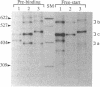
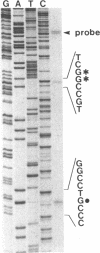
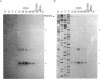
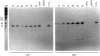
Abstract
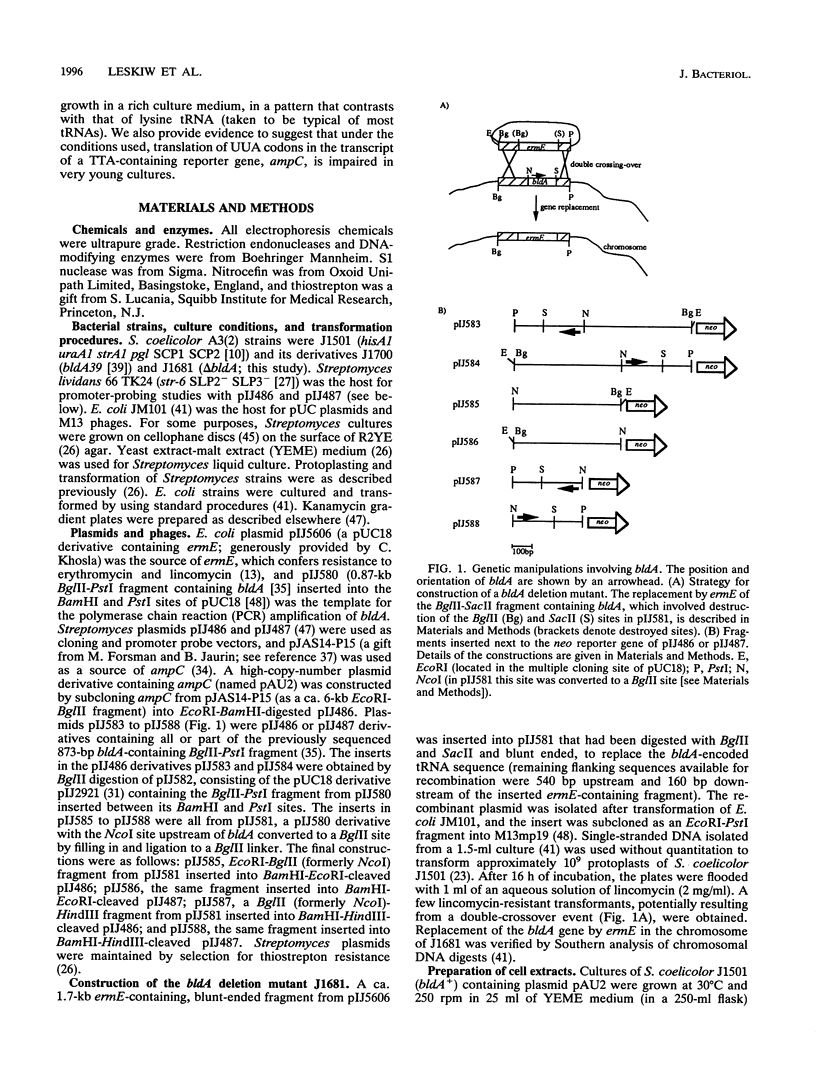
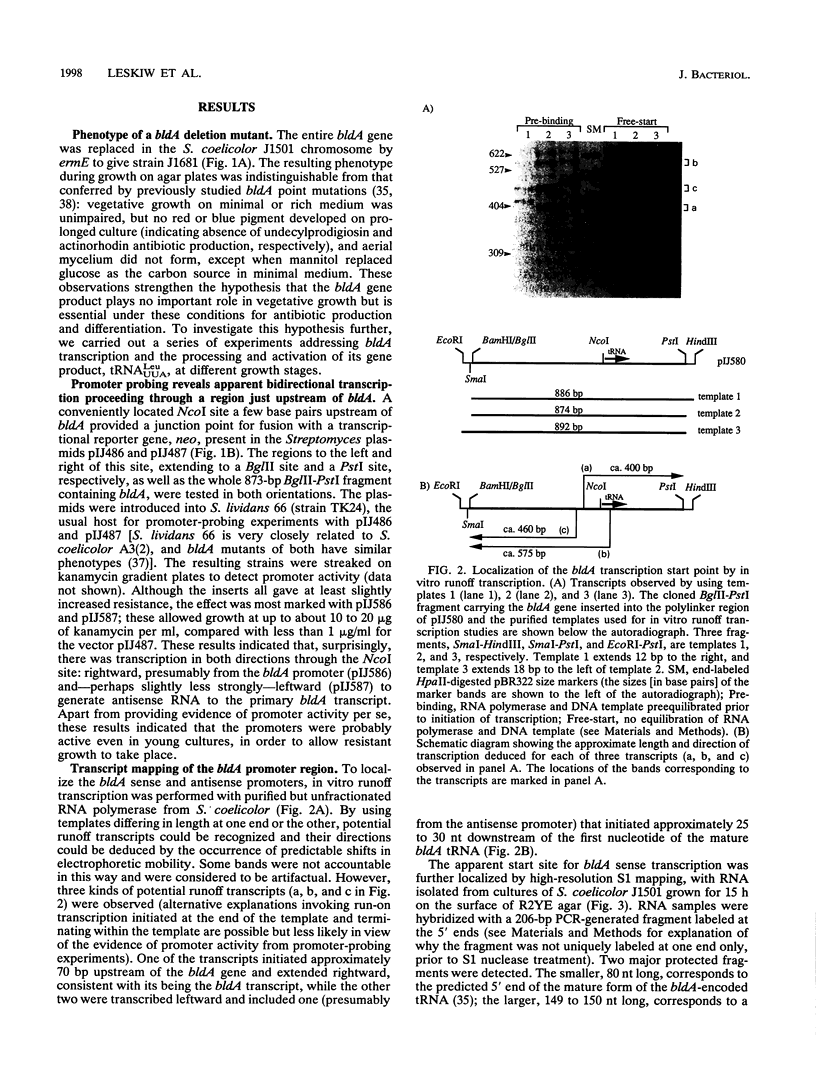
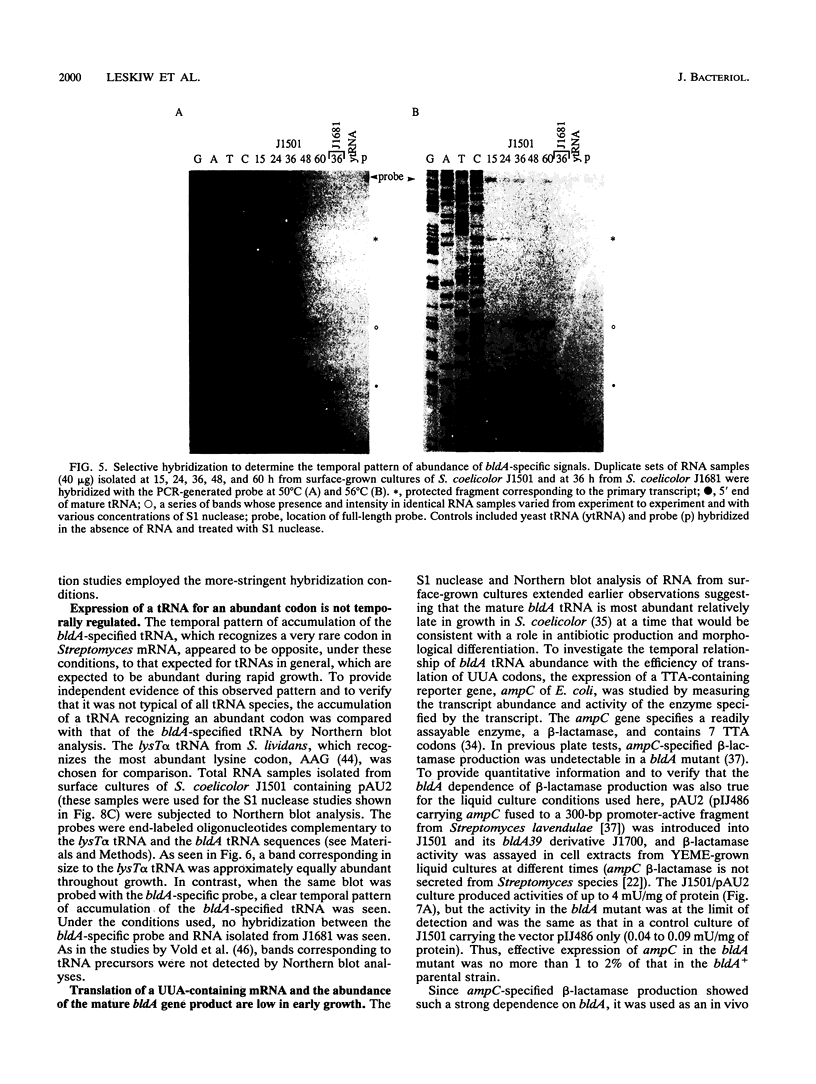
Deletion of the bldA gene of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), which encodes the only tRNA for the rare UUA codon, had no obvious effects on primary growth but interfered with aerial mycelium formation and antibiotic production. To investigate the possible regulatory role of bldA, its transcription start point was identified, and time courses were determined for the appearance of its primary transcript, the processing of the primary transcript to give a mature 5' end, and the apparent efficiency of translation of ampC mRNA, which contains multiple UUA codons. The bldA promoter was active at all times, but processing of the 5' end of the primary transcript was comparatively inefficient in young cultures. This may perhaps involve an antisense RNA, evidence of which was provided by promoter probing and in vitro transcription. The presence of low levels of the processed form of the tRNA in young cultures followed by increased abundance in older cultures contrasted with the pattern observed for accumulation of a different, presumably typical tRNA which was approximately equally abundant throughout growth. The increased accumulation of the 5' processed form of bldA tRNA coincided with more-efficient translation of ampC mRNA in older cultures, supporting the hypothesis that in at least some physiological conditions, bldA may have a regulatory influence on events late in growth, such as morphological differentiation and antibiotic production.
