Abstract
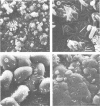
A packed-bed bioreactor with activated-carbon particles as a carrier matrix material inoculated with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was operated at a pH of 1.35 to 1.5 to convert ferrous sulfate to ferric sulfate. Despite the low operating pH, trace amounts of precipitates were produced in both the reactor and the oxidized effluent. X-ray diffraction and chemical analyses indicated that the precipitates were well-ordered potassium jarosite. The chemical analyses also revealed a relative deficiency of Fe and an excess of S in the reactor sample compared with the theoretical composition of potassium jarosite.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lazaroff N., Sigal W., Wasserman A. Iron Oxidation and Precipitation of Ferric Hydroxysulfates by Resting Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):924–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.924-938.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]