Abstract
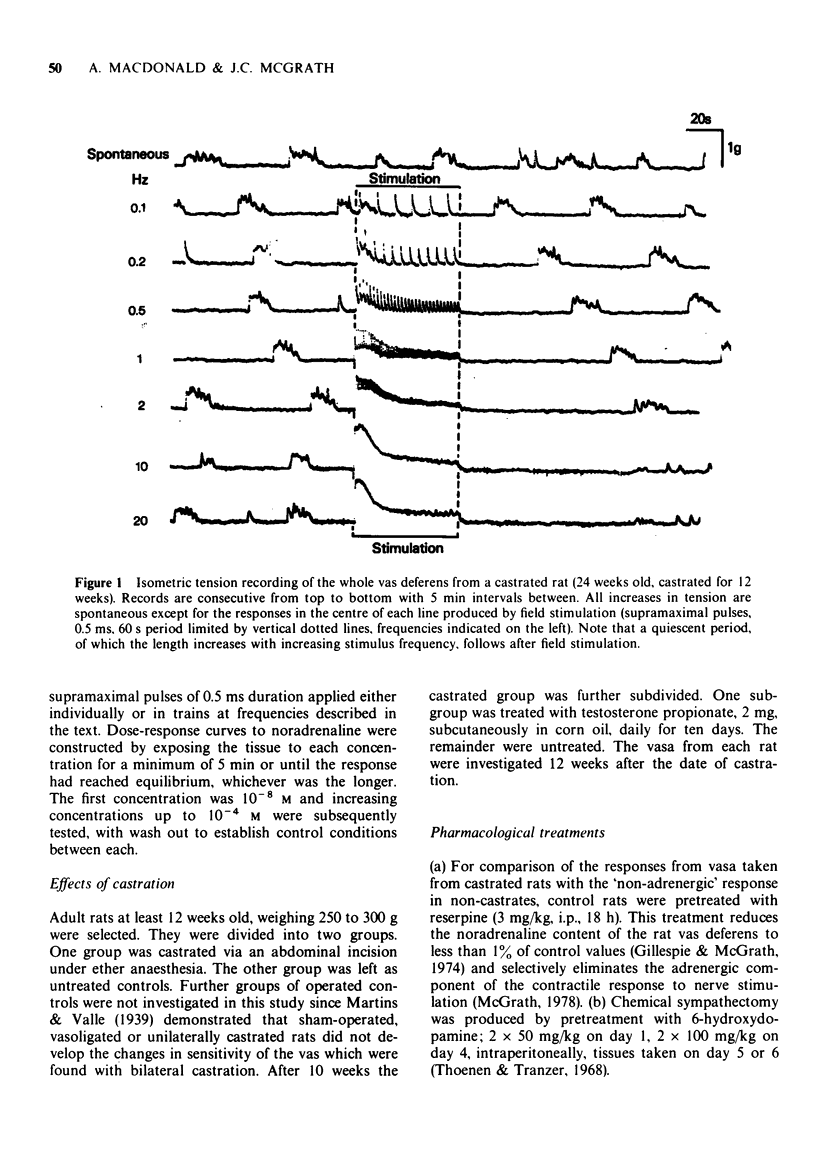
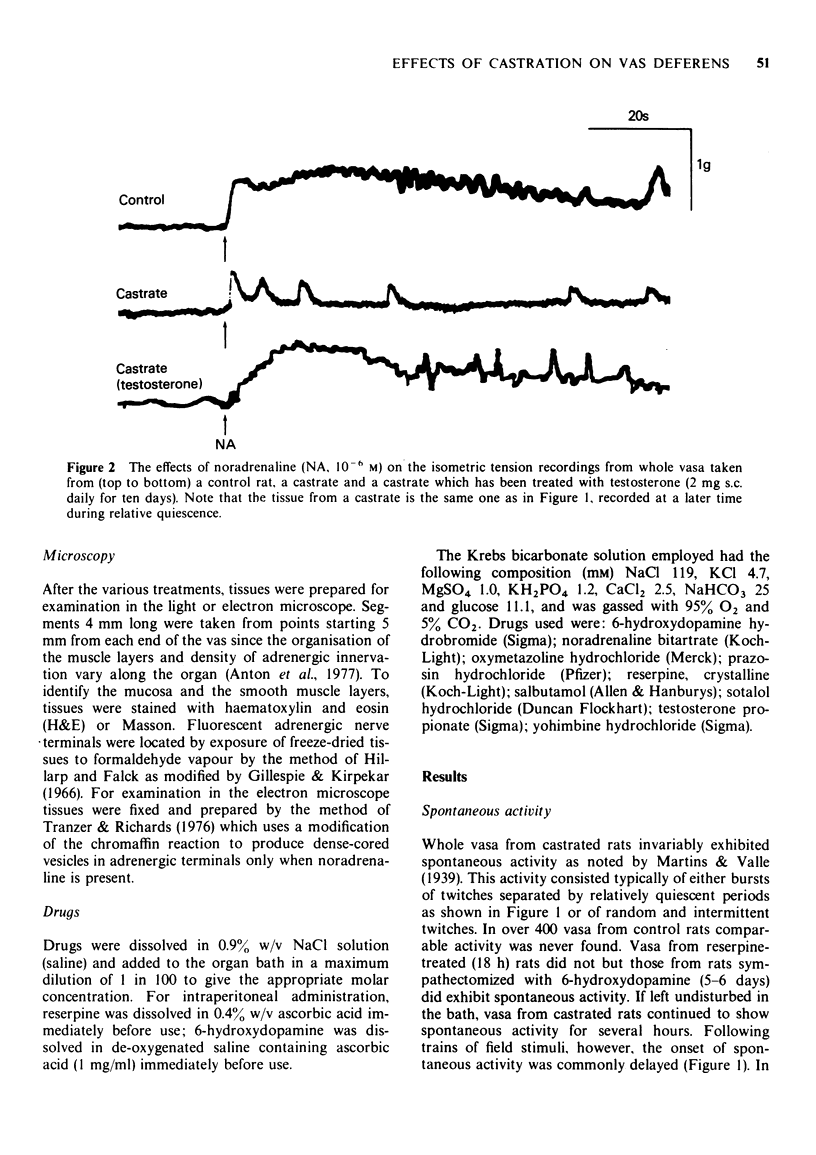
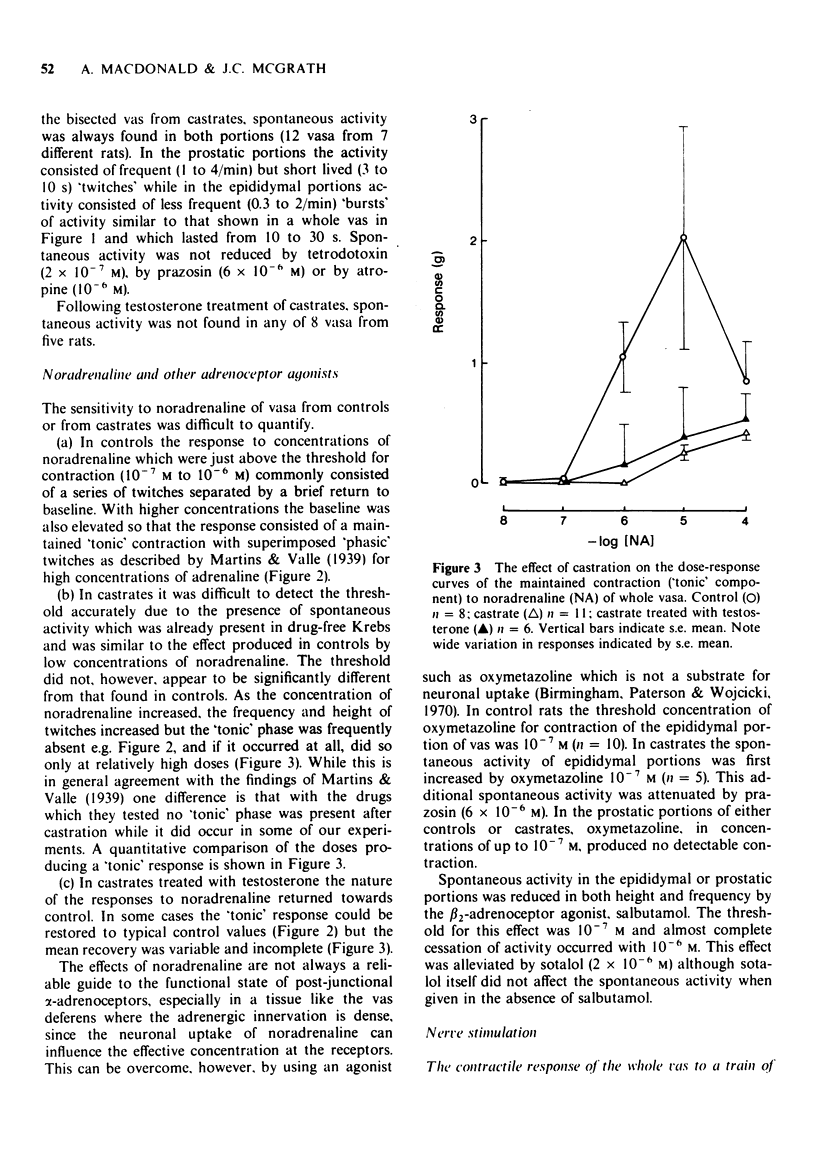
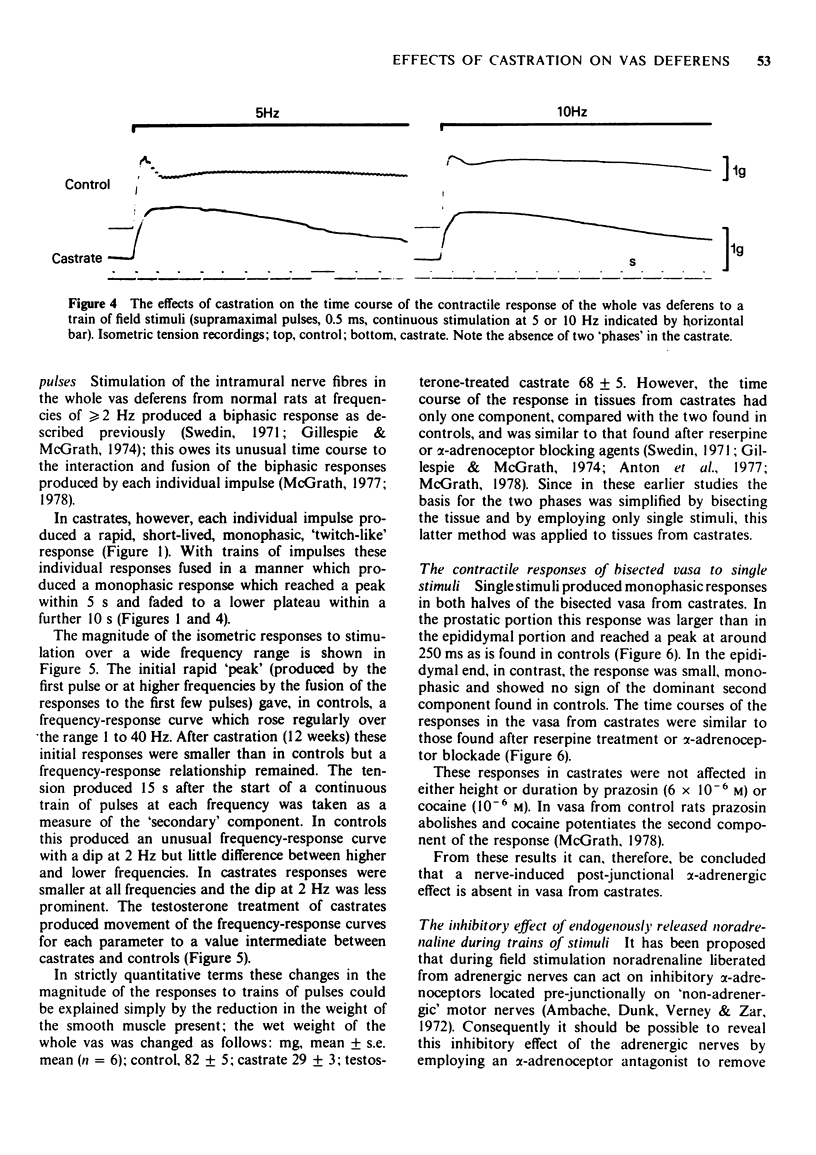
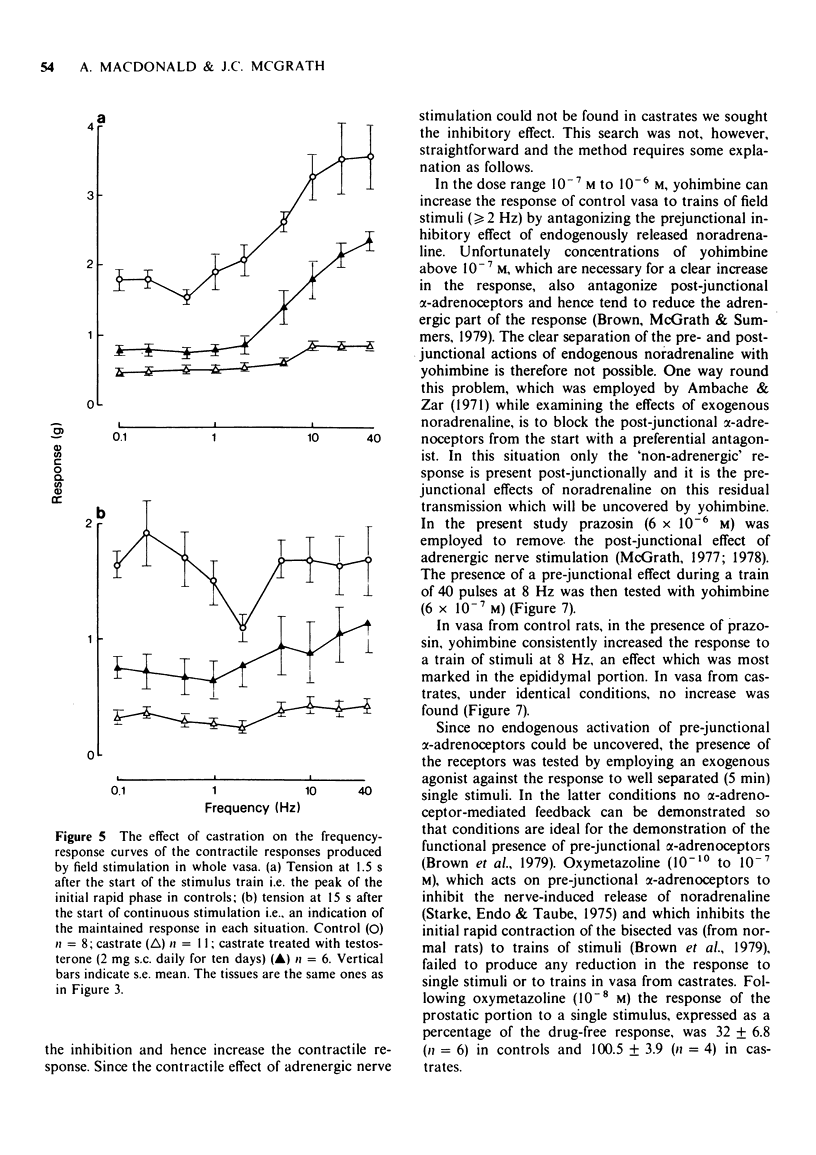
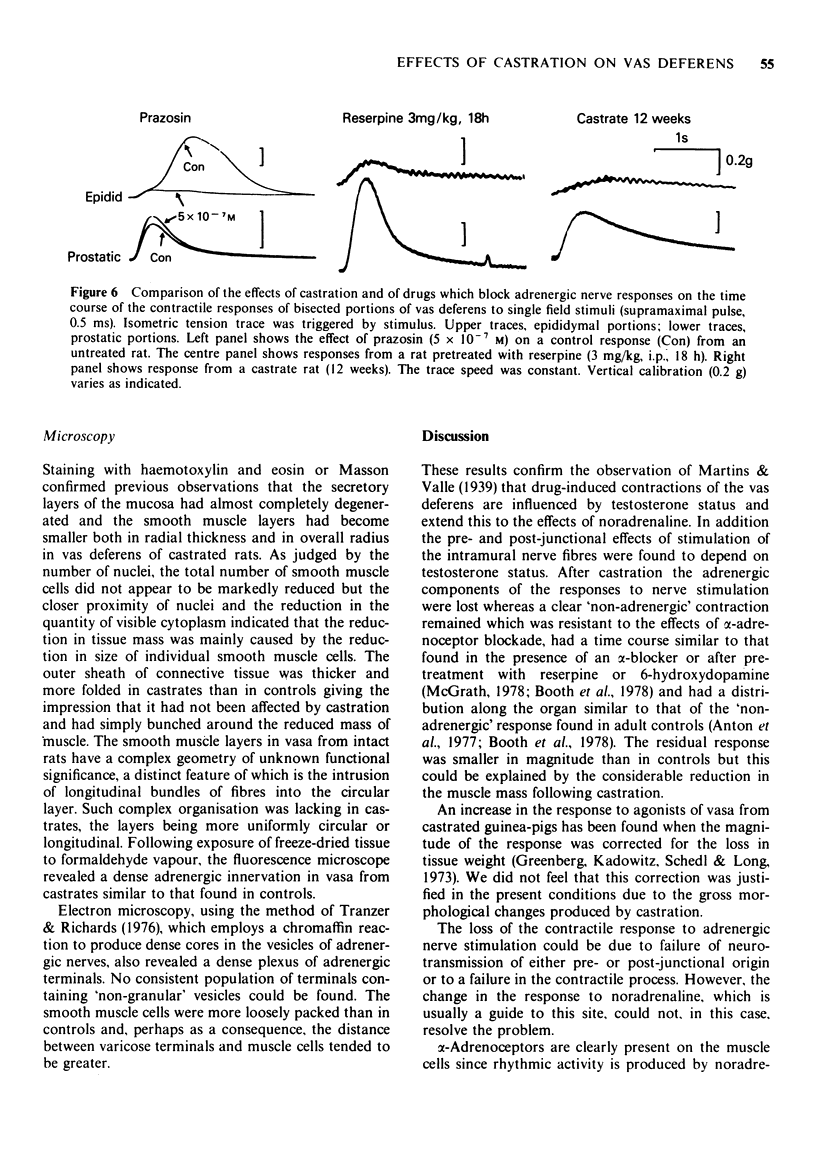
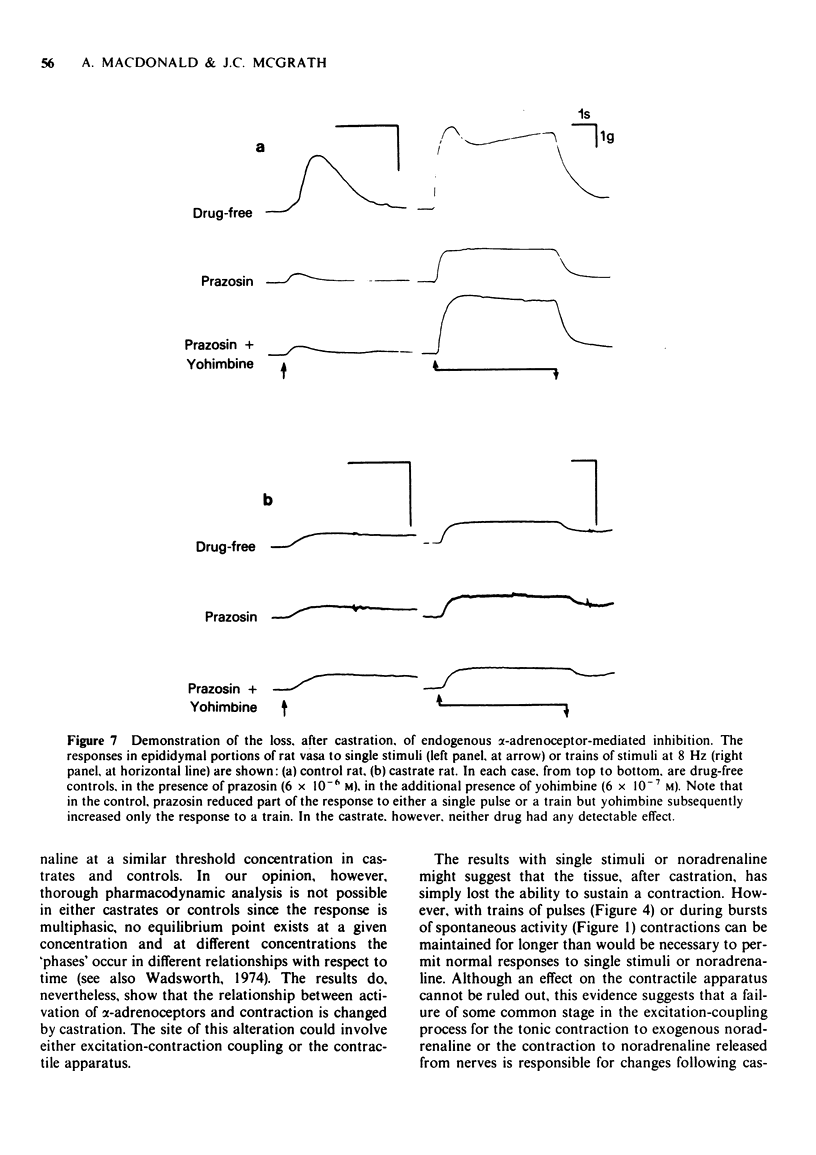
1 Responses to adrenoceptor agonist drugs and to field stimulation were examined in vasa deferentia from adult castrated or intact rats. Isometric tension was recorded in vitro from whole or transversely bisected vasa. 2 After castration vasa exhibited spontaneous contraction, noradrenaline no longer produced a 'tonic' contraction but increased the 'phasic' spontaneous activity and salbutamol inhibited spontaneous activity by a beta-adrenoceptor-mediated mechanism. 3 After castration the 'adrenergic' components of the contractile responses to field stimulation were lost whereas 'non-adrenergic' responses remained, pre-junctional inhibition