Abstract
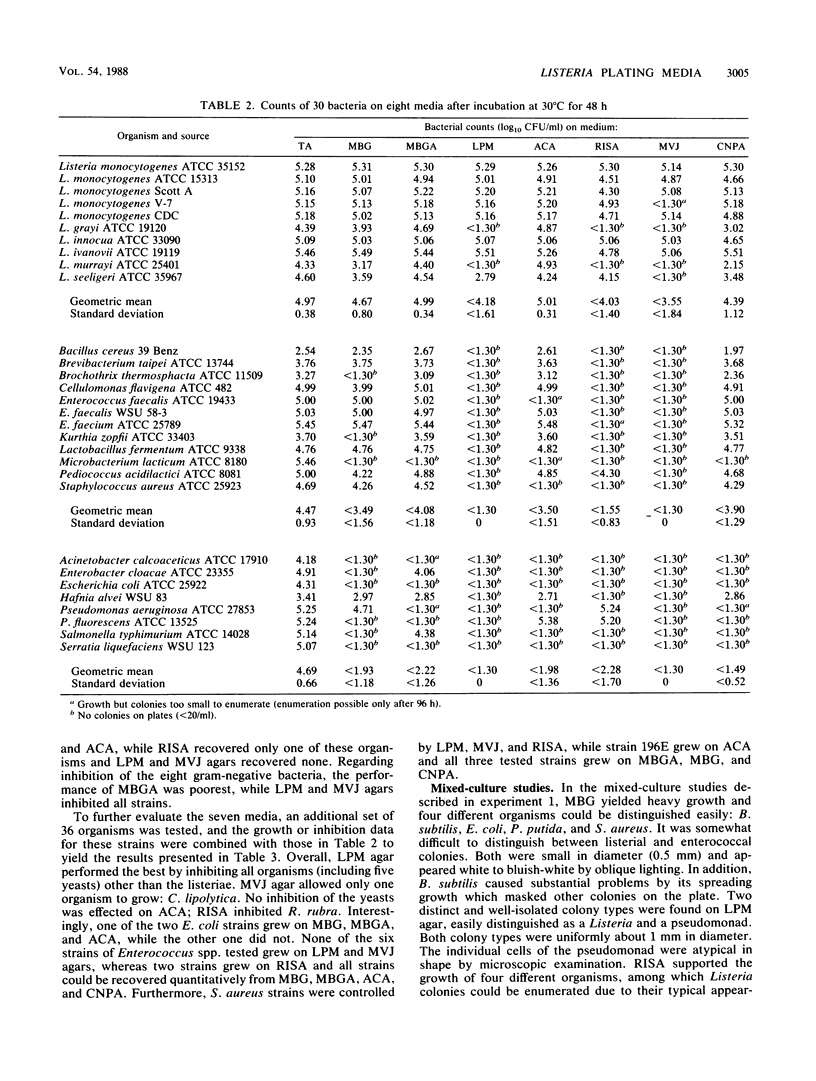
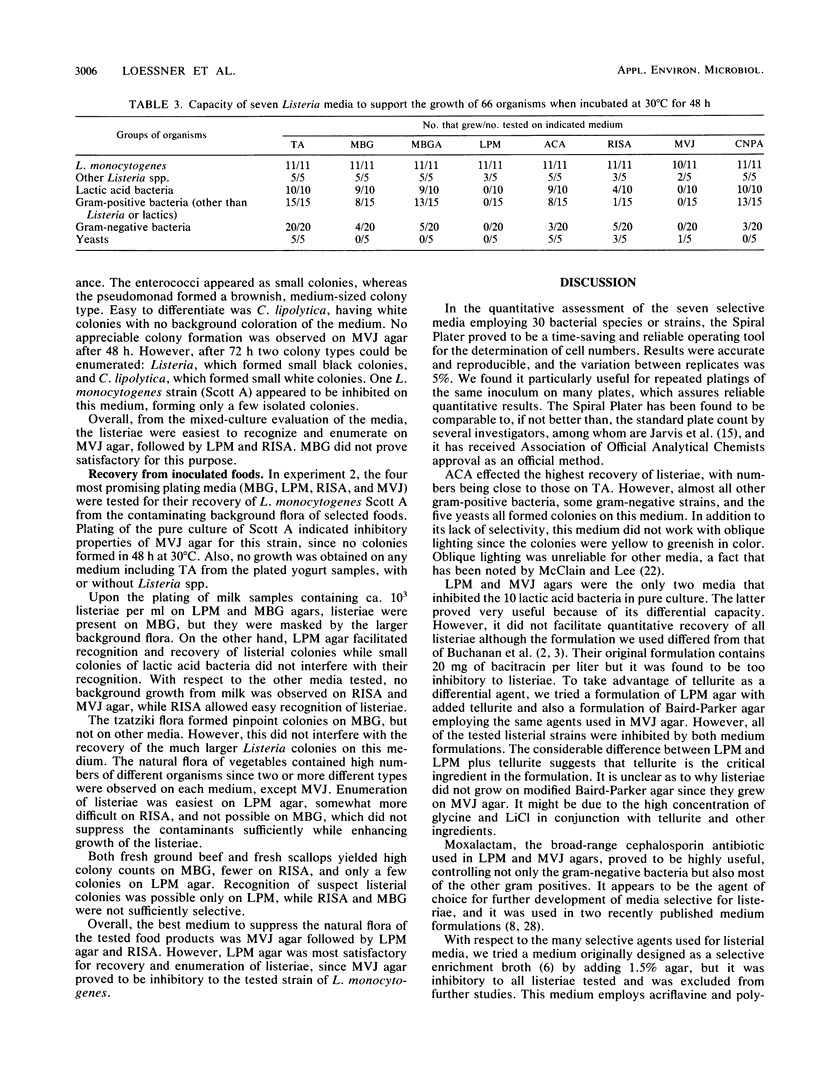
The suitability of seven media for the enumeration of Listeria spp. was evaluated at 30 degrees C for 48 h. The media tested were (i) the original McBride Listeria agar formulation (with glycine); (ii) modified McBride agar containing glycine anhydride; (iii) LiCl-phenylethanol-moxalactam (LPM) agar; (iv) acriflavine-ceftazidime agar; (v) Rodriguez isolation agar (RISA); (vi) modified Vogel-Johnson (MVJ) agar; (vii) cyclohexanedione-nalidixic acid-phenylethanol agar; and tryptose agar as control. A total of 66 organisms were used including 11 Listeria monocytogenes strains and 5 other Listeria spp. For L. monocytogenes strains only, all media performed highly similarly. Of the other Listeria spp., only two grew on MVJ agar and three each grew on LPM and RISA. Only LPM agar inhibited the 50 non-listeriae, including five yeasts, while MVJ agar inhibited all but one yeast. The McBride Listeria agar formulation that contained glycine anhydride was less selective than the original. When pure cultures of 10 bacteria (including one L. monocytogenes strain) were combined and plated on four media, L. monocytogenes colonies were easiest to enumerate on MVJ agar, followed by LPM and RISA. These media ranked in the same order when plated with homogenates of various foods to which was added L. monocytogenes Scott A, but LPM agar was the best overall since Scott A was inhibited by MVJ. Upon microscopic examination of listerial colonies from the plating media, atypical cell morphology was noted with cells being about twofold in size on LPM, MVJ, and acriflavine-ceftazidime agars. Overall, LPM agar was the most suitable of the media tested even though it was inhibitory to Listeria grayi and Listeria murrayi.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannerman E. S., Bille J. A new selective medium for isolating Listeria spp. from heavily contaminated material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):165–167. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.165-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan R. L., Smith J. L., Stahl H. G., Archer D. L. Listeria methods development research at the Eastern Regional Research Center, U.S. Department of Agriculture. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):651–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despierres M. Isolement de Listeria monocytogenes dans un milieu défavorable à Streptococcus faecalis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Oct;121(4):493–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez Rodriguez L., Suárez Fernández G., Fernández Garayzabal J. F., Rodriguez Ferri E. New methodology for the isolation of Listeria microorganisms from heavily contaminated environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1188–1190. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1188-1190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. W. Historical perspectives on methodology to detect Listeria monocytogenes. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):644–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Selective-enrichment procedure for isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from fecal and biologic specimens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1127–1129. