Abstract
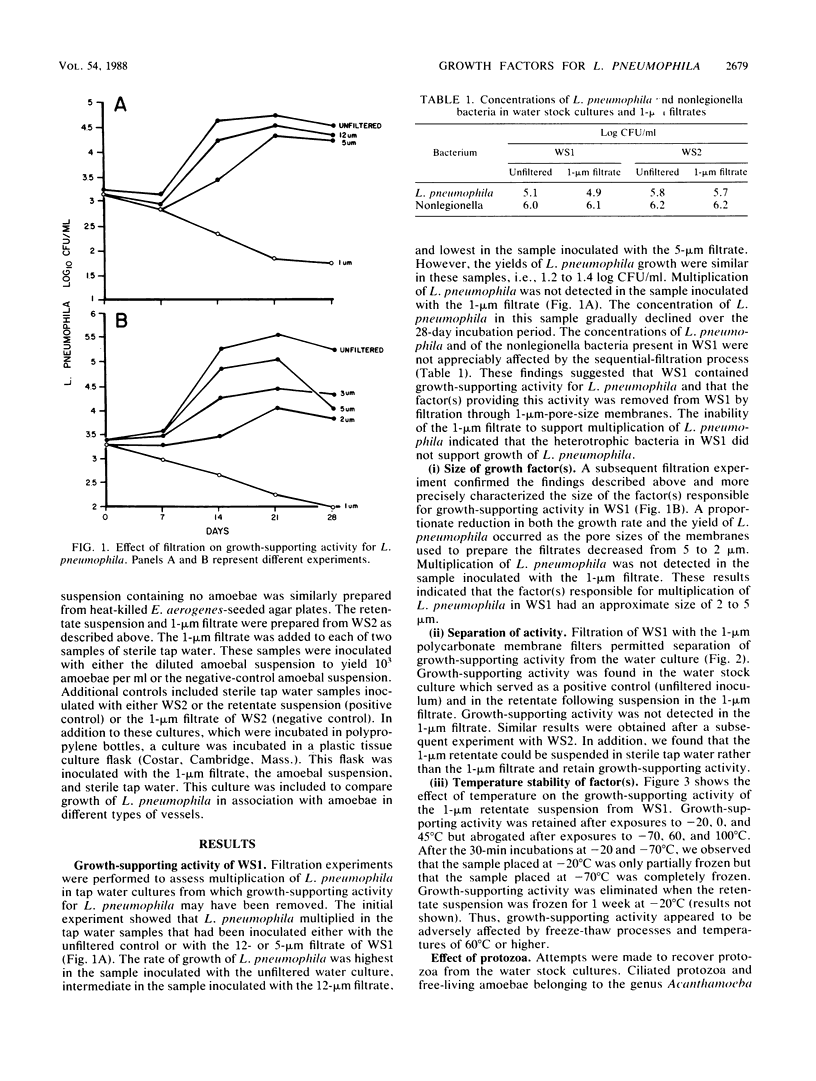
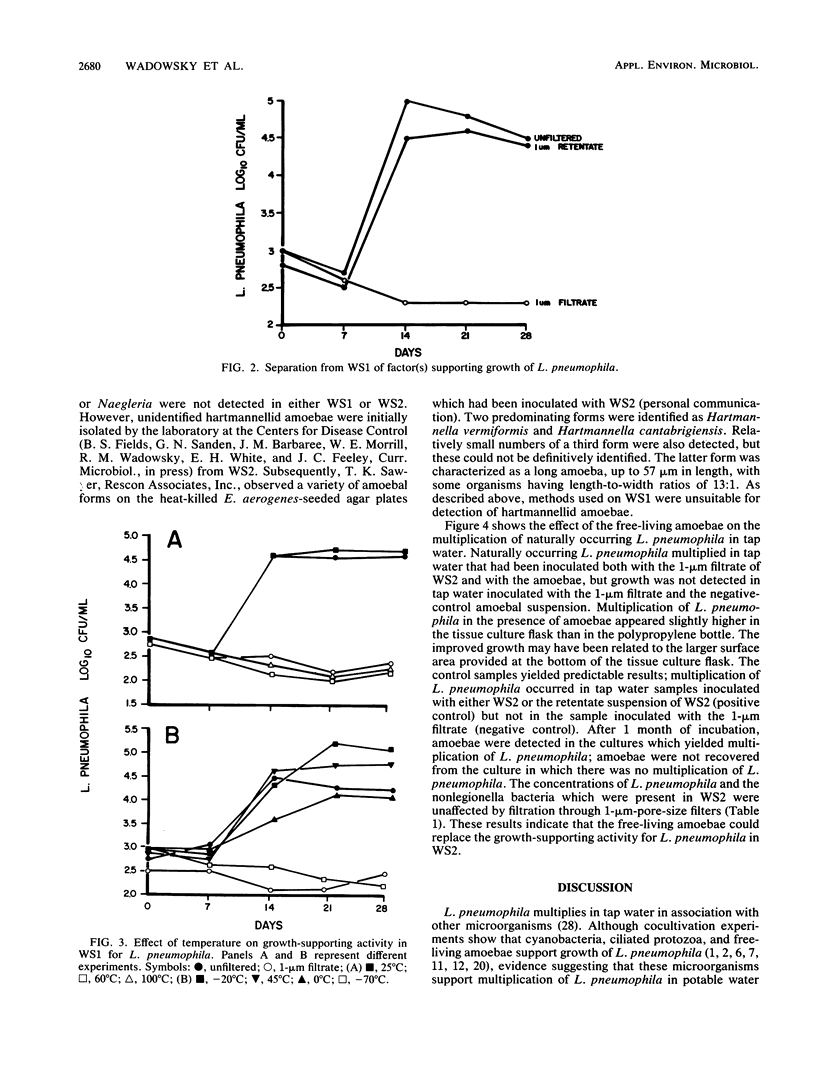
Photosynthetic cyanobacteria, heterotrophic bacteria, free-living amoebae, and ciliated protozoa may support growth of Legionella pneumophila. Studies were done with two tap water cultures (WS1 and WS2) containing L. pneumophila and associated microbiota to characterize growth-supporting activity and assess the relative importance of the microbiota in supporting multiplication of L. pneumophila. The water cultures were incubated in the dark at 35 degrees C. The growth-supporting factor(s) was separated from each culture by filtration through 1-micron-pore-size membrane filters. The retentate was then suspended in sterile tap water. Multiplication of L. pneumophila occurred when both the retentate suspension and the filtrate from either culture were inoculated into sterile tap water. L. pneumophila did not multiply in tap water inoculated with only the filtrate, even though filtration did not reduce the concentration of L. pneumophila or heterotrophic bacteria in either culture. Growth-supporting activity of the retentate suspension from WS1 was inactivated at 60 degrees C but unaffected at 0, 25, and 45 degrees C after 30-min incubations. Filtration experiments indicated that the growth-supporting factor(s) in WS1 was 2 to 5 micron in diameter. Ciliated protozoa were not detected in either culture. Hartmannellid amoebae were conclusively demonstrated in WS2 but not in WS1. L. pneumophila multiplied in tap water inoculated with the amoebae (10(3)/ml) and the 1-micron filtrate of WS2. No multiplication occurred in tap water inoculated with the filtrate only. Growth-supporting activity for L. pneumophila may be present in plumbing systems; hartmannellid amoebae appear to be important determinants of multiplication of L. pneumophila in some tap water cultures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand C. M., Skinner A. R., Malic A., Kurtz J. B. Interaction of L. pneumophilia and a free living amoeba (Acanthamoeba palestinensis). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Oct;91(2):167–178. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaree J. M., Fields B. S., Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Isolation of protozoa from water associated with a legionellosis outbreak and demonstration of intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):422–424. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.422-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M., Yu V. L., Stout J., Goetz A., Muder R. R., Taylor F. Legionellaceae in the hospital water-supply. Epidemiological link with disease and evaluation of a method for control of nosocomial legionnaires' disease and Pittsburgh pneumonia. Lancet. 1983 Aug 6;2(8345):307–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Comparative study of selective media for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from potable water. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):697–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.697-699.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Barbaree J. M., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Morrill W. E., Sanden G. N., Dykstra M. J. Comparison of guinea pig and protozoan models for determining virulence of Legionella species. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):553–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.553-559.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke M., Seidel K. M. Association between Legionella pneumophila and amoebae in water. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):690–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta J. M., States S. J., McGlaughlin J. E., Overmeyer J. H., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Wolford R. S., Yee R. B. Enhanced chlorine resistance of tap water-adapted Legionella pneumophila as compared with agar medium-passaged strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.21-26.