Abstract
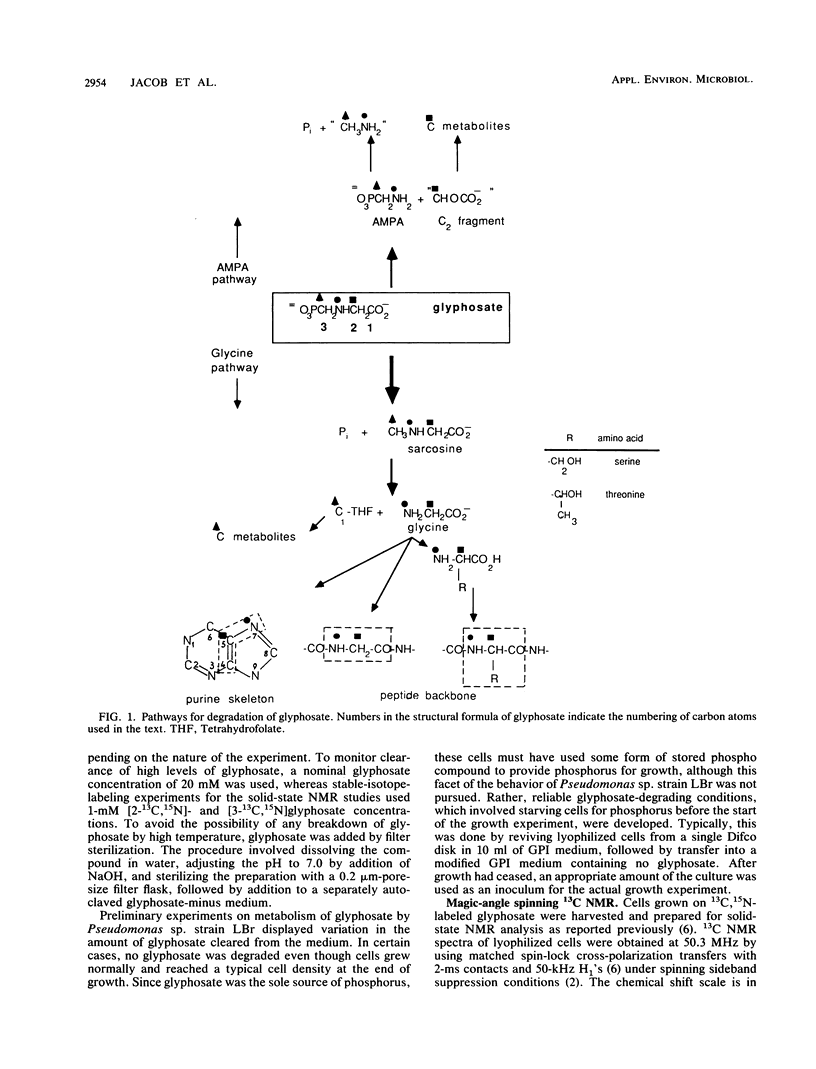
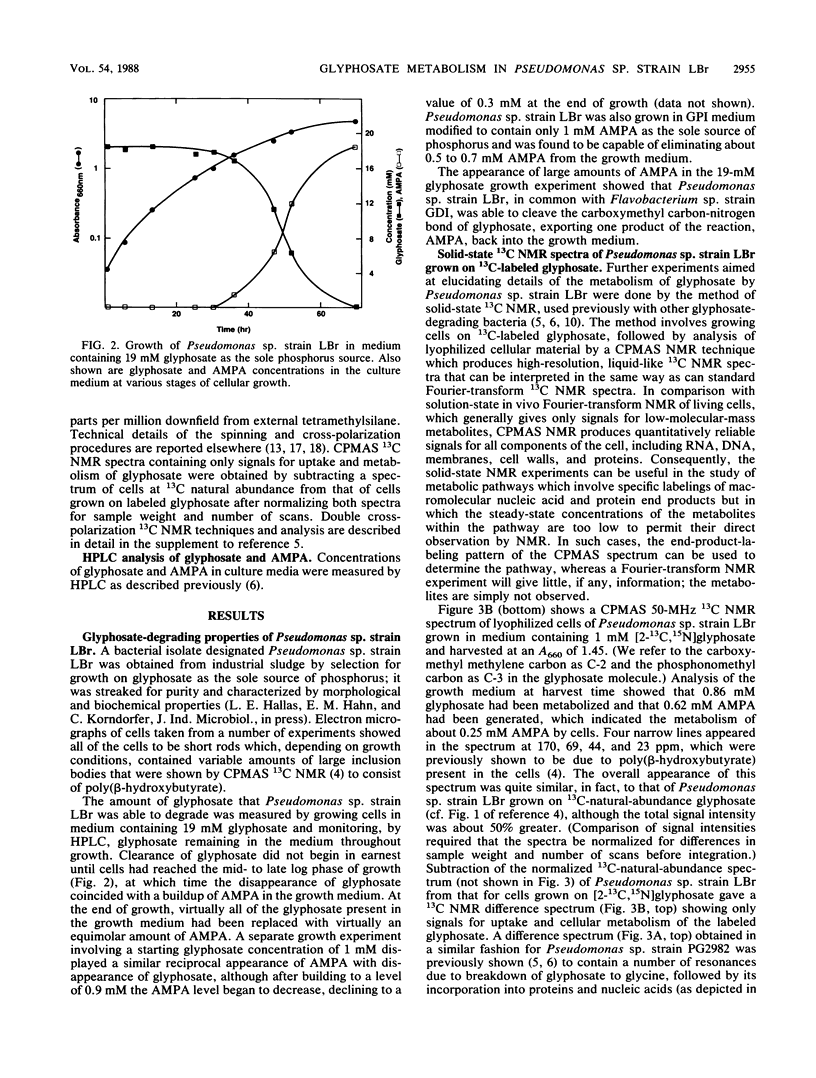
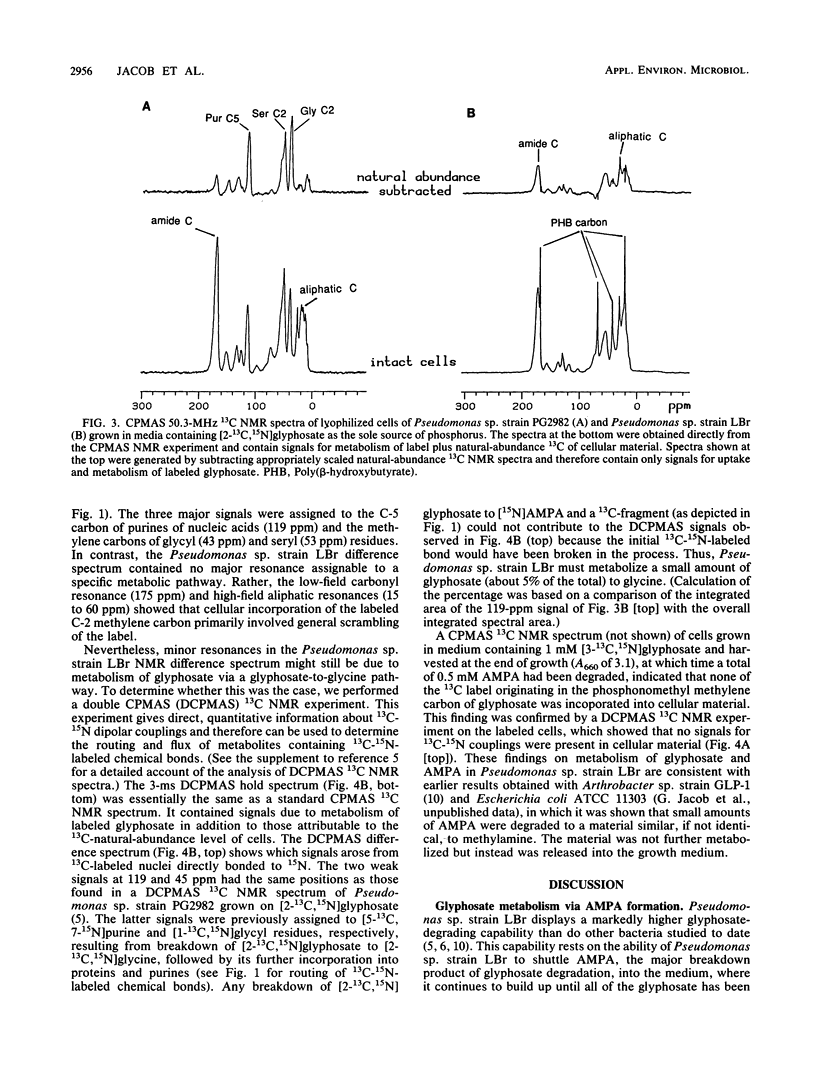
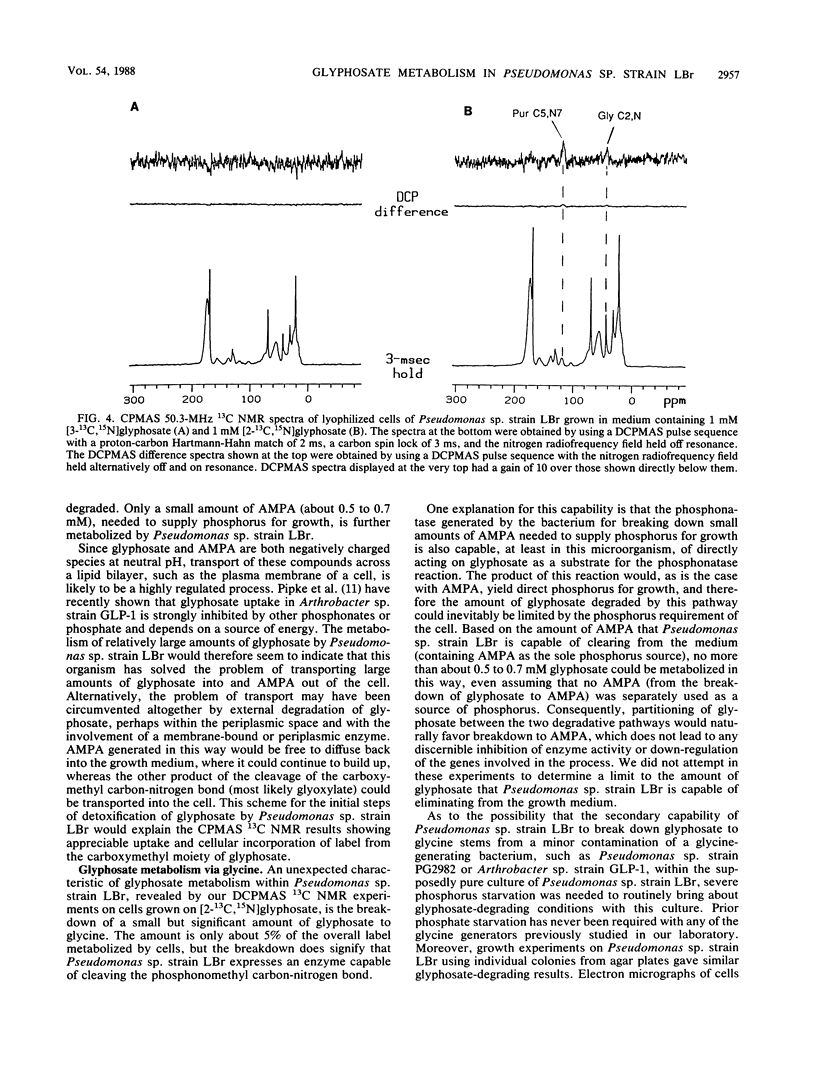
Metabolism of glyphosate (N-phosphonomethylglycine) by Pseudomonas sp. strain LBr, a bacterium isolated from a glyphosate process waste stream, was examined by a combination of solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance experiments and analysis of the phosphonate composition of the growth medium. Pseudomonas sp. strain LBr was capable of eliminating 20 mM glyphosate from the growth medium, an amount approximately 20-fold greater than that reported for any other microorganism to date. The bacterium degraded high levels of glyphosate, primarily by converting it to aminomethylphosphonate, followed by release into the growth medium. Only a small amount of aminomethylphosphonate (about 0.5 to 0.7 mM), which is needed to supply phosphorus for growth, could be metabolized by the microorganism. Solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of strain LBr grown on 1 mM [2-13C,15N]glyphosate showed that about 5% of the glyphosate was degraded by a separate pathway involving breakdown of glyphosate to glycine, a pathway first observed in Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. Thus, Pseudomonas sp. strain LBr appears to possess two distinct routes for glyphosate detoxification.