Abstract
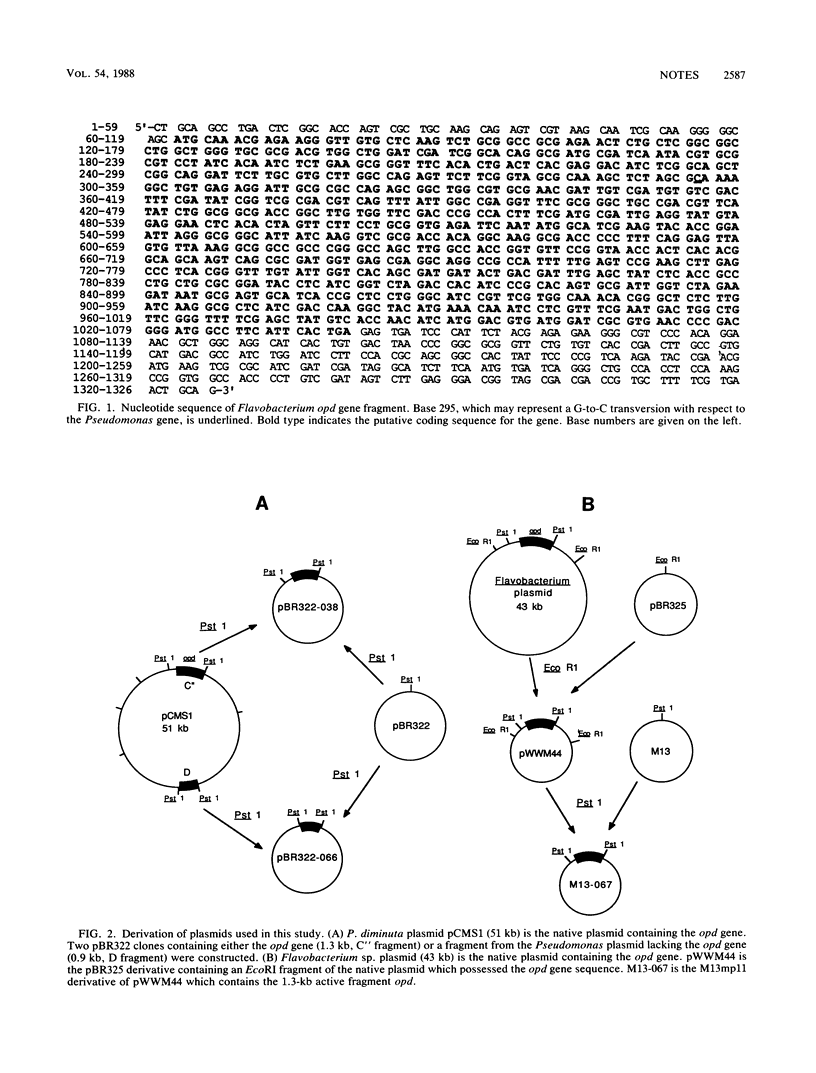
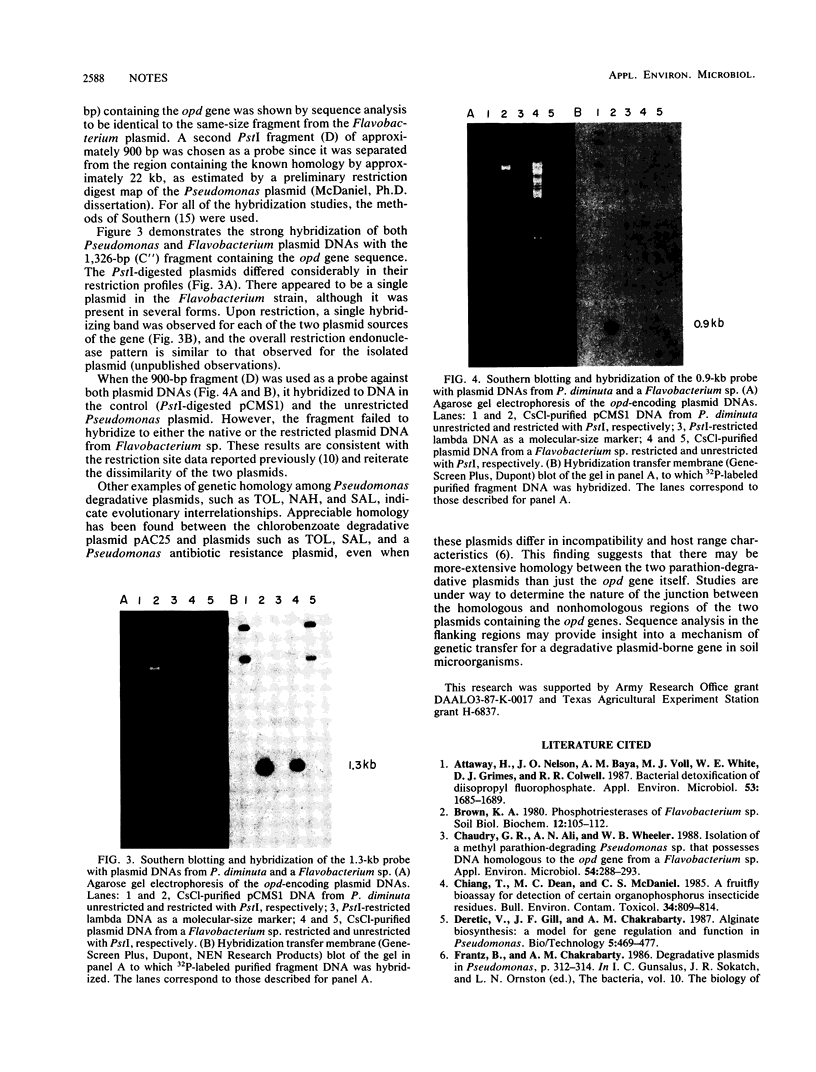
The opd (organophosphate-degrading) gene derived from a 43-kilobase-pair plasmid (pSM55) of a Flavobacterium sp. (ATCC 27551) has a sequence identical to that of the plasmid-borne gene of Pseudomonas diminuta. Hybridization studies with DNA fragments obtained by restriction endonuclease digestion of plasmid DNAs demonstrated that the identical opd sequences were encoded on dissimilar plasmids from the two sources.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attaway H., Nelson J. O., Baya A. M., Voll M. J., White W. E., Grimes D. J., Colwell R. R. Bacterial detoxification of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1685–1689. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1685-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Ali A. N., Wheeler W. B. Isolation of a methyl parathion-degrading Pseudomonas sp. that possesses DNA homologous to the opd gene from a Flavobacterium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):288–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.288-293.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T., Dean M. C., McDaniel C. S. A fruit fly bioassay with phosphotriesterase for detection of certain organophosphorus insecticide residues. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1985 Jun;34(6):809–814. doi: 10.1007/BF01609811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. E., Donarski W. J., Wild J. R., Raushel F. M. Mechanism and stereochemical course at phosphorus of the reaction catalyzed by a bacterial phosphotriesterase. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1591–1597. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel C. S., Harper L. L., Wild J. R. Cloning and sequencing of a plasmid-borne gene (opd) encoding a phosphotriesterase. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2306–2311. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2306-2311.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel C. S., Wild J. R. Detection of organophosphorus pesticide detoxifying bacterial colonies, using UV-photography of parathion-impregnated filters. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1988 Mar;17(2):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01056024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulbry W. W., Karns J. S., Kearney P. C., Nelson J. O., McDaniel C. S., Wild J. R. Identification of a plasmid-borne parathion hydrolase gene from Flavobacterium sp. by southern hybridization with opd from Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):926–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.926-930.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serdar C. M., Gibson D. T., Munnecke D. M., Lancaster J. H. Plasmid Involvement in Parathion Hydrolysis by Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):246–249. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.246-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N., Yoshida T. A Flavobacterium sp. that degrades diazinon and parathion. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;19(7):873–875. doi: 10.1139/m73-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]