Abstract
1 The activity pattern of analogues of the enkephalins was determined in four parallel assays, the inhibition of the electrically evoked contraction of the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens at 36°C and the inhibition of [3H]-naltrexone and [3H]-leucine-enkephalin binding at 0 to 4°C in homogenates of guinea-pig brain.
2 The activity pattern was best characterized by the ratio of the potency in the guinea-pig ileum to that in the mouse vas deferens (G.p.i./M.v.d.) and the ratio of the potency in inhibiting [3H]-naltrexone binding to that in inhibiting [3H]-leucine-enkephalin binding (Nal/Leu).
3 The enkephalins had low G.p.i./M.v.d. (0.02 to 0.09) and low Nal/Leu (0.05 to 0.18) ratios whereas the corresponding values for morphine were 7.0 and 7.5.
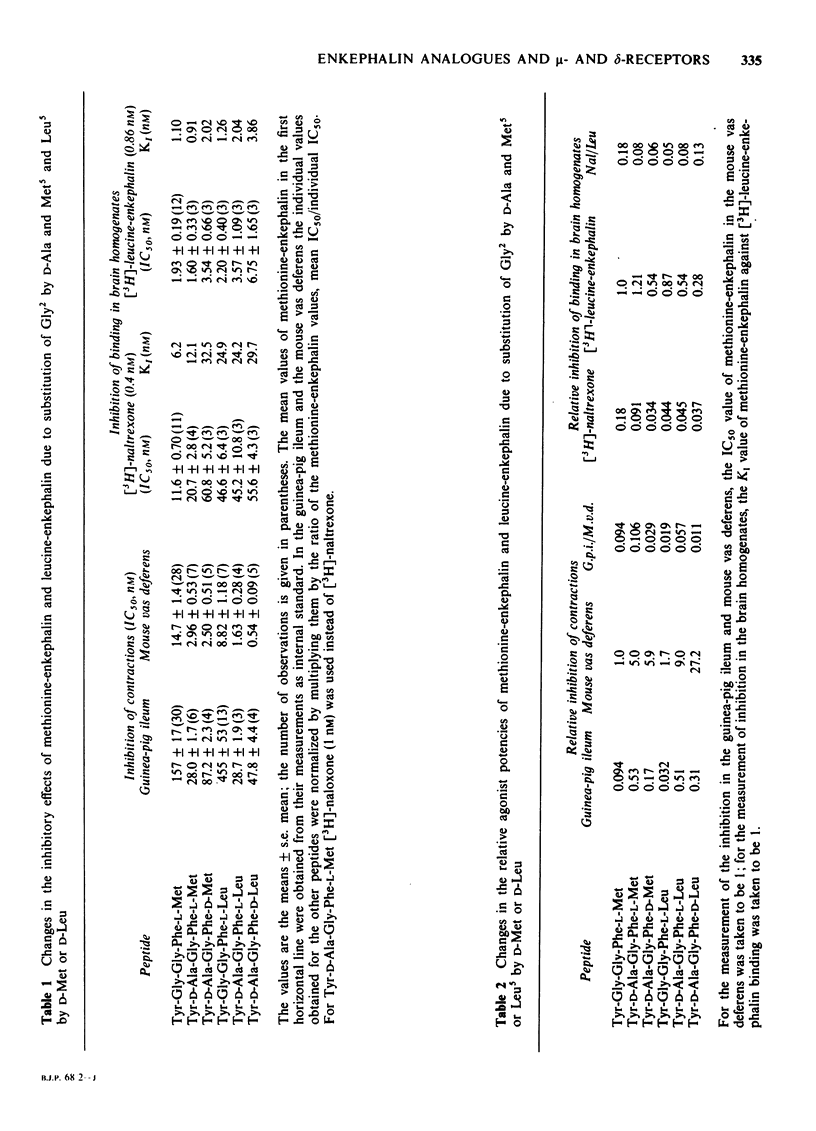
4 Analogues obtained by substituting D-Ala for Gly2 and D-Met or D-Leu for L-Met5 or L-Leu5 showed only minor changes in G.p.i./M.v.d. (0.01 to 0.11) and in Nal/Leu (0.06 to 0.13) ratios.