Full text
PDF


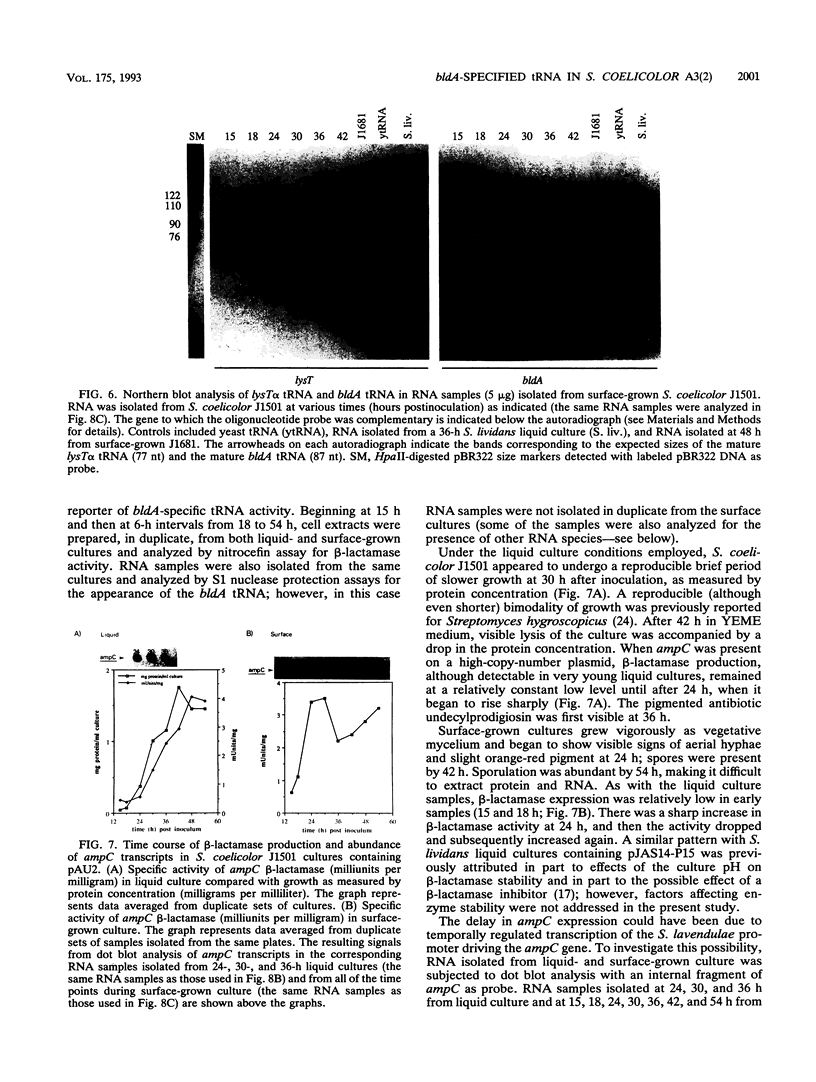




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamidis T., Riggle P., Champness W. Mutations in a new Streptomyces coelicolor locus which globally block antibiotic biosynthesis but not sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2962–2969. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2962-2969.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Guthrie E. P., Chater K. F. Phage vectors that allow monitoring of transcription of secondary metabolism genes in Streptomyces. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jul;9(7):652–656. doi: 10.1038/nbt0791-652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttner M J, Fearnley I M, Bibb M J. The agarase gene (dagA) of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):101–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00329843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champness W. C. New loci required for Streptomyces coelicolor morphological and physiological differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1168–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1168-1174.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champness W., Riggle P., Adamidis T., Vandervere P. Identification of Streptomyces coelicolor genes involved in regulation of antibiotic synthesis. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., King A. A., Suarez J. E. The expression of Streptomyces and Escherichia coli drug-resistance determinants cloned into the Streptomyces phage phi C31. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danchin A., Dondon L. Regulatory features of tRNA Leu I expression in Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1280–1286. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon N., Leadlay P. F. A repeated decapeptide motif in the C-terminal domain of the ribosomal RNA methyltransferase from the erythromycin producer Saccharopolyspora erythraea. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80186-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distler J., Ebert A., Mansouri K., Pissowotzki K., Stockmann M., Piepersberg W. Gene cluster for streptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus: nucleotide sequence of three genes and analysis of transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):8041–8056. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.8041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Moreno M. A., Caballero J. L., Hopwood D. A., Malpartida F. The act cluster contains regulatory and antibiotic export genes, direct targets for translational control by the bldA tRNA gene of Streptomyces. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90120-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Moreno M. A., Martín-Triana A. J., Martínez E., Niemi J., Kieser H. M., Hopwood D. A., Malpartida F. abaA, a new pleiotropic regulatory locus for antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2958–2967. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2958-2967.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsman M., Jaurin B. Chromogenic identification of promoters in Streptomyces lividans by using an ampC beta-lactamase promoter-probe vector. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00337754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geistlich M., Losick R., Turner J. R., Rao R. N. Characterization of a novel regulatory gene governing the expression of a polyketide synthase gene in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):2019–2029. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie E. P., Chater K. F. The level of a transcript required for production of a Streptomyces coelicolor antibiotic is conditionally dependent on a tRNA gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6189–6193. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6189-6193.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillemann D., Pühler A., Wohlleben W. Gene disruption and gene replacement in Streptomyces via single stranded DNA transformation of integration vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):727–731. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt T. G., Chang C., Laurent-Winter C., Murakami T., Garrels J. I., Davies J. E., Thompson C. J. Global changes in gene expression related to antibiotic synthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(8):969–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J. Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2257–2269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. The Leeuwenhoek lecture, 1987. Towards an understanding of gene switching in Streptomyces, the basis of sporulation and antibiotic production. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Nov 22;235(1279):121–138. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Hara O., Beppu T. Cloning of a pleiotropic gene that positively controls biosynthesis of A-factor, actinorhodin, and prodigiosin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1238–1248. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1238-1248.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Kito M., Nishiyama M., Furuya K., Hong S. K., Miyake K., Beppu T. Primary structure of AfsR, a global regulatory protein for secondary metabolite formation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90412-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Malpartida F., Hopwood D. A., Beppu T. afsB stimulates transcription of the actinorhodin biosynthetic pathway in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):355–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00339742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Ward J. M., Bibb M. J. Unusual transcriptional and translational features of the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene (aph) from Streptomyces fradiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):415–429. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Cohen S. N. Streptomyces contain Escherichia coli-type A + T-rich promoters having novel structural features. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor E. J., Baylis H. A., Chater K. F. Pleiotropic morphological and antibiotic deficiencies result from mutations in a gene encoding a tRNA-like product in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1305–1310. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Bibb M. J., Chater K. F. The use of a rare codon specifically during development? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2861–2867. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Lawlor E. J., Fernandez-Abalos J. M., Chater K. F. TTA codons in some genes prevent their expression in a class of developmental, antibiotic-negative, Streptomyces mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2461–2465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J. A morphological and genetic mapping study of bald colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):299–315. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piret J. M., Chater K. F. Phage-mediated cloning of bldA, a region involved in Streptomyces coelicolor morphological development, and its analysis by genetic complementation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.965-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud A., Zalacain M., Holt T. G., Tizard R., Thompson C. J. Nucleotide sequence analysis reveals linked N-acetyl hydrolase, thioesterase, transport, and regulatory genes encoded by the bialaphos biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4454–4463. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4454-4463.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlmeier R., Schmieger H. Nucleotide sequences of tRNA genes in Streptomyces lividans 66. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4027–4027. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soliveri J., Brown K. L., Buttner M. J., Chater K. F. Two promoters for the whiB sporulation gene of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and their activities in relation to development. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6215–6220. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6215-6220.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vold B. S., Okamoto K., Murphy B. J., Green C. J. Transcriptional analysis of Bacillus subtilis rRNA-tRNA operons. I. The tRNA gene cluster of rrnB has an internal promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14480–14484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Janssen G. R., Kieser T., Bibb M. J., Buttner M. J., Bibb M. J. Construction and characterisation of a series of multi-copy promoter-probe plasmid vectors for Streptomyces using the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene from Tn5 as indicator. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):468–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00422072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]