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Current views on the relationships between amoebae, legionellae and man. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):678–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Ho J. L., Meyer R. D., Gorman G. W., Edelstein P. H., Mallison G. F., Finegold S. M., Fraser D. W. Potable water as a source of Legionnaires' disease. JAMA. 1985 Mar 8;253(10):1412–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Ceraso M., Stephenson T. E., Wolford R. S., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Yee R. B. Effects of metals on Legionella pneumophila growth in drinking water plumbing systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1149–1154. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1149-1154.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Kuchta J. M., Oleck B. M., Lipovich M. J., Wolford R. S., Wadowsky R. M., McNamara A. M., Sykora J. L., Keleti G. Survival and multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in municipal drinking water systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):979–986. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.979-986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States S. J., Conley L. F., Towner S. G., Wolford R. S., Stephenson T. E., McNamara A. M., Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. An alkaline approach to treating cooling towers for control of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1775–1779. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1775-1779.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Muraca P. Legionnaires' disease acquired within the homes of two patients. Link to the home water supply. JAMA. 1987 Mar 6;257(9):1215–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh M. J., Miller R. D. Amino acid requirements for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):865–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.865-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. O., Swann R. A., Bartlett C. L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from water systems: methods and preliminary results. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 14;282(6263):515–517. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6263.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Domingue E. L. Cocultivation of Legionella pneumophila and free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):954–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.954-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Wolford R., McNamara A. M., Yee R. B. Effect of temperature, pH, and oxygen level on the multiplication of naturally occurring Legionella pneumophila in potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1197–1205. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1197-1205.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Effect of non-Legionellaceae bacteria on the multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1206-1210.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Glycine-containing selective medium for isolation of Legionellaceae from environmental specimens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):768–772. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.768-772.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B., Mezmar L., Wing E. J., Dowling J. N. Hot water systems as sources of Legionella pneumophila in hospital and nonhospital plumbing fixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1104-1110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Satellite growth of Legionella pneumophila with an environmental isolate of Flavobacterium breve. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1447–1449. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1447-1449.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. M. Multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in unsterilized tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1330–1334. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1330-1334.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