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazor T. M., Hallas L. E. Glyphosate-degrading microorganisms from industrial activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):432–434. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.432-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., FOSTER J. W. Experiments with some microorganisms which utilize ethane and hydrogen. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):592–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.592-603.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob G. S., Garbow J. R., Schaefer J. Direct measurement of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) in a pseudomonad by solid-state 13C NMR. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16785–16787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob G. S., Garbow J. R., Schaefer J., Kishore G. M. Solid-state NMR studies of regulation of N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine and glycine metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1552–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob G. S., Schaefer J., Stejskal E. O., McKay R. A. Solid-state NMR determination of glyphosate metabolism in a Pseudomonas sp. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5899–5905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore G. M., Jacob G. S. Degradation of glyphosate by Pseudomonas sp. PG2982 via a sarcosine intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12164–12168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Which Utilizes the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):316–320. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.316-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipke R., Amrhein N., Jacob G. S., Schaefer J., Kishore G. M. Metabolism of glyphosate in an Arthrobacter sp. GLP-1. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipke R., Schulz A., Amrhein N. Uptake of Glyphosate by an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):974–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.974-978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueppel M. L., Brightwell B. B., Schaefer J., Marvel J. T. Metabolism and degradation of glyphosphate in soil and water. J Agric Food Chem. 1977 May-Jun;25(3):517–528. doi: 10.1021/jf60211a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer J., Skokut T. A., Stejskal E. O., McKay R. A., Varner J. E. Estimation of protein turnover in soybean leaves using magic angle double cross-polarization nitrogen 15 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11574–11579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Braymer H. D. Glyphosate catabolism by Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.702-707.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücken H. C., Amrhein N. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1207–1212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90547-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


