Abstract
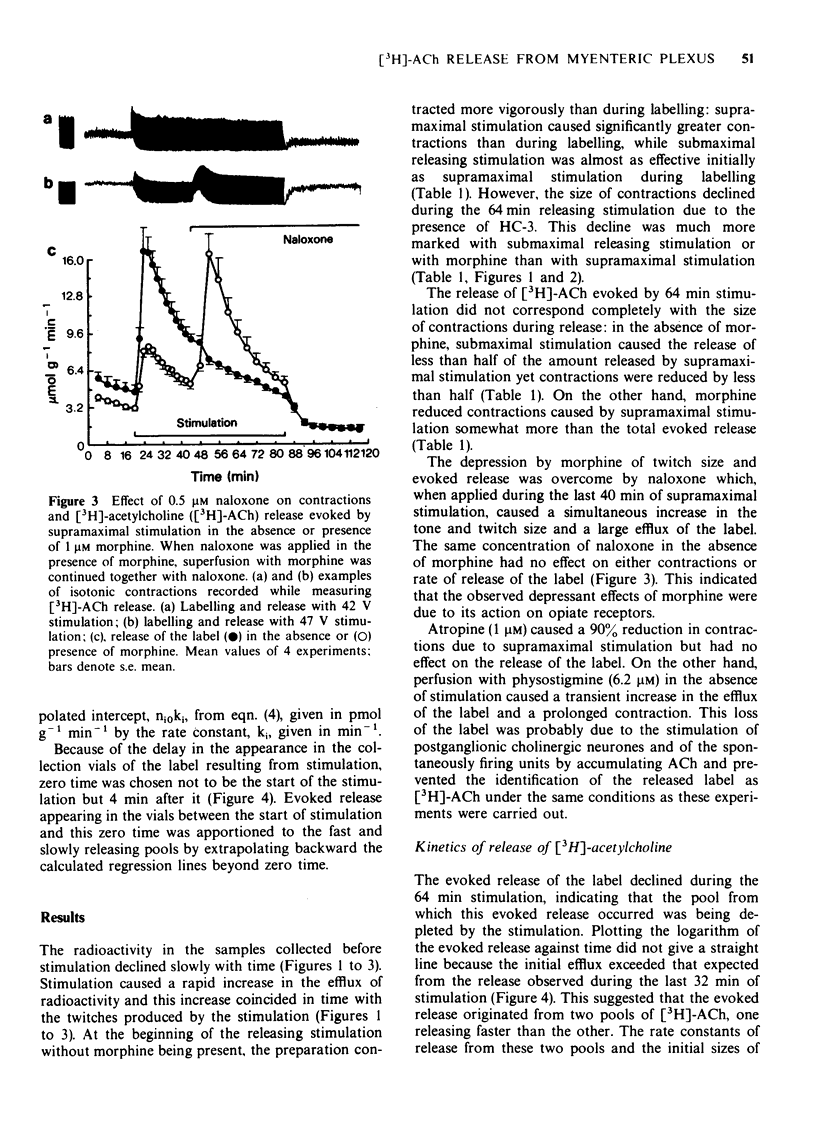
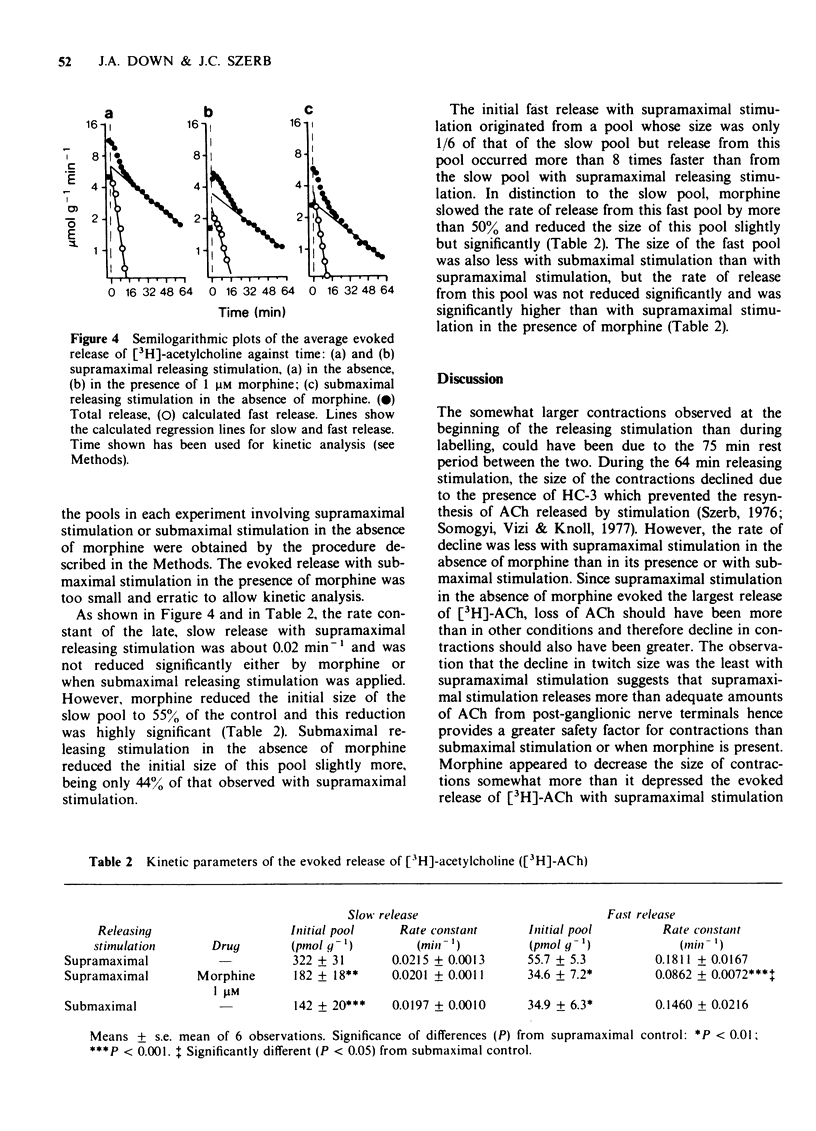
1 Longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus preparations from the guinea-pig ileum were superfused at a constant rate while isotonic contractions were monitored. 2 The preparations were superfused with [3H]-choline while stimulated supramaximally at 0.1 Hz followed by washout in the presence of hemicholinium-3. The evoked release of the label due to a second 0.1 Hz stimulation in the absence of an anticholinesterase was measured. 3 Evoked efflux of the label was initially fast followed by a slower phase. 4 Morphine reduced the size of the pool and the rate of the initial fast efflux and the size of the pool but not the rate of the slow efflux evoked by supramaximal stimulation. 5 Submaximal stimulation reduced only the size of the pools from which the fast and slow efflux originated. 6 Naloxone reversed the depression of contractions and evoked release produced by morphine. 7 Results suggest that 0.1 Hz stimulation releases [3H]-acetylcholine simultaneous from two pools. The fast release may originate from spontaneously firing units whose rate of discharge is depressed by morphine, while the slow release originates from neurones which do not fire spontaneously and whose threshold to field stimulation is increased by morphine.
Full text
PDF


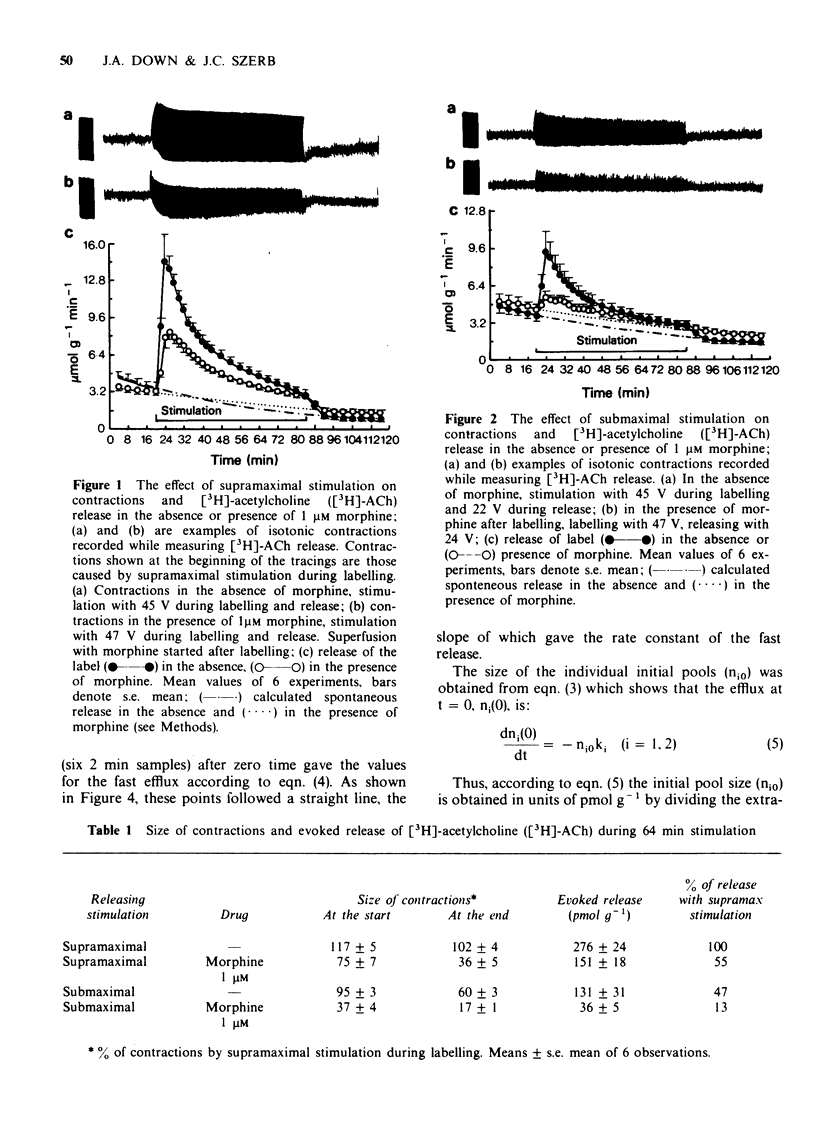



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox B. M., Weinstock M. The effect of analgesic drugs on the release of acetylcholine from electrically stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B., Lomas D. M. The effects of eserine and neostigmine on the guinea-pig ileum and on ileal longitudinal muscle strips. