Abstract
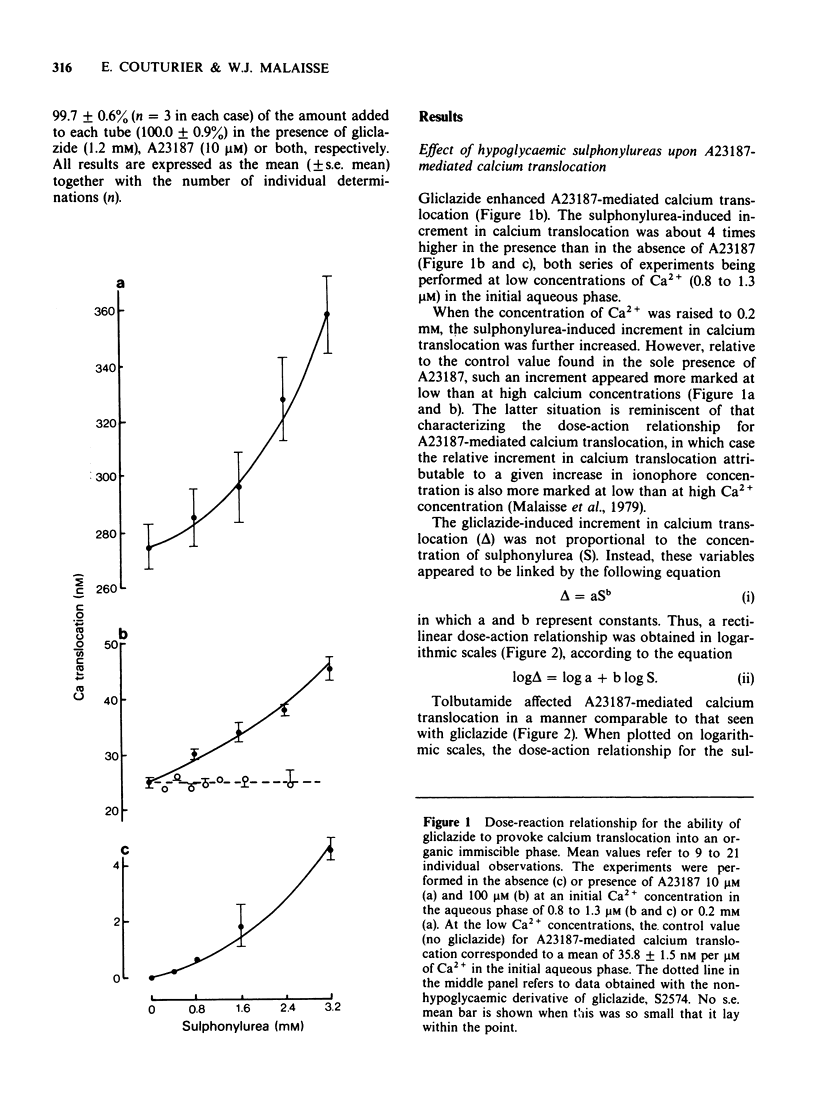
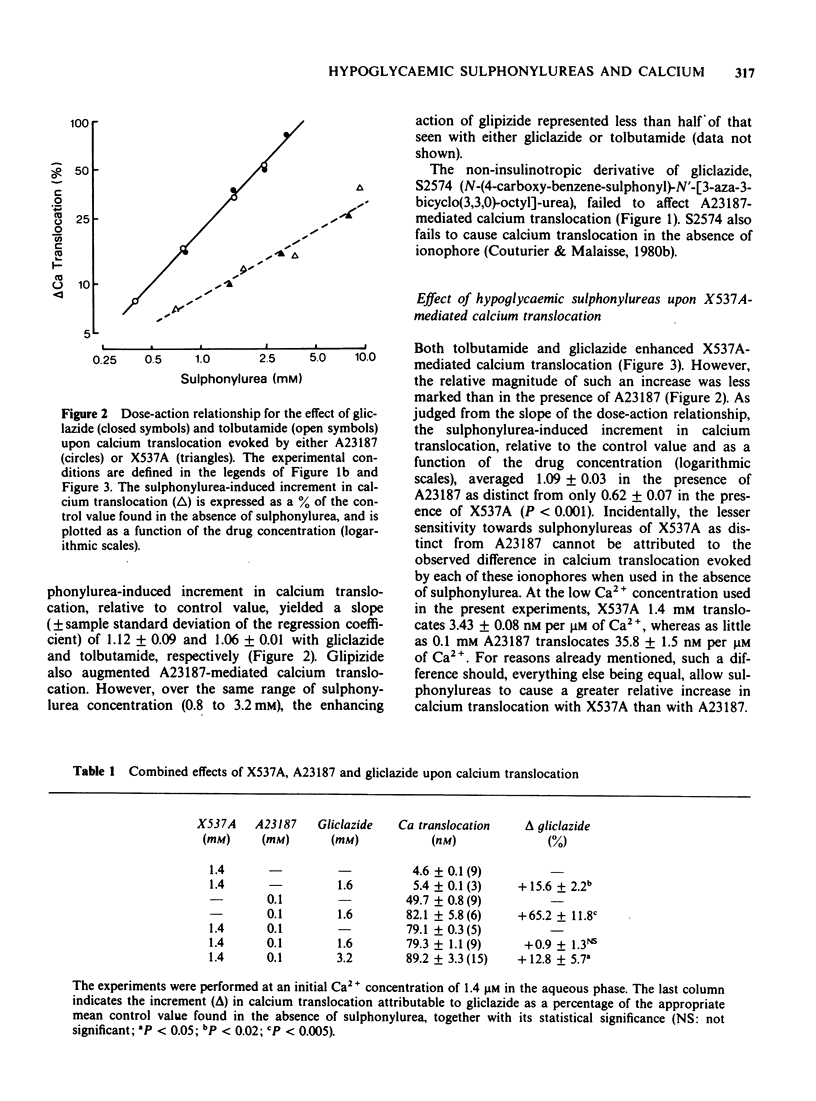
