Jpn. 1968 Mar;29(2):137–192. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.29.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT G., VOLINI F. I., MINICK O. T., ORFEI E., DELAHUERGA J. EFFECT OF IRON LOADING UPON THE FORMATION OF COLLAGEN IN THE HEPATIC INJURY INDUCED BY CARBON TETRACHLORIDE. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jul;45:129–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT G., VOLINI F. I., ORFEI E., MINICK O. T., DELAHUERGA J. EFFECT OF HEPATIC INJURIES UPON IRON STORAGE IN THE LIVER. Lab Invest. 1963 Nov;12:1094–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Bothwell T. H., Seftel H. C., Wapnick A. A., Charlton R. W. The role of ascorbic acid in the metabolism of storage iron. Br J Haematol. 1971 Feb;20(2):155–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. R., Seftel H. C., Torrance J. D., Charlton R. W., Bothwell T. H. Accelerated oxidative catabolism of ascorbic acid in siderotic Bantu. Am J Clin Nutr. 1967 Jun;20(6):641–647. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/20.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD R. A., PECHET G. S. EXPERIMENTAL HEMOCHROMATOSIS IN RATS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jan;46:85–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megyesi C., Samols E., Marks V. Glucose tolerance and diabetes in chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1967 Nov 18;2(7525):1051–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega P. Light and electron microscopy of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) poisoning in the rat liver. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):657–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., Richter G. W. Ferritin synthesis by free and membrane-bound (poly)ribosomes of rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):399–403. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER P. E. Precision in the classification of cirrhosis of the liver. Am J Pathol. 1960 Jul;37:21–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITZLEBEN C. L., CHAFFEY N. J. A study of iron-induced liver damage. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:723–729. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wapnick A. A., Lynch S. R., Charlton R. W., Seftel H. C., Bothwell T. H. The effect of ascorbic acid deficiency on desferrioxamine-induced urinary iron excretion. Br J Haematol. 1969 Dec;17(6):563–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wapnick A. A., Lynch S. R., Seftel H. C., Charlton R. W., Bothwell T. H., Jowsey J. The effect of siderosis and ascorbic acid depletion on bone metabolism, with special reference to osteoporosis in the Bantu. Br J Nutr. 1971 May;25(3):367–376. doi: 10.1079/bjn19710101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]