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;24(7):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb09054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Goldstein A. Effect of synaptic transmission blockade on morphine action in the guinea-pig myenteric plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenpreis S., Greenberg J., Belman S. Prostaglandins reverse inhibition of electrically-induced contractions of guinea pig ileum by morphine, indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 31;245(148):280–282. doi: 10.1038/newbio245280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenpreis S., Sato T., Takayanagi I., Comaty J. E., Takagi K. Mechanism of morphine block of electrical activity in ganglia of Auerbach's plexus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;40(2):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Gilbert J. C. Effects of physostigmine and electrical stimulation on the acetylcholine content of the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;39(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbinger H. Modulation by oxotremorine and atropine of acetylcholine release evoked by electrical stimulation of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;300(2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00505045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J., Vizi E. S. Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from parasympathetic nerve terminals. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):263–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Waterfield A. A. In vitro models in the study of structure-activity relationships of narcotic analgesics. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:29–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS G. P. The inhibition by morphine of the action of smooth muscle stimulants on the guinea-pig intestine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Sep;15:425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tonini M. The mechanism of action of narcotic analgesics in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. Enkephalin inhibits firing of myenteric neurones. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):460–461. doi: 10.1038/264460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. CHOLINERGIC TRANSMISSION AND ACETYLCHOLINE OUTPUT. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Dec;41:2637–2653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S., Zar M. A. The mechanism of acetylcholine release from parasympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):819–848. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Takayanagi I., Takagi K. Pharmacological properties of electrical activities obtained from neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;23(5):665–671. doi: 10.1254/jjp.23.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: antagonism by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. Muscarinic feedback inhibition of acetylcholine release from the myenteric plexus in the quinea pig ileum and its status after chronic exposure to morphine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;55(4):909–916. doi: 10.1139/y77-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi G. T., Vizi E. S., Knoll J. Effect of hemicholinium-3 on the release and net synthesis of acetylcholine in Auerbach's plexus of guinea pig ileum. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):791–796. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C. Endogenous acetylcholine release and labelled acetylcholine formation from [3H]choline in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;53(4):566–574. doi: 10.1139/y75-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szerb J. C. Storage and release of labelled acetylcholine in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1976 Feb;54(1):12–22. doi: 10.1139/y76-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Release of 3H-acetylcholine from isolated guinea pig ileum. A radiochemical method for studying the release on the cholinergic neurotransmitter in the intestine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Nov;101(3):302–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb06012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


