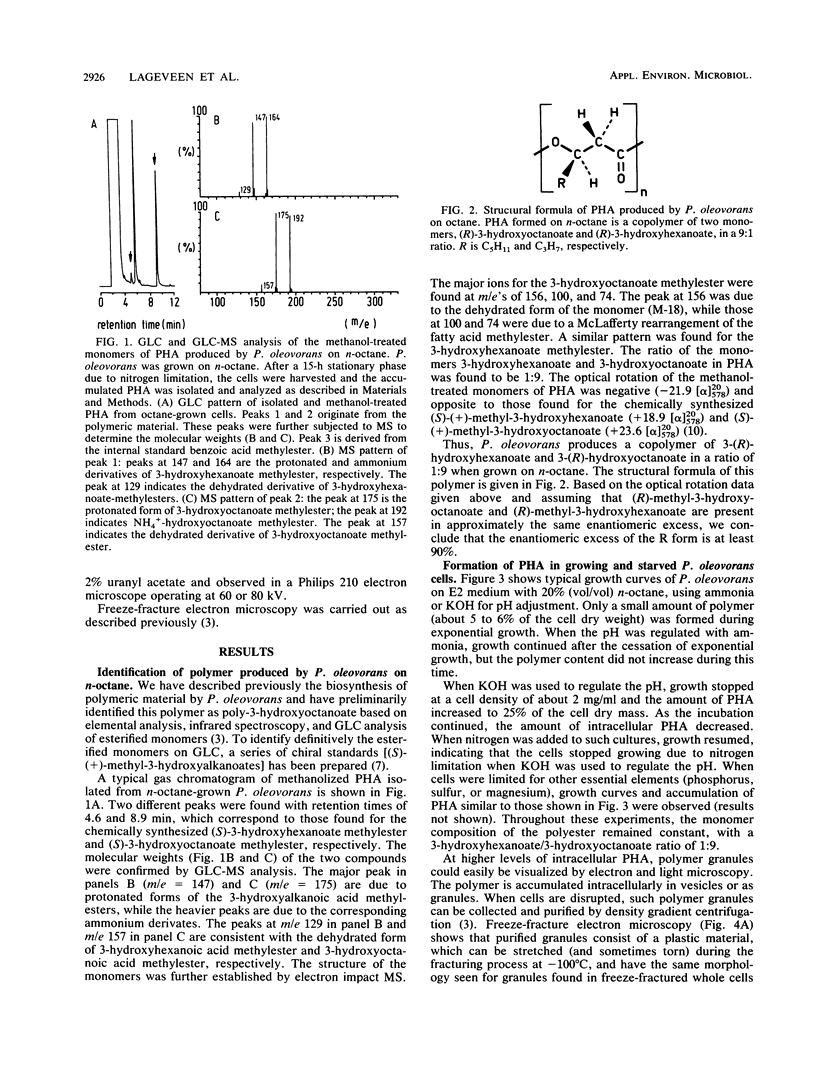
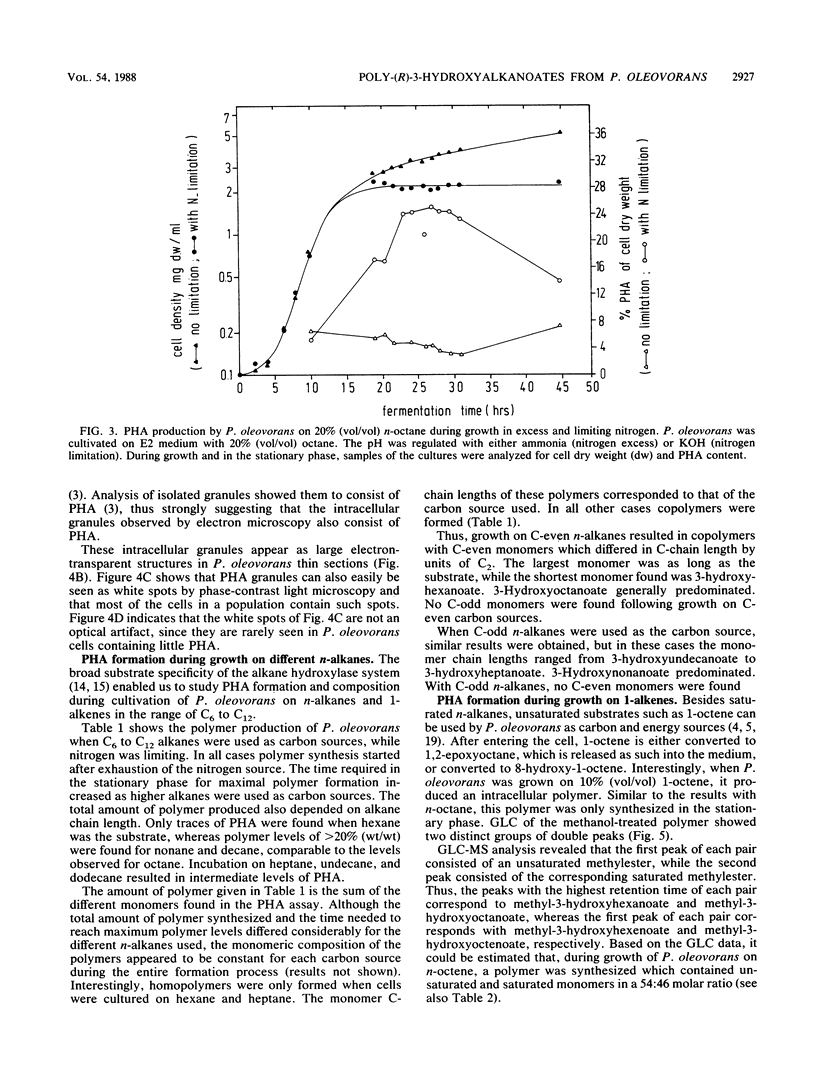
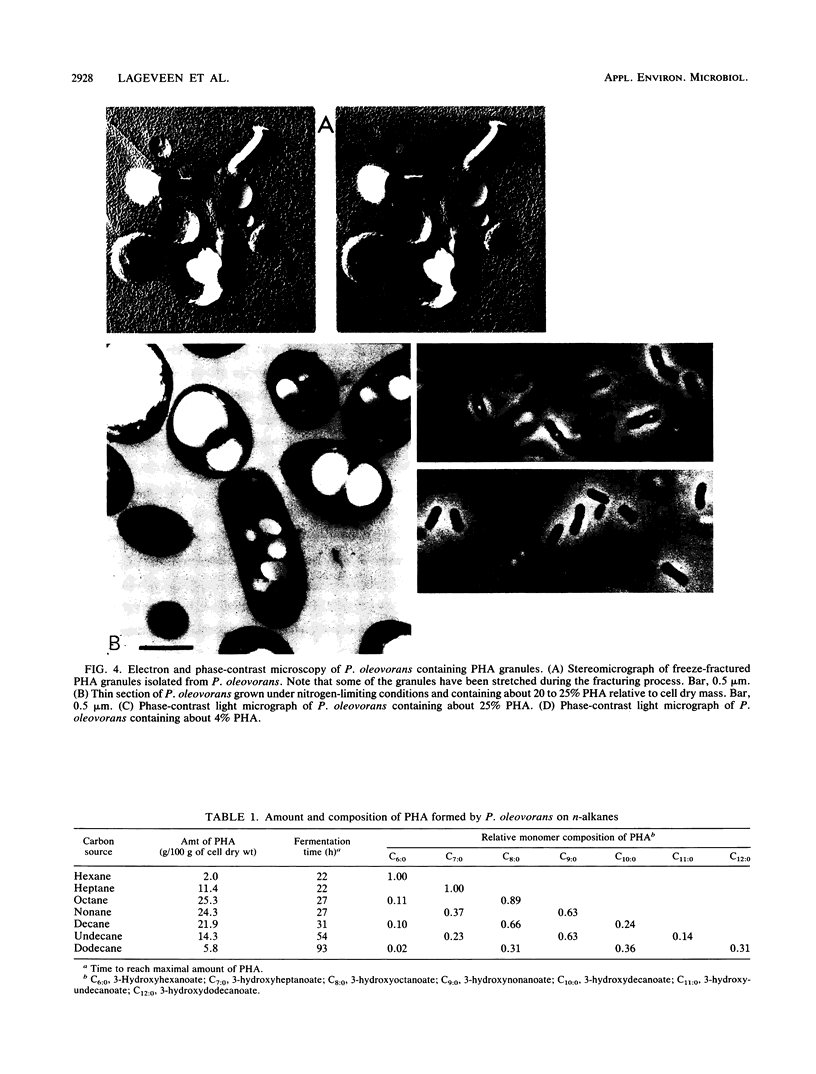
Abstract
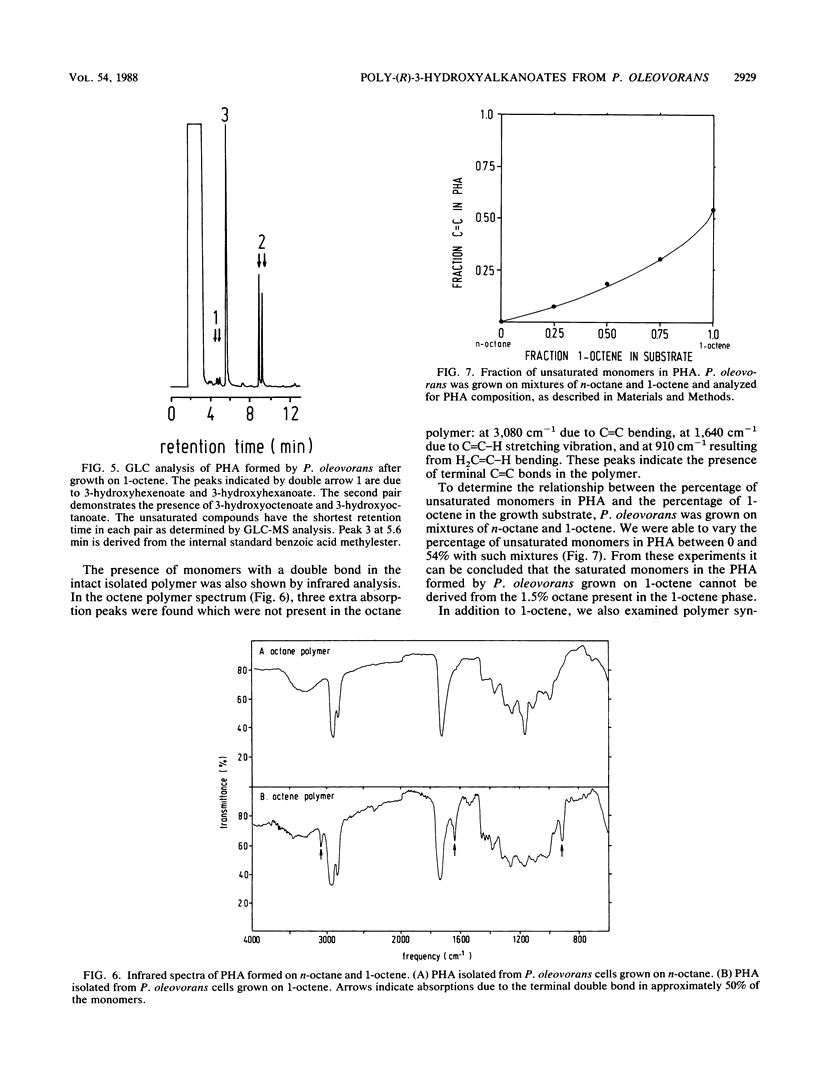
Pseudomonas oleovorans grows on C6 to C12n-alkanes and 1-alkenes. These substrates are oxidized to the corresponding fatty acids, which are oxidized further via the β-oxidation pathway, yielding shorter fatty acids which have lost one or more C2 units. P. oleovorans normally utilizes β-oxidation pathway intermediates for growth, but in this paper we show that the intermediate 3-hydroxy fatty acids can also be polymerized to intracellular poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) when the medium contains limiting amounts of essential elements, such as nitrogen. The monomer composition of these polyesters is a reflection of the substrates used for growth of P. oleovorans. The largest monomer found in PHAs always contained as many C atoms as did the n-alkane used as a substrate. Monomers which were shorter by one or more C2 units were also observed. Thus, for C-even substrates, only C-even monomers were found, the smallest being (R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate. For C-odd substrates, only C-odd monomers were found, with (R)-3-hydroxyheptanoate as the smallest monomer. 1-Alkenes were also incorporated into PHAs, albeit less efficiently and with lower yields than n-alkanes. These PHAs contained both saturated and unsaturated monomers, apparently because the 1-alkene substrates could be oxidized to carboxylic acids at either the saturated or the unsaturated ends. Up to 55% of the PHA monomers contained terminal double bonds when P. oleovorans was grown on 1-alkenes. The degree of unsaturation of PHAs could be modulated by varying the ratio of alkenes to alkanes in the growth medium. Since 1-alkenes were