Abstract
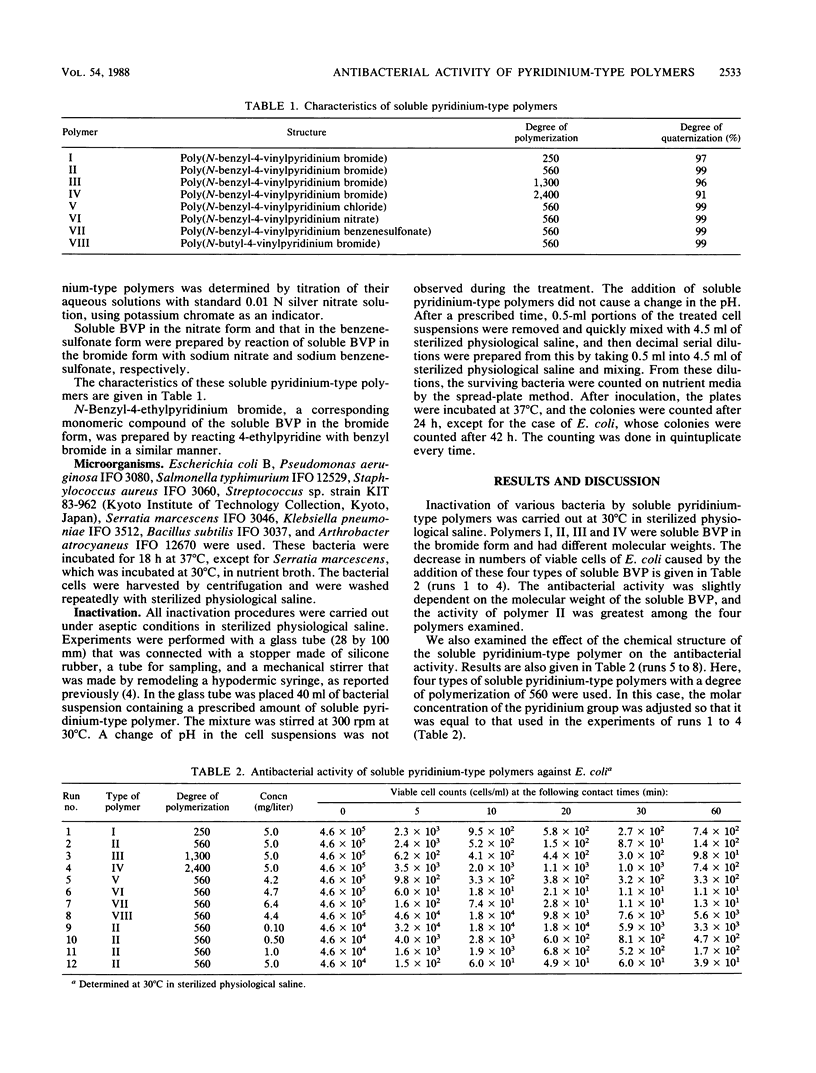
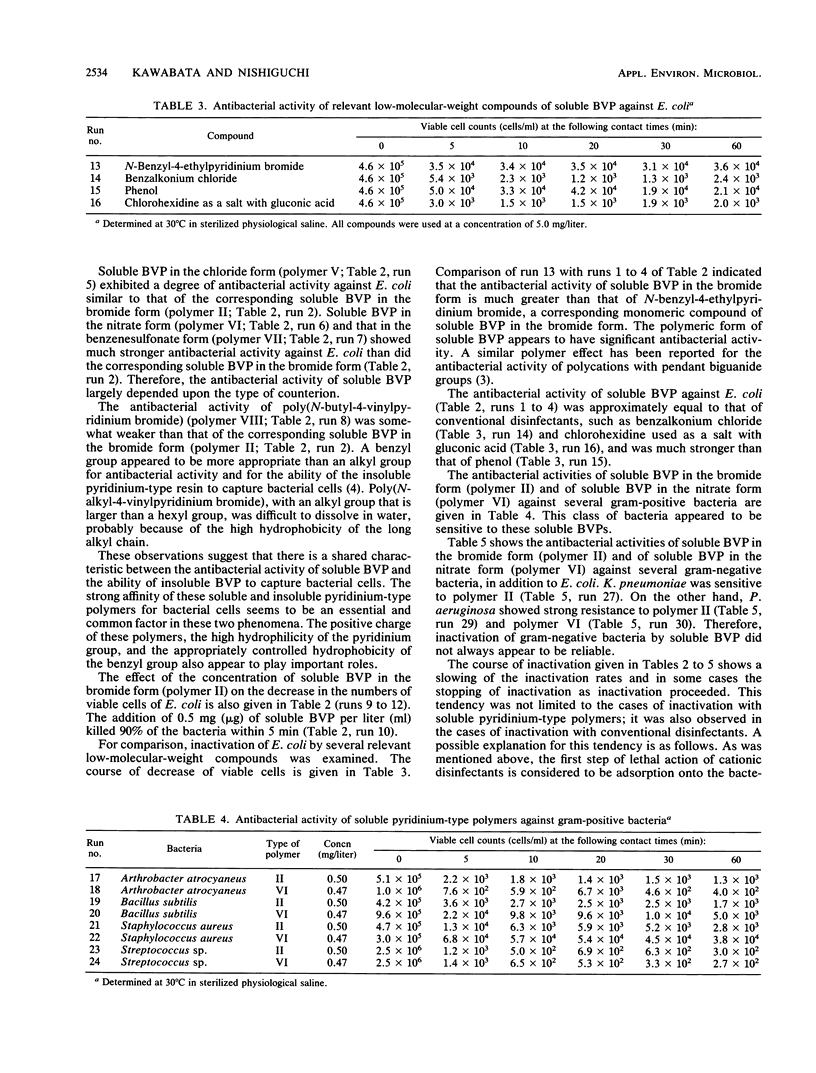
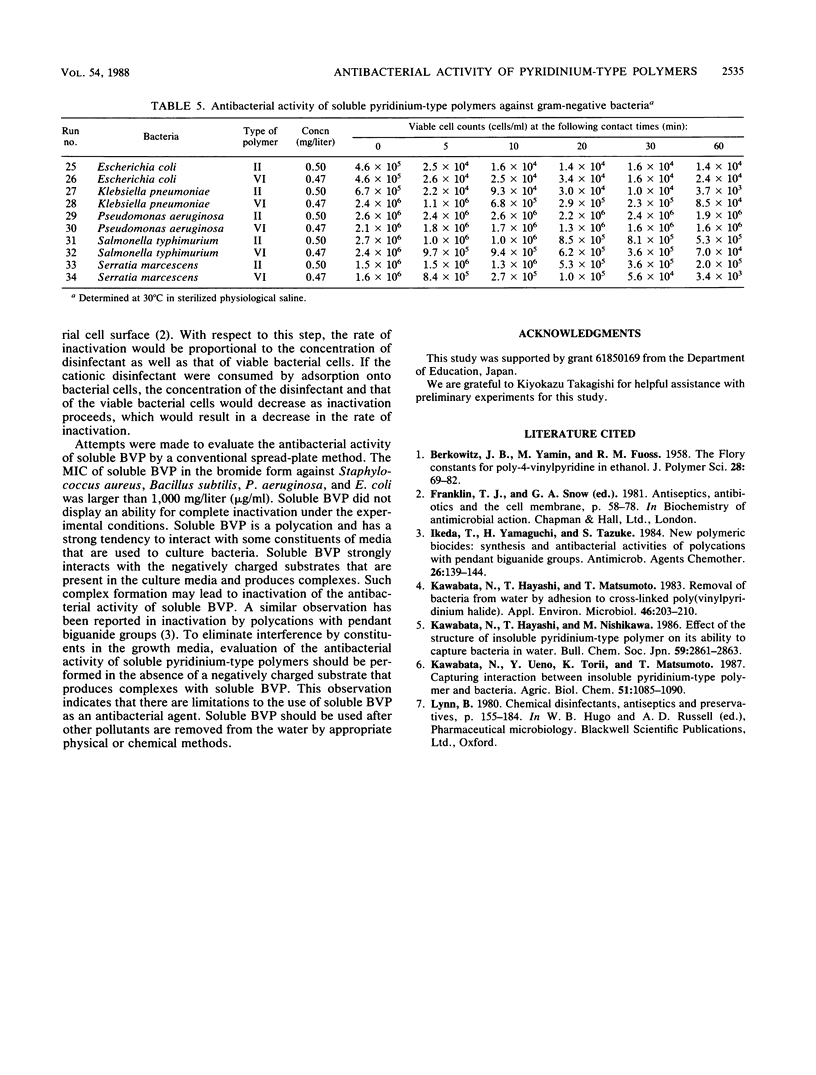
Cross-linked poly(N-benzyl-4-vinylpyridinium halide) (designated insoluble BVP) was previously reported to capture bacterial cells alive by contact with them. The corresponding linear polymer poly(N-benzyl-4-vinylpyridinium salt) (designated soluble BVP) was found to exhibit antibacterial activity. This soluble pyridinium-type polymer showed strong antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria, whereas it was less active against gram-negative bacteria. The antibacterial activity of this cationic, polymeric disinfectant was considerably greater than that of the corresponding monomeric compound and was approximately equal to that of conventional disinfectants such as benzalkonium chloride and chlorohexidine.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ikeda T., Yamaguchi H., Tazuke S. New polymeric biocides: synthesis and antibacterial activities of polycations with pendant biguanide groups. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata N., Hayashi T., Matsumoto T. Removal of bacteria from water by adhesion to cross-linked poly(vinylpyridinium halide). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.203-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