of field stimulation-induced contractions by either endogenous or exogenous activation was lost but adrenergic terminals could still be demonstrated microscopically. 4 Testosterone treatment partially reversed these effects of castration. 5 The relevance of these results to the nature of neurotransmission and to the genesis of spontaneous contraction in the vas deferens is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Dunk L. P., Verney J., Zar M. A. Inhibition of post-ganglionic motor transmission in vas deferens by indirectly acting sympathomimetic drugs. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton P. G., Duncan M. E., McGrath J. C. An analysis of the anatomical basis for the mechanical response to motor nerve stimulation of the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):23–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham A. T., Paterson G., Wójcicki J. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Aug;39(4):748–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., McGrath J. C., Summers R. J. The effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on responses of transmurally stimulated prostatic and epididymal portions of the isolated vas deferens of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;66(4):553–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb13694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B., Iwayama T., Burnstock G. Long-lasting supersensitivity of the rat vas deferens to norepinephrine after chronic guanethidine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Apr;185(1):60–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly D. K., Bhattacharya B. B. Adrenergic beta receptors in vas deferens. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1970 Jun;185(2):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Kirpekar S. M. The histological localization of noradrenaline in the cat spleen. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):69–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., McGrath J. C. The effect of pithing and of nerve stimulation on the depletion of noradrenaline by reserpine in the rat anococcygeus muscle and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;52(4):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore D. P., McGrath J. C. Effects of castration on the mechanical response to motor nerve stimulation of the rat vas deferens [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;61(3):473P–474P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Kadowitz P. J., Schedl H. P., Long J. P. Effect of age and testosterone on calcium content and reactivity of guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jun;185(3):505–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurkiewicz N. H., Jurkiewicz A., Gomes C. B., Aucelio J. G. Pharmacodynamic analysis of the rat isolated vas deferens after transplantation to intestinal wall. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Oct;203(1):112–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. J., Westfall D. P., Fleming W. W. The correlation between spontaneous contractions and postjunctional supersensitivity of the smooth muscle of the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jan;192(1):136–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Adrenergic and 'non-adrenergic' components in the contractile response of the vas deferens to a single indirect stimulus. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Adrenergic motor responses to single pulse stimulation in the rat vas deferens [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):52P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock D., Muir T. C., MacDonald A., Henderson G. Morphine-induced changes in the sensitivity of the isolated colon and vas deferens of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;20(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-Hydroxydopamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(3):271–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00536990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranzer J. P., Richards J. G. Ultrastructural cytochemistry of biogenic amines in nervous tissue: methodologic improvements. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Nov;24(11):1178–1193. doi: 10.1177/24.11.63507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth R. M. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of noradrenaline on the isolated guinea-pig vas deferens. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1974 Mar-Apr;1(2):135–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1974.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



