Abstract
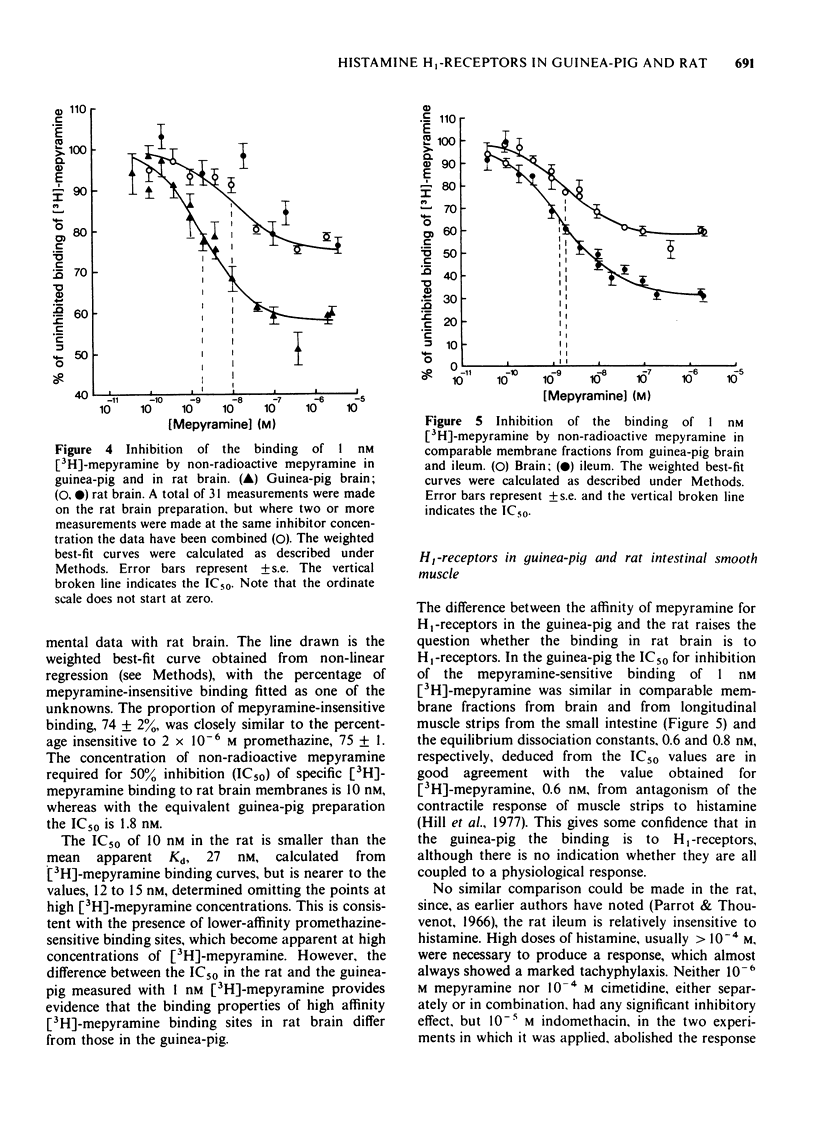
1 The equilibrium dissociation constant, Kd, for mepyramine binding to a particulate fraction from rat brain, 9.1 nM, determined from inhibition of the binding of 1 nM [3H]-mepyramine, was distinctly higher than that, 0.83 nM, measured on an equivalent preparation from guinea-pig brain.