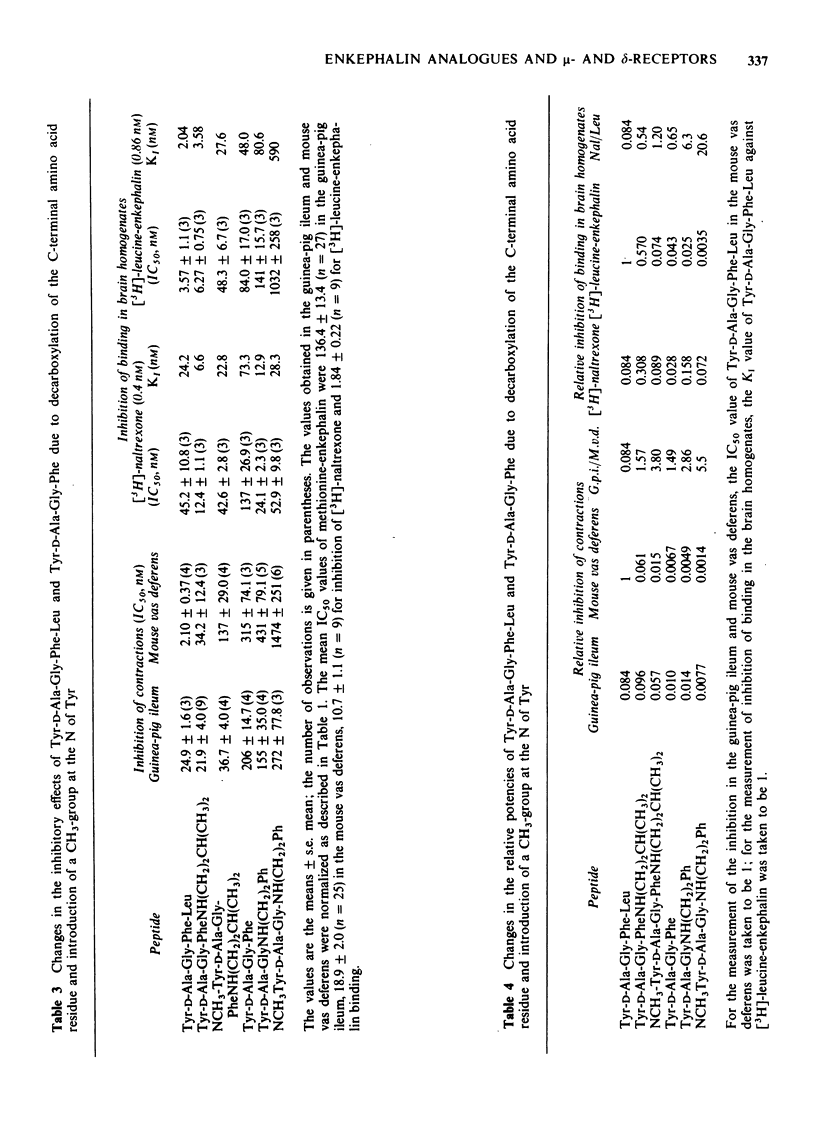
5 Analogues in which resistance to enzymatic degradation was brought about by amidation of the C-terminal carboxylic group or methylation of the amino group of tyrosine or both modifications, had G.p.i./M.v.d. ratios of 1.2 to 5.5 and Nal/Leu ratios of 0.5 to 21. High values (2.1 and 3.4) were found for the potent antinociceptive analogue of Sandoz, Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-NCH3Phe-Met(O)-ol.
6 In the mouse vas deferens, some of the analogues with high G.p.i./M.v.d. and Nal/Leu ratios were tested for antagonism by naloxone and found to require less than the high concentration needed for the natural enkephalins. C57/BL mice, which have a lowered sensitivity to morphine but a normal response to peptides with low G.p.i./M.v.d. and Nal/Leu ratios, had a lowered sensitivity to analogues with high ratios.
7 In the alkaloid-like series of narcotic analgesic drugs, ketobemidone, levorphanol, methadone, etorphine and the antagonist Mr 2266 had lower Nal/Leu ratios (1.0 to 2.8) than morphine, normorphine, naloxone and naltrexone (8 to 12).
8 It would appear that compounds with low G.p.i./M.v.d. and Nal/Leu ratios interact mainly with δ-receptors in the brain and peripheral nervous system while compounds with high ratios interact mainly with μ-receptors. For antinociceptive action μ-receptors may be more important than δ-receptors.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter M. G., Goff D., Miller A. A., Saunders I. A. Effect of a potent synthetic opioid pentapeptide in some anti-nociceptive and behavioural tests in mice and rats [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):455P–456P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambrook J. M., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Mode of deactivation of the enkephalins by rat and human plasma and rat brain homogenates. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):782–783. doi: 10.1038/262782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M., Waterfield A. A. Assessment in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens of benzomorphans which have strong antinociceptive activity but do not substitute for morphine in the dependent monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Loh H. H. 3H-Leu5-enkephalin specific binding to synaptic membrane-comparison with 3H-dihydromorphine and 3H-naloxone. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;21(3):409–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Properties of opiate-receptor binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer D., Buescher H. H., Hill R. C., Pless J., Bauer W., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Huguenin R. A synthetic enkephalin analogue with prolonged parenteral and oral analgesic activity. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):547–549. doi: 10.1038/268547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rónai A. Z., Berzétei I., Bajusz S. Differentiation between opioid peptides by naltrexone. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 15;45(4):393–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. The opiate receptor binding interactions of 3H-methionine enkephalin, an opioid peptide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 1;47(3):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely J. I., Rónai A. Z., Dunai-Kovács Z., Miglécz E., Berzétri I., Bajusz S., Gráf L. (D-met2, pro5)-enkephalinamide: a potent morphine-like analgesic. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 1;43(3):293–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



