Abstract
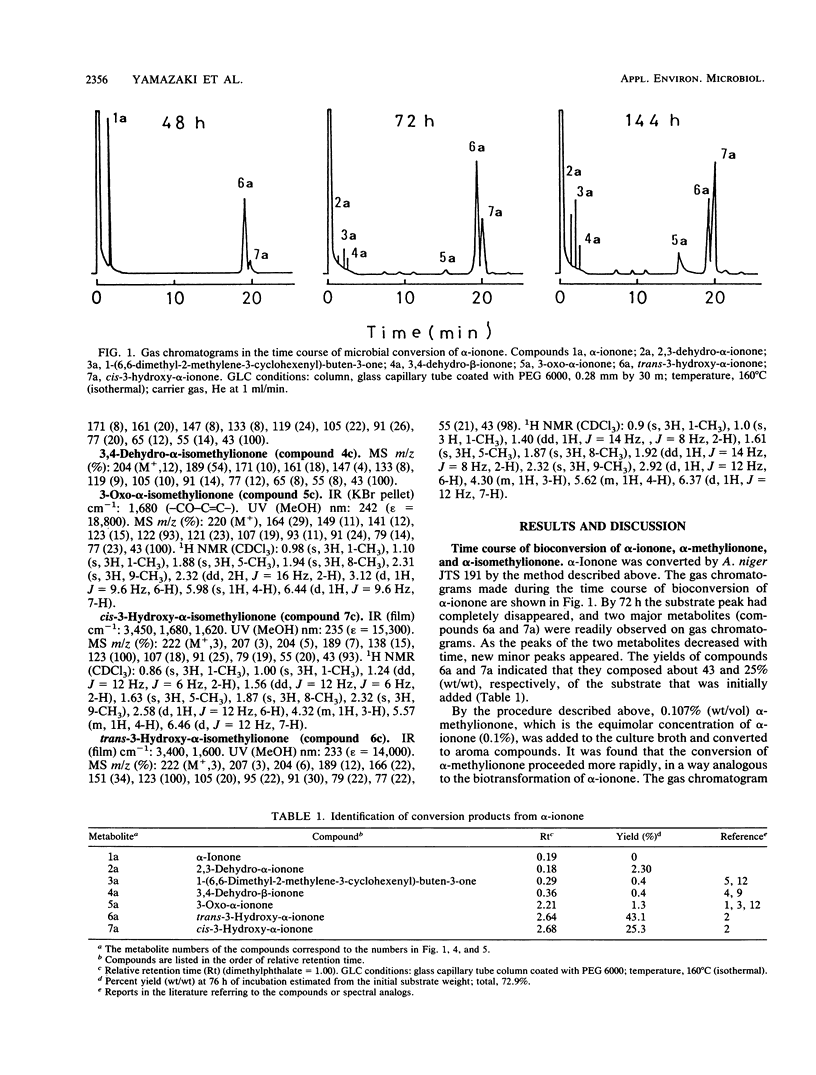
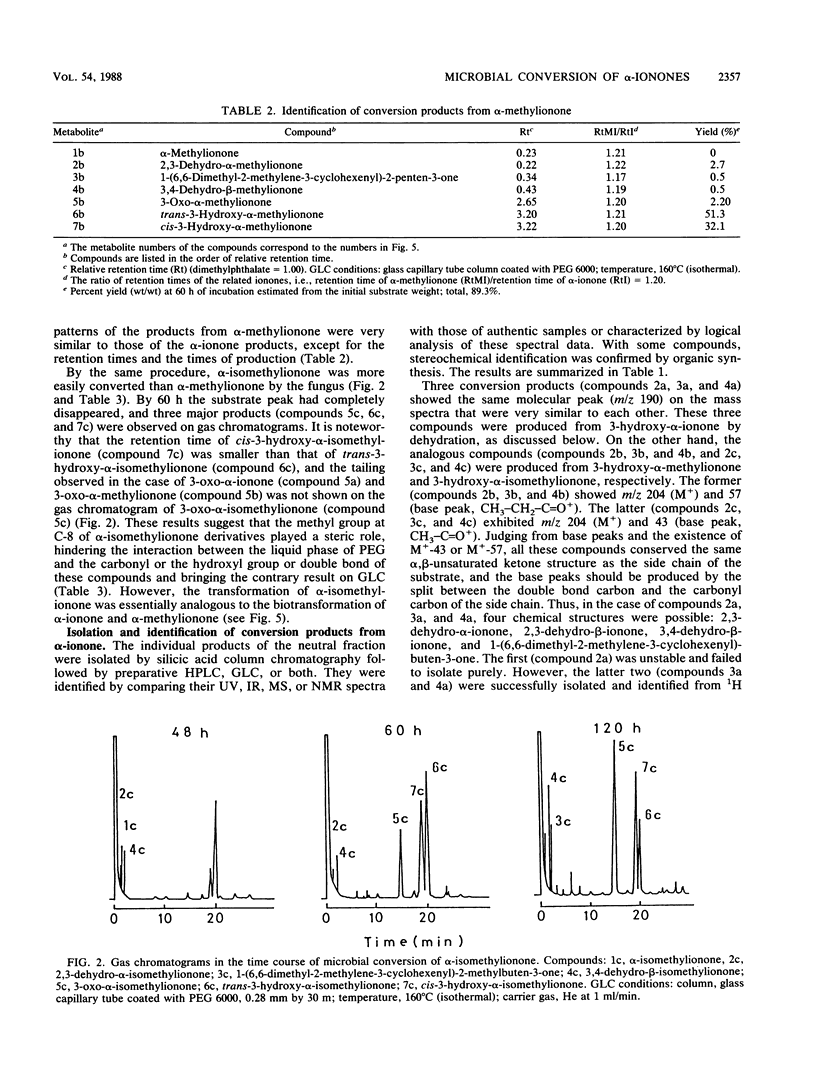
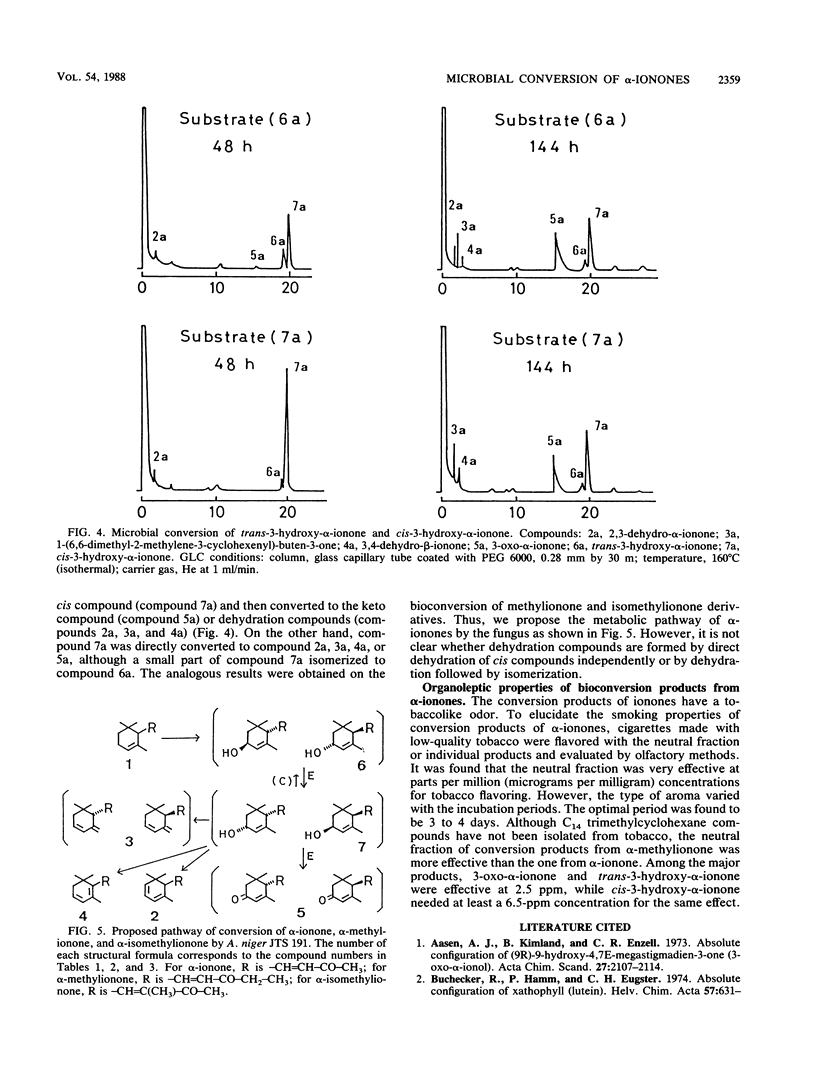
α-Ionone, α-methylionone, and α-isomethylionone were converted by Aspergillus niger JTS 191. The individual bioconversion products from α-ionone were isolated and identified by spectrometry and organic synthesis. The major products were cis-3-hydroxy-α-ionone, trans-3-hydroxy-α-ionone, and 3-oxo-α-ionone. 2,3-Dehydro-α-ionone, 3,4-dehydro-β-ionone, and 1-(6,6-dimethyl-2-methylene-3-cyclohexenyl)-buten-3-one were also identified. Analogous bioconversion products from α-methylionone and α-isomethylionone were also identified. From results of gas-liquid chromatographic analysis during the fermentation, we propose a metabolic pathway for α-ionones and elucidation of stereochemical features of the bioconversion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis D. L., Stevens K. L., Jurd L. Chemistry of tobacco constituents. Oxidation of alpha-ionone and the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of 5-keto-alpha-ionone. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Jan-Feb;24(1):187–189. doi: 10.1021/jf60203a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami Y., Fukunaga Y., Arita M., Kisaki T. Microbial Transformation of beta-Ionone and beta-Methylionone. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):610–617. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.610-617.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