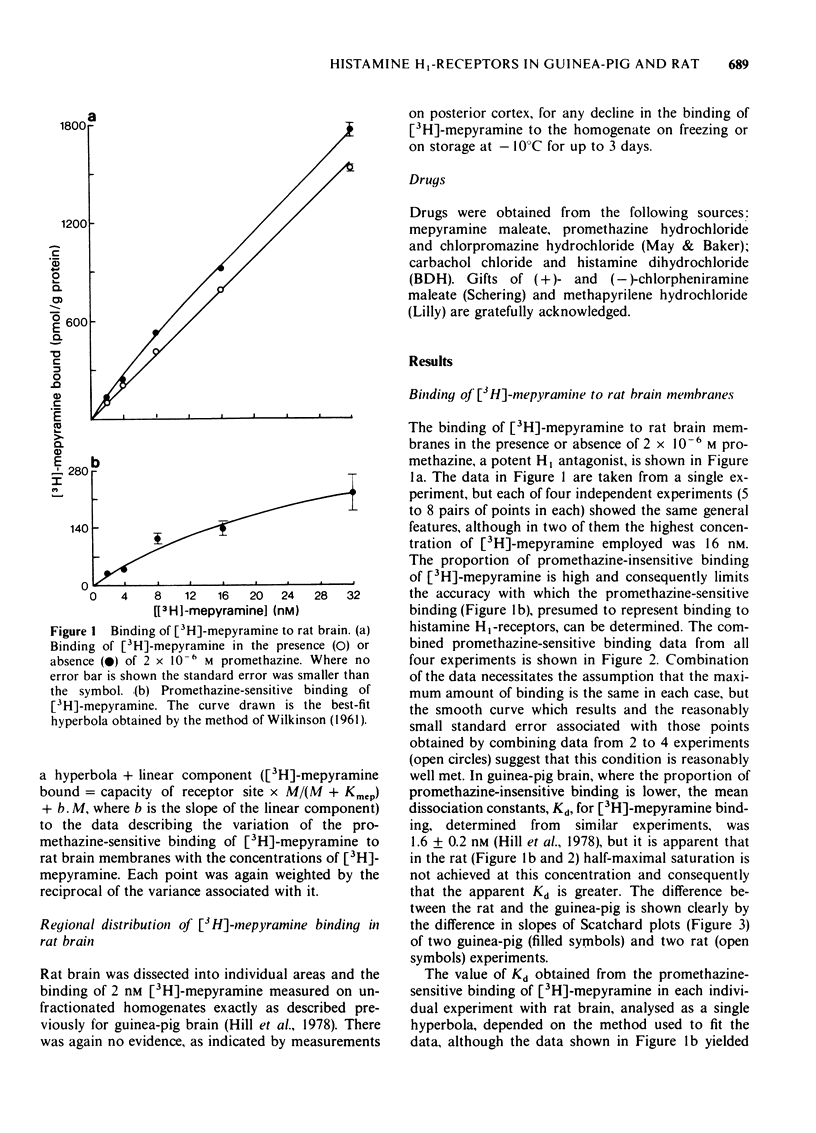
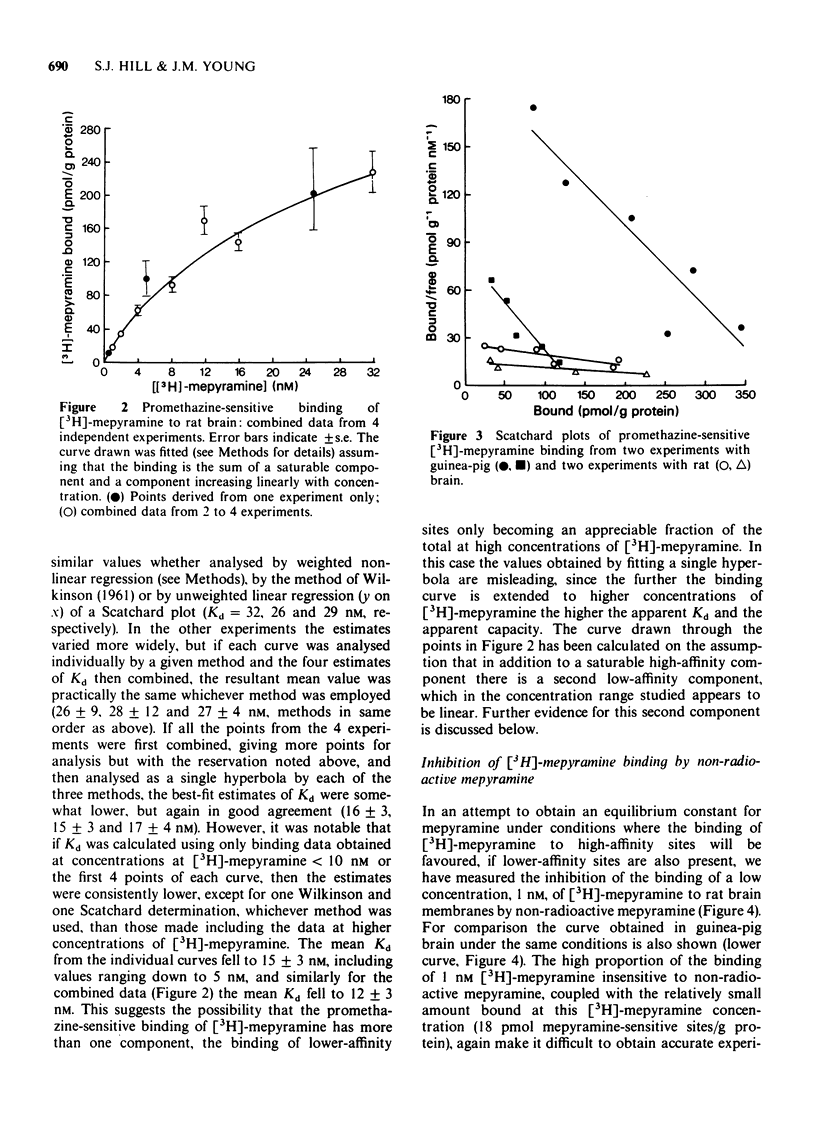
2 In rat brain the dissociation constant for mepyramine, determined from the binding of [3H]-mepyramine sensitive to inhibition by 2 × 10-6 M promethazine, was higher than the constant obtained from the inhibition of the binding of 1 nM [3H]-mepyramine by non-radioactive mepyramine. This suggests that the promethazine-sensitive binding of [3H]-mepyramine includes a lower affinity non-receptor component, which becomes apparent at higher concentrations of [3H]-mepyramine.
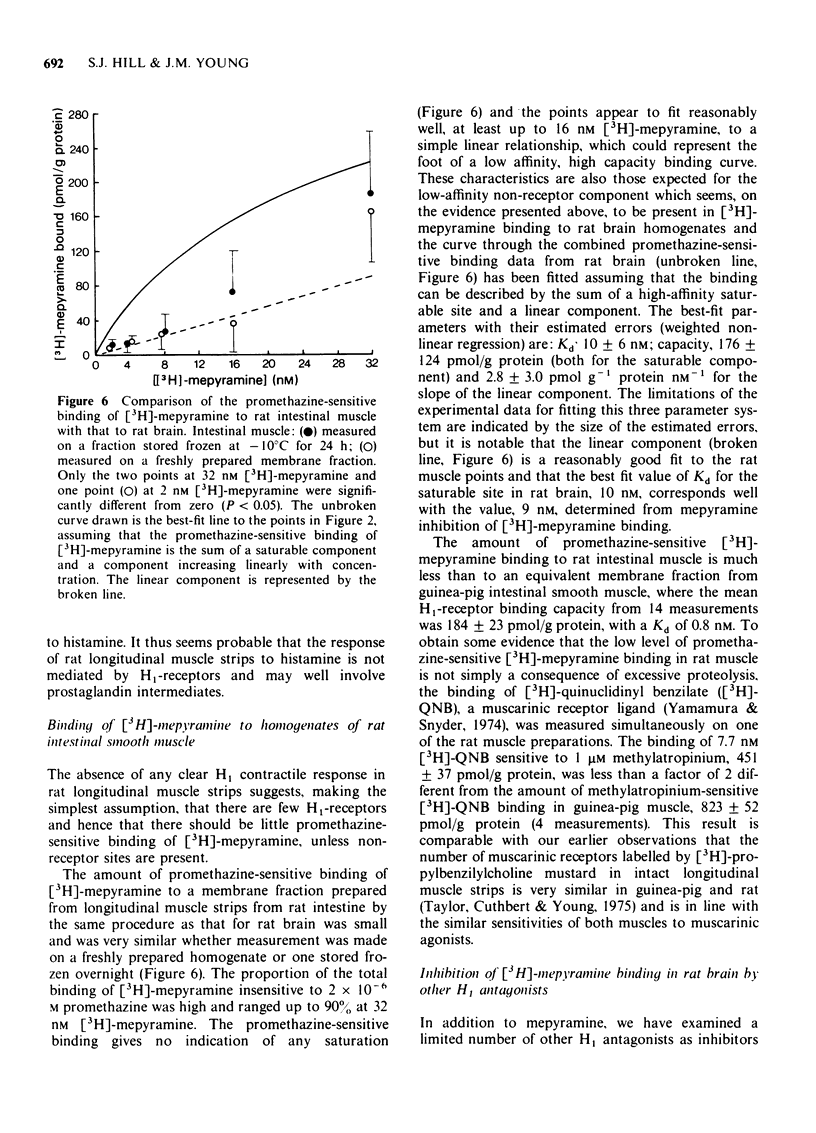
3 In the guinea-pig the dissociation constant for mepyramine determined from inhibition of [3H]-mepyramine binding was in good agreement with the value obtained from inhibition of the contractile response of intestinal smooth muscle to histamine. No similar comparison was possible in the rat. Rat ileum was much less sensitive to histamine and the contraction produced was not inhibited by 10-6 M mepyramine, indicating that it is not mediated by H1-receptors.
4 Low levels of promethazine-sensitive [3H]-mepyramine binding were present in membrane fractions prepared from the longitudinal muscle from rat small intestine, but the characteristics of this binding suggest that it may be largely to lower affinity, non-receptor sites.
5 Promethazine was practically equipotent as an inhibitor of [3H]-mepyramine binding in rat and guinea-pig brain. Chlorpheniramine showed stereospecificity in the rat as in the guinea-pig, although the potency of the (+)-isomer in the rat was only a tenth of that in the guinea-pig. Histamine had nearly the same IC50 in both species.
