Abstract
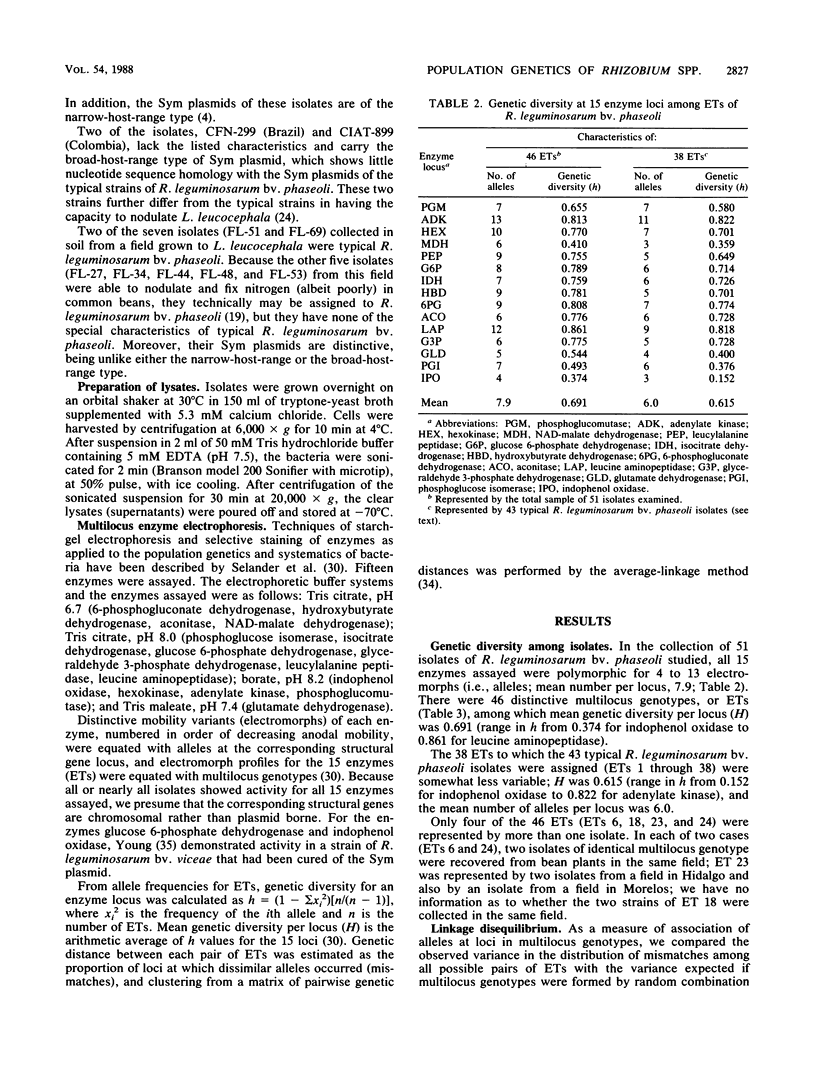
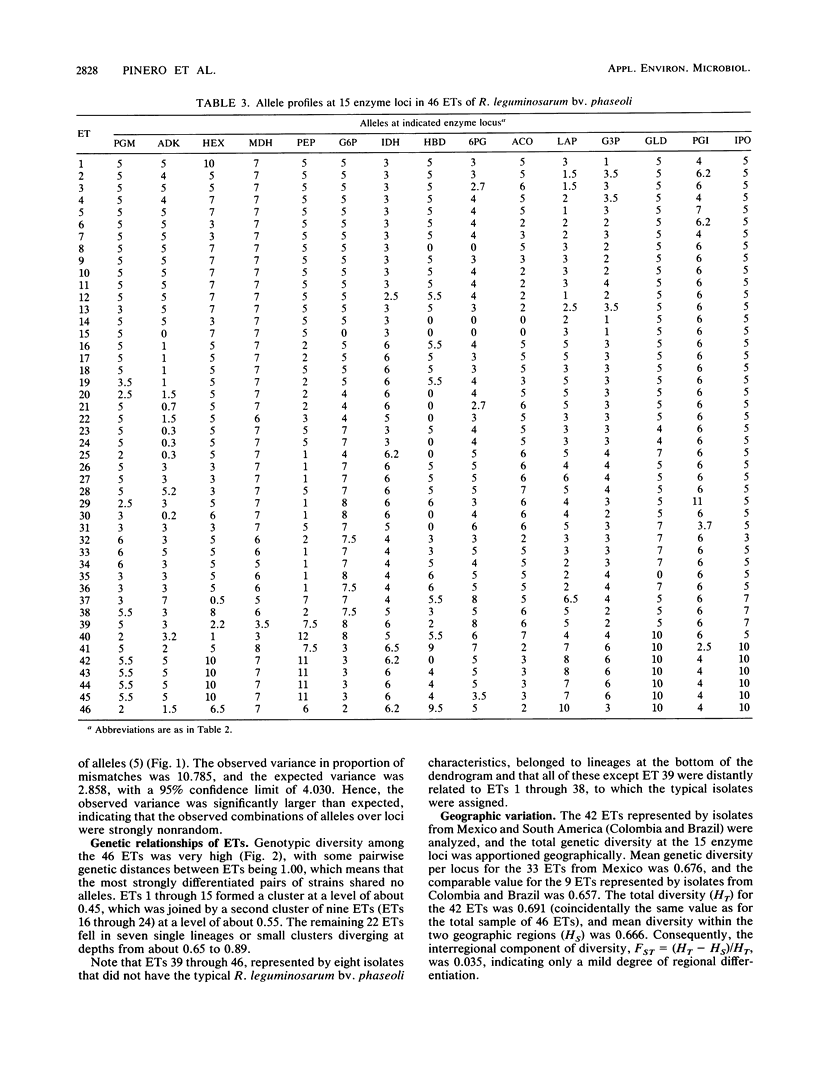
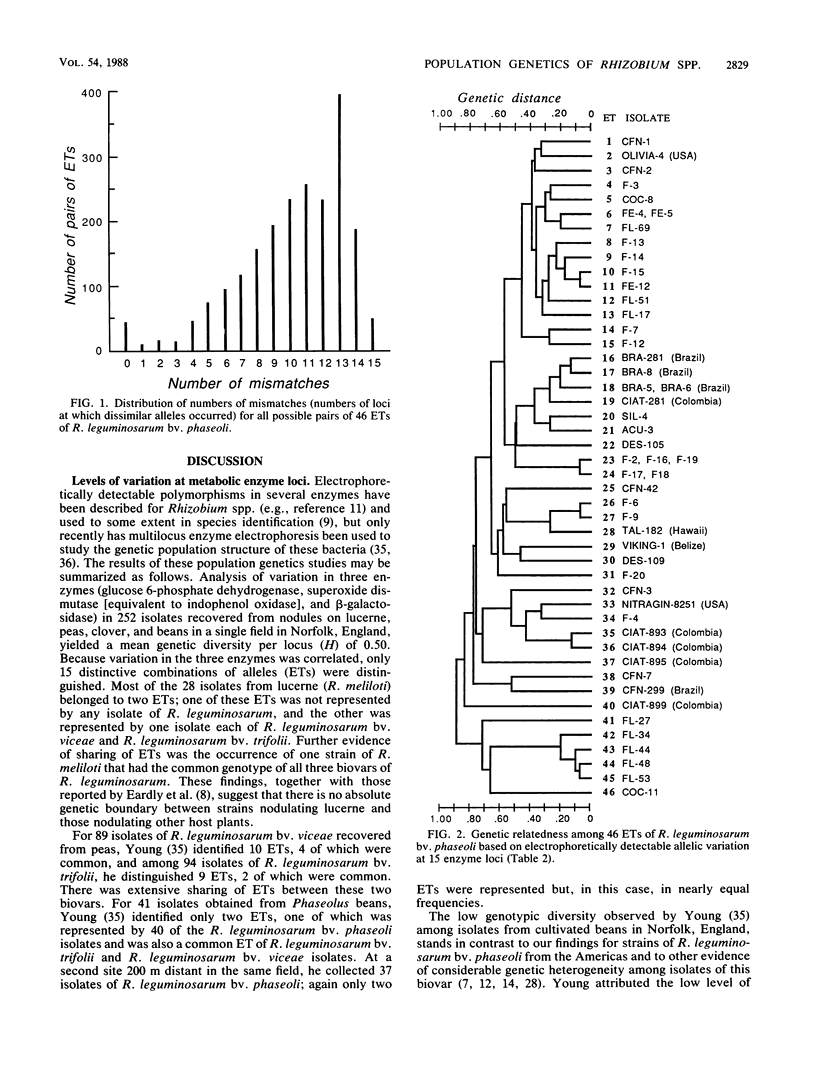
Fifty-one isolates of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli from various geographic and ecological sources, largely in Mexico, were characterized by the electrophoretic mobilities of 15 metabolic enzymes, and 46 distinctive multilocus genotypes (electrophoretic types [ETs]) were distinguished on the basis of allele profiles at the enzyme loci. Mean genetic diversity per enzyme locus among the 46 ETs was 0.691, the highest value yet recorded for any species of bacterium. The occurrence of strong nonrandom associations of alleles over loci suggested a basically clonal population structure, reflecting infrequent recombination of chromosomal genes. Multilocus genotypic diversity was unusually high, with the most strongly differentiated pairs of ETs having distinctive alleles at all 15 loci and major clusters of ETs diverging at genetic distances as large as 0.89. This great diversity in the chromosomal genome raises the possibility that R. leguminosarum biovar phaseoli is a polyphyletic assemblage of strains. As other workers have suggested, the inclusion of all strains capable of nodulating beans in a single biovar or species is genetically unrealistic and taxonomically misleading. A biologically meaningful classification of Rhizobium spp. should be based on assessment of variation in the chromosomal genome rather than on phenotypic characters, especially those mediated for the most part or wholly by plasmid-borne genes, such as host relationships.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Heuzenroeder M., Kusecek B., Ochman H., Caugant D., Selander R. K., Väisanen-Rhen V., Korhonen T. K., Stuart S., Orskov F. Clonal analysis of Escherichia coli O2:K1 isolated from diseased humans and animals. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.268-276.