also shortened before being polymerized, as was the case for n-alkanes, copolymers which varied with respect to both monomer chain length and the percentage of terminal double bonds were formed during nitrogen-limited growth of P. oleovorans on 1-alkenes. Such polymers are expected to be useful for future chemical modifications.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott B. J., Hou C. T. Oxidation of 1-alkenes to 1,2-epoxyalkanes by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.86-91.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay R. H., White D. C. Polymeric Beta-Hydroxyalkanoates from Environmental Samples and Bacillus megaterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.71-78.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grund A., Shapiro J., Fennewald M., Bacha P., Leahy J., Markbreiter K., Nieder M., Toepfer M. Regulation of alkane oxidation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.546-556.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May S. W., Abbott B. J. Enzymatic epoxidation. II. Comparison between the epoxidation and hydroxylation reactions catalyzed by the -hydroxylation system of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1725–1730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E. J., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. IV. Purification and properties of the omega-hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3882–3889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn W. D. A molecular view of fatty acid catabolism in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Jun;50(2):179–192. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.2.179-192.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D. Octene epoxidation by a cold-stable alkane-oxidizing isolate of Pseudomonas oleovorans. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):574–577. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.574-577.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. C., Finnerty W. R. Characterization of intracytoplasmic hydrocarbon inclusions from the hydrocarbon-oxidizing Acinetobacter species HO1-N. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.481-489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M. Inclusion bodies of prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):167–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DER LINDEN A. C. EPOXIDATION OF ALPHA-OLEFINS BY HEPTANE-GROWN PSEUDOMONAS CELLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:157–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90484-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witholt B. Method for isolating mutants overproducing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and its precursors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):350–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.350-364.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
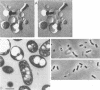
- de Smet M. J., Eggink G., Witholt B., Kingma J., Wynberg H. Characterization of intracellular inclusions formed by Pseudomonas oleovorans during growth on octane. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):870–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.870-878.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smet M. J., Wynberg H., Witholt B. Synthesis of 1,2-Epoxyoctane by Pseudomonas oleovorans During Growth in a Two-Phase System Containing High Concentrations of 1-Octene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):811–816. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.811-816.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]