Abstract
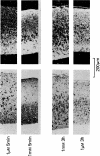
1 Freshly cut guniea-pig olfactory cortex slices contained 2.2 mmol gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)/kg tissue weight. This declined during in vitro incubation at 25 degrees C in the absence of exogenous GABA, but increased to 6.95 mmol/kg after 1.5 h incubation in 1 mM GABA. 2 Uptake of [3H]-GABA (1 microM) was inhibited by 1 mM (+/-)-nipecotic acid (-83%), beta-amino-n-butyric acid (BABA) (-59%), L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid (DABA) (-63%), (+/-)cis-3-aminocyclohexane carboxylic acid (ACHC) (-53%), and 3-aminopropanesulphonic acid (3-APS) (-26%), but was increased by beta-alanine (BALA) (+23%). 3 Autoradiographs showed steep concentration gradients of radioactivity across slices incubated for short periods in [3H]-GABA. 4 Efflux of [3H]-GABA from pre-loaded slices was accelerated strongly by nipecotic acid, BABA, DABA and ACHC but weakly or not all by BALA or 3-APS. 5 Nipecotic acid (1 mM) potentiated the surface-depolarization of the slice produced by GABA but not that produced by 3-APS. 6 The depolarizing actions of DABA, BABA, nipecotic acid and ACHC, but not that of 3-APS or BALA, were potentiated when the endogenous GABA content of slices was raised. 7 It is concluded that: (a) the depolarizing action of exogenous GABA is limited by cellular uptake; (b) surface-depolarizations produced by nipecotic acid, DABA, BABA and ACHC may be mediated by the release of GABA; and (c) neuronal, rather than glial, transport systems are responsible for these effects.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):85–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beart P. M., Johnston G. A. GABA uptake in rat brain slices: inhibition by GABA analogues and by various drugs. J Neurochem. 1973 Feb;20(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenbach M. A., Stevens C. F. Synaptic organization of cat olfactory cortex as revealed by intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Mar;32(2):204–214. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. -Aminobutyric acid uptake by sympathetic ganglia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):89–91. doi: 10.1038/newbio238089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A., Collins G. G., Galvan M., Marsh S., Yamini G. Indirect effects of amino-acids on sympathetic ganglion cells mediated through the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid from glial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 May;57(1):73–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. Depolarizing actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related compounds on rat superior cervical ganglia in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):205–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A., White R. D., Yamini G. [3H]gamma-Aminobutyric acid uptake into neuroglial cells of rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Galvan M. Influence of neuroglial transport on the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on mammalian ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Galvan M. Responses of the guinea-pig isolated olfactory cortex slice to gamma-aminobutyric acid recorded with extracellular electrodes. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):347–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marsh S. Axonal GABA-receptors in mammalian peripheral nerve trunks. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 3;156(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Scholfield C. N. Depolarization of neurones in the isolated olfactory cortex of the guinea-pig by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;65(2):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. M., Collins G. G. The release of endogenous amino acids from the rat visual cortex. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):383–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crnic D. M., Hammerstad J. P., Cutler R. W. Accelerated efflux of ( 14 C) and ( 3 H) amino acids from superfused slices of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):203–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Game C. J., Lodge D. The in vivo inactivation of GABA and other inhibitory amino acids in the cat nervous system. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Jun 30;25(4):413–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00241731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Scholfield C. N. Cellular uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid influences its potency on neurones of olfactory cortex in vitro [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:129P–130P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J. A., Scholfield C. N., Brown D. A. Evoked surface-positive potentials in isolated mammalian olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 16;76(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A. Autoradiographic identification of cerebral and cerebellar cortical neurons accumulating labeled gamma-aminobutyric acid ( 3 H-GABA). Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(4):354–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00235032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Kelly J. S. Uptake and metabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid by neurones and glial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 1;24(9):933–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. P., Neal M. J. Selective inhibition of neuronal GABA uptake by cis-1,3-aminocyclohexane carboxylic acid. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):281–284. doi: 10.1038/264281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A. Inhibition of GABA uptake in rat brain slices by nipecotic acid, various isoxazoles and related compounds. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasher R. S. Uptake of GABA by neuronal and nonneuronal cells in dispersed cell cultures of postnatal rat cerebellum. J Neurobiol. 1975 Nov;6(6):597–608. doi: 10.1002/neu.480060606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Does uptake limit the actions of GABA agonists in vivo? Experiments with muscimol, isoguvacine and THIP in cat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1525–1528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Johnston G. A., Curtis D. R., Brand S. J. Effects of the Areca nut constituents arecaidine and guvacine on the action of GABA in the cat central nervous system. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 18;136(3):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Bowery N. G. Cis-3-aminocyclohexanecarboxylic acid: a substrate for the neuronal GABA transport system. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 9;138(1):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90793-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Bayless J. D., Ban M. Potency of inhibitors for gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake by mouse brain subcellular particles at 0 degrees. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):558–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Federico R., Coletti A., Levi G. Release and exchange studies relating to the synaptosomal uptake of GABA. J Neurochem. 1975 Jun;24(6):1243–1250. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon F., Kelly J. S. Selective uptake of (3H)beta-alanine by glia: association with glial uptake system for GABA. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 21;86(2):243–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90700-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Martin D. L. The effects of L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid on the uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid by a synaptosomal fraction from rat brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. P. Studies on the GABA pathway. I. The inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid-alpha-ketoglutaric acid transaminase in vitro and in vivo by U-7524 (amino-oxyacetic acid). Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Feb;5:323–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitsch-Dick F., Jessell T. M., Kelly J. S. The selective neuronal uptake and release of [3H]DL-2,4-diaminobutyric acid by rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1978 Apr;30(4):799–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Brown D. A., Kelly J. S., Schon F. Autoradiographic localization of sites of (3H)gamma-aminobutyric acid accumulation in peripheral autonomic ganglia. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 7;63:479–486. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]