Abstract
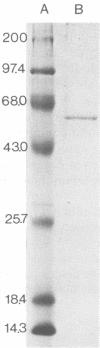
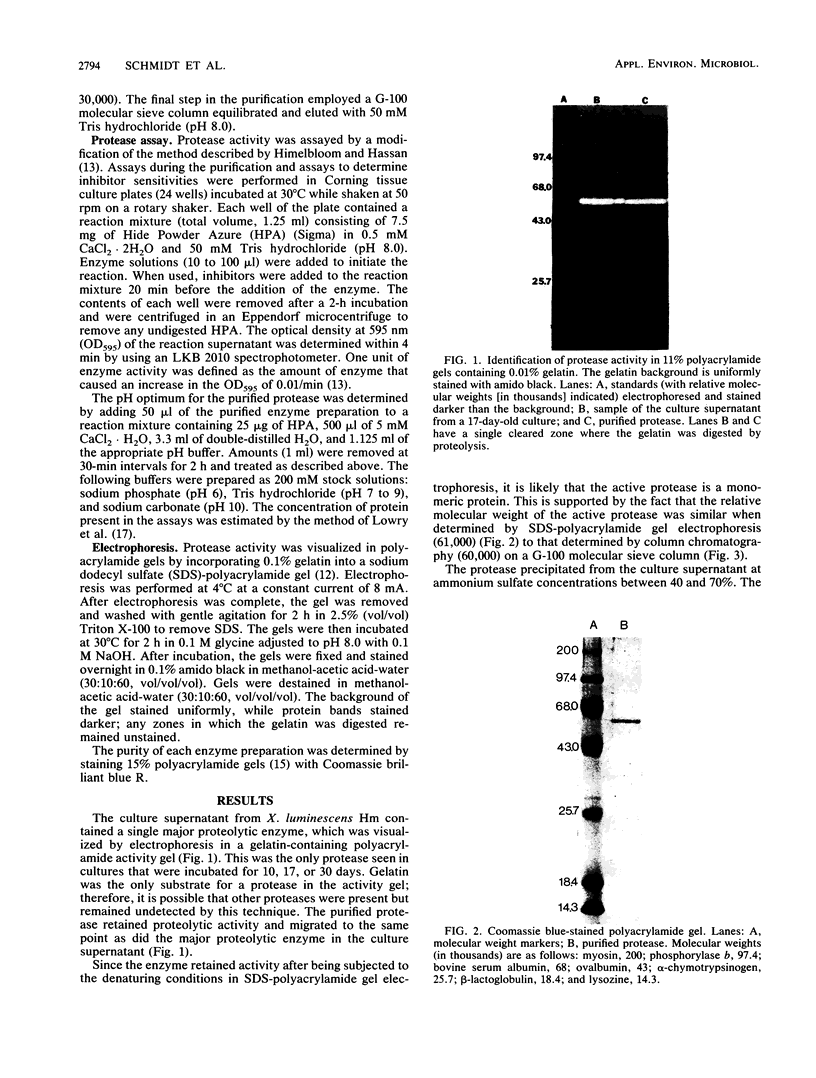
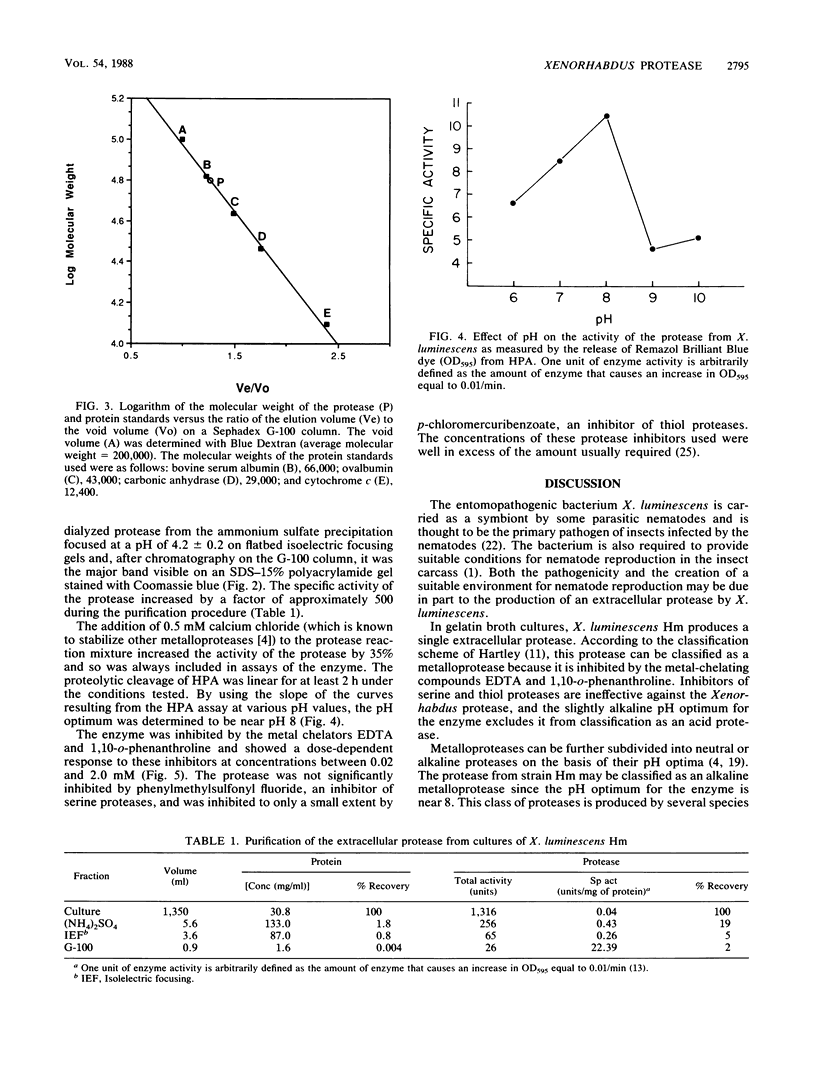
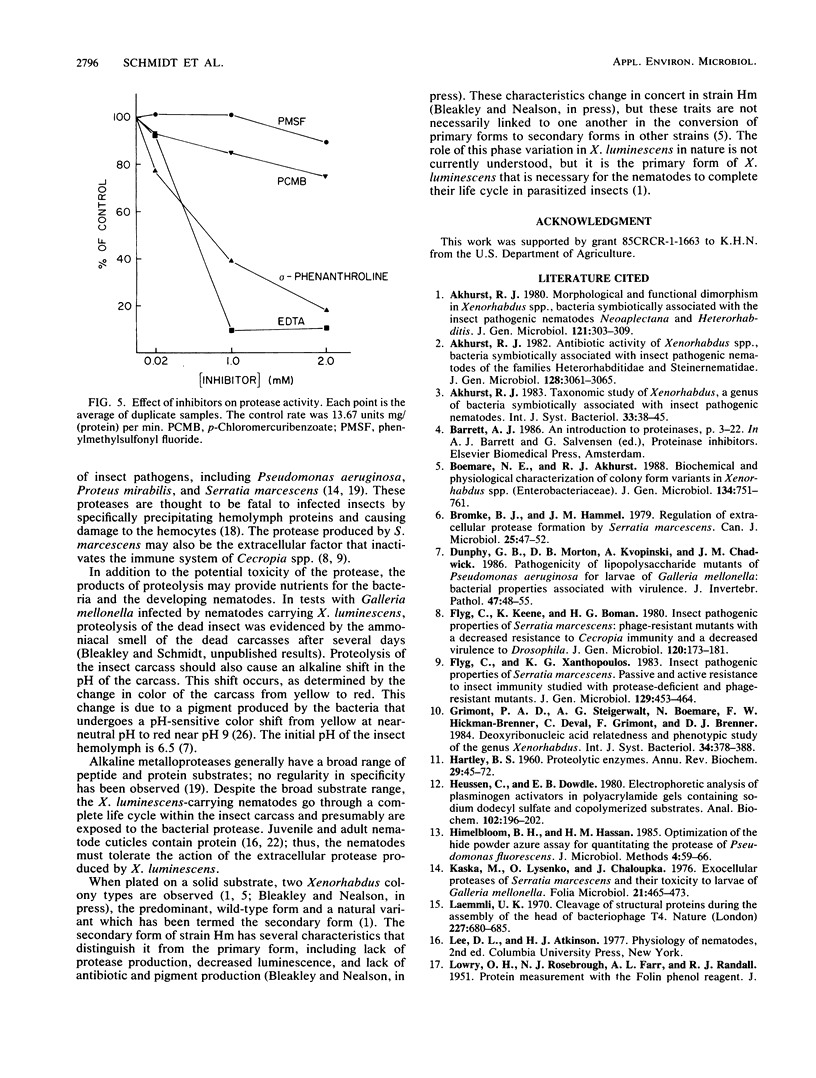
Xenorhabdus luminescens Hm cultured in gelatin broth produced a single extracellular protease. The protease was purified by a factor of 500 and characterized as a monomeric protein with an approximate molecular weight of 61,000. On the basis of inhibitor studies and its pH optimum, the protease was classified as an alkaline metalloprotease with a pH optimum near 8; the isoelectric point of the enzyme is 4.2 ± 0.2. The protease may be a major factor in the ecology of X. luminescens, which is carried as a symbiom of some parasitic nematodes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J. Antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus spp., bacteria symbiotically associated with insect pathogenic nematodes of the families Heterorhabditidae and Steinernematidae. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3061–3065. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromke B. J., Hammel J. M. Regulation of extracellular protease formation by Serratia marcescens. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m79-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flyg C., Kenne K., Boman H. G. Insect pathogenic properties of Serratia marcescens: phage-resistant mutants with a decreased resistance to Cecropia immunity and a decreased virulence to Drosophila. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Sep;120(1):173–181. doi: 10.1099/00221287-120-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S. Proteolytic enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1960;29:45–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.29.070160.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussen C., Dowdle E. B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaska M., Lysenko O., Chaloupka J. Exocellular proteases of Serratia marcescens and their toxicity to larvae of Galleria mellonella. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1976;21(6):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF02876938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysenko O. Non-sporeforming bacteria pathogenic to insects: incidence and mechanisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:673–695. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morihara K. Comparative specificity of microbial proteinases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):179–243. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poinar G. O., Jr, Thomas G. M. Significance of Achromobacter nematophilus Poinar and Thomas (Achromobacteraceae: Eubacteriales) in the development of the nematode, DD-136 (Neoaplectana sp. Steinernematidae). Parasitology. 1966 May;56(2):385–390. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000070980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. H., Schmidt T. M., Nealson K. H. Identification of an anthraquinone pigment and a hydroxystilbene antibiotic from Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1602–1605. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1602-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler M. E., Milam J. R., Smith R. L., Schank S. C., Zuberer D. A. Isolation of Azospirullum from diverse geographic regions. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jun;25(6):693–697. doi: 10.1139/m79-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]