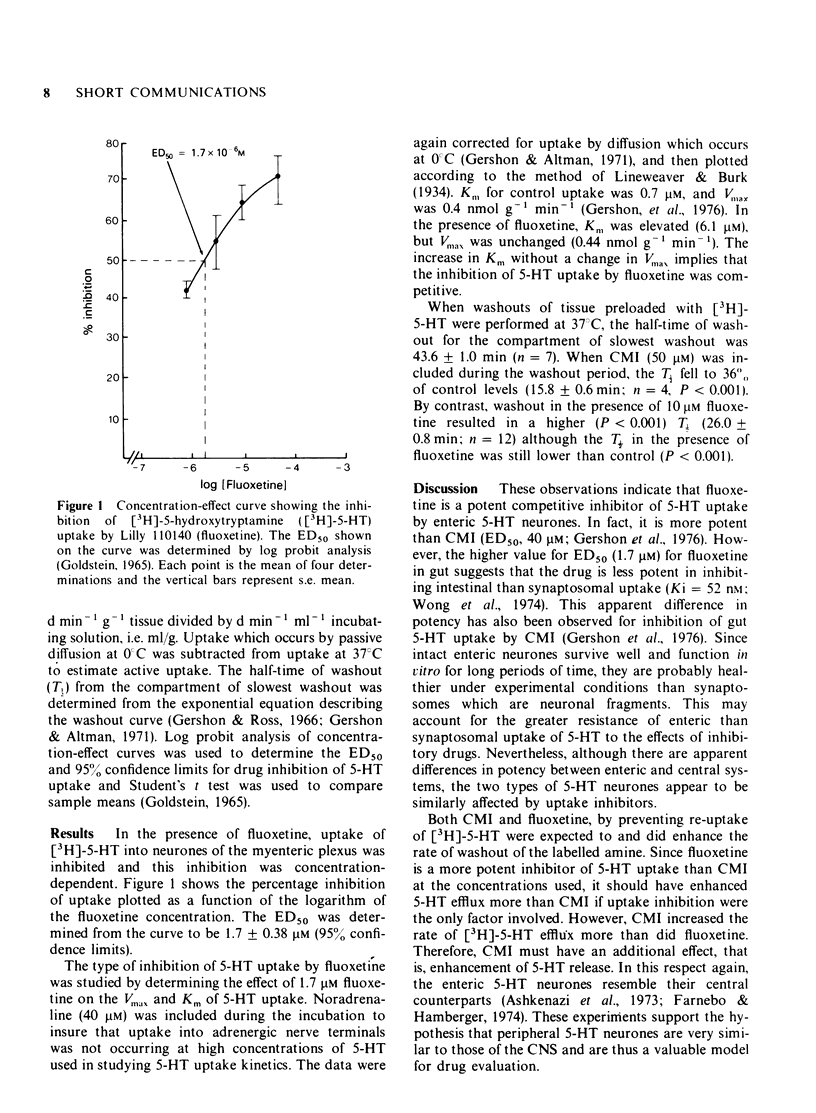
Abstract
The effect of fluoxetine on uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) by enteric 5-hydroxytryptaminergic neurones has been analyzed in order to compare further these neurones with 5-HT neurones of the CNS. In addition, the effects of fluoxetine and chlorimipramine on efflux of [3H]-5-HT from the myenteric plexus were also evaluated. Fluoxetine was found to be a competitive inhibitor of 5-HT uptake by the myenteric plexus and was a more potent inhibitor of 5-HT uptake than was chlorimipramine. However, chlorimipramine enhanced the efflux of [3H]-5-HT more than could be explained by inhibition of 5-HT uptake and, therefore, appears to have the additional action of releasing the amine. These observations, similar to those of others studying central neurones, support the view that enteric 5-HT neurones resemble those of the CNS and are a useful model for the evaluation of drugs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi R., Holman R. B., Vogt M. Release of transmitters into the perfused third cerebral ventrical of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):195–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnebo L. O., Hamberger B. Regulation of (3H)5-hydroxytryptamine release from rat brain slices. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;26(8):642–644. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb10680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Altman R. F. An analysis of the uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by the myenteric plexus of the small intestine of the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Oct;179(1):29–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Dreyfus C. F., Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Serotonergic neurons in the peripheral nervous system: identification in gut by immunohistochemical localization of tryptophan hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3086–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Robinson R. G., Ross L. L. Serotonin accumulation in the guinea-pig myenteric plexus: ion dependence, structure-activity relationship and the effect of drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Sep;198(3):548–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Ross L. L. Location of sites of 5-hydroxytryptamine storage and metabolism by radioautography. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(2):477–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonakait G. M., Tamir H., Rapport M. M., Gershon M. D. Detection of a soluble serotonin-binding protein in the mammalian myenteric plexus and other peripheral sites of serotonin storage. J Neurochem. 1977 Feb;28(2):277–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Horng J. S., Bymaster F. P., Hauser K. L., Molloy B. B. A selective inhibitor of serotonin uptake: Lilly 110140, 3-(p-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-N-methyl-3-phenylpropylamine. Life Sci. 1974 Aug 1;15(3):471–479. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