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1127-1129.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Sanders G. W., Speirs J. I. Methodology for isolation of Listeria from foods--a Canadian perspective. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):675–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden D. A., Beuchat L. R., Brackett R. E. Direct plating technique for enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes in foods. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden D. A., Beuchat L. R., Brackett R. E. Evaluation of selective direct plating media for their suitability to recover uninjured, heat-injured, and freeze-injured Listeria monocytogenes from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1451-1456.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao D. Y., Beuchat L. R., Brackett R. E. Comparison of media and methods for detecting and enumerating Listeria monocytogenes in refrigerated cabbage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):955–957. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.955-957.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McClain D. Improved Listeria monocytogenes selective agar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1215–1217. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1215-1217.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett J. Isolation and identification of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy products. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):658–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Sumarah R. K., MacDonald M. A. A synthetic based medium for the isolation of Listeria monocytogenes. Clin Invest Med. 1984;7(4):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrothalassitis P. A method for the rapid isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from infected material. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;43(1):47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D., Lee W. H. Development of USDA-FSIS method for isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from raw meat and poultry. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):660–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralovich B., Forray A., Mérö E., Málovics H., Százados I. New selective medium for isolation of L. monocytogenes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(1):88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Hof H., Schrettenbrunner A., Malinverni R., Bille J. Méningite purulente aiguë à Listeria seeligeri chez un adulte immunocompétent. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1986 Feb 22;116(8):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan B., Hayes P. S., Przybyszewski V. A., Plikaytis B. D. Evaluation of enrichment and plating media for isolating Listeria monocytogenes. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):664–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Netten P., van de Ven A., Perales I., Mossel D. A. A selective and diagnostic medium for use in the enumeration of Listeria spp. in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1988 May;6(3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(88)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