6 The evidence suggests that the high-affinity [3H]-mepyramine binding sites in rat brain can be described as H1-receptors, but that these differ structurally from H1-receptors in the guinea-pig.
7 The regional distribution of [3H]-mepyramine binding in rat brain was not the same as that in guinea-pig brain, the most notable difference being the very much lower level in rat cerebellum compared to guinea-pig cerebellum.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang R. S., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneity of histamine H1-receptors: species variations in [3H]mepyramine binding of brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1979 Jun;32(6):1653–1663. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Histamine H1-receptors in brain labeled with 3H-mepyramine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Apr 15;48(4):463–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegstrand L. R., Kanof P. D., Greengard P. Histamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in mammalian brain. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):163–165. doi: 10.1038/260163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Emson P. C., Young J. M. The binding of [3H]mepyramine to histamine H1 receptors in guinea-pig brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Young J. M., Marrian D. H. Specific binding of 3H-mepyramine to histamine H1 receptors in intestinal smooth muscle. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):361–363. doi: 10.1038/270361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Young J. M. The binding properties of [3H]-mepyramine in the brain of the guinea-pig and the rat [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 May;66(1):93P–93P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrian D. H., Hill S. J., Sanders J. K., Young J. M. A convenient synthesis of [3H]mepyramine and certain related [3H]antihistamines. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;30(10):660–662. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Garbarg M., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological characterization of histamine receptors mediating the stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in slices from guinea-pig hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):971–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portaleone P., Pagnini G., Crispino A., Genazzani E. Histamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in hypothalamus of rat brain: H1 and H2 receptors. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1371–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Tricyclic antidepressants block histamine H1 receptors of mouse neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):176–177. doi: 10.1038/274176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C. Histaminergic mechanisms in brain. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:325–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. K., Cuthbert A. W., Young M. Muscarinic receptors in rat intestinal muscle: comparison with the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;31(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran V. T., Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Histamine H1 receptors identified in mammalian brain membranes with [3H]mepyramine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