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Pluschke G. Clonal analysis of descent and virulence among selected Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:185–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brom S., Martinez E., Dávila G., Palacios R. Narrow- and Broad-Host-Range Symbiotic Plasmids of Rhizobium spp. Strains That Nodulate Phaseolus vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1280–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1280-1283.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. H., Feldman M. W. Population structure of multilocus associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5913–5916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Mocca L. F., Frasch C. E., Frøholm L. O., Zollinger W. D., Selander R. K. Genetic structure of Neisseria meningitidis populations in relation to serogroup, serotype, and outer membrane protein pattern. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2781–2792. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2781-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardly B. D., Hannaway D. B., Bottomley P. J. Characterization of Rhizobia from Ineffective Alfalfa Nodules: Ability to Nodulate Bean Plants [Phaseolus vulgaris (L.) Savi.]. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1422–1427. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1422-1427.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Pardo M. A., Leija A., Martínez E., Romero D., Piñero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Genomic instability in Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1191-1196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fottrell P. F., O'Hora A. Multiple forms of D (-)3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase in Rhizobium. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(3):287–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein G. T., De Ley J., Tijtgat R. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology and taxonomy of Agrobacterium, Rhizobium, and Chromobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.116-124.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE R. T. Nodule bacteria associated with the indigenous leguminosae of South-Western Australia. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:351–359. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latreille J., Barlogie B., Dosik G., Johnston D. A., Drewinko B., Alexanian R. Cellular DNA content as a marker of human multiple myeloma. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez E., Palacios R., Sánchez F. Nitrogen-fixing nodules induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring Rhizobium phaseoli plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2828–2834. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2828-2834.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett M. L., Colwell R. R. Adansonian analysis of the Rhizobiaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(2):245–266. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Bemis D. A., Ishikawa H., Selander R. K. Clonal diversity and host distribution in Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2793–2803. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2793-2803.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Leps W. T., Silver L. E., Brill W. J. Use of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to identify and classify Rhizobium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):414–422. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.414-422.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Gibson A. H., Dudman W. F., Watson J. M. Evidence for genetic exchange and recombination of Rhizobium symbiotic plasmids in a soil population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2942–2947. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2942-2947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Musser J. M., Caugant D. A., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Population genetics of pathogenic bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Demetriou L., Apte R. G. Rhizobium Population Genetics: Enzyme Polymorphism in Rhizobium leguminosarum from Plants and Soil in a Pea Crop. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.397-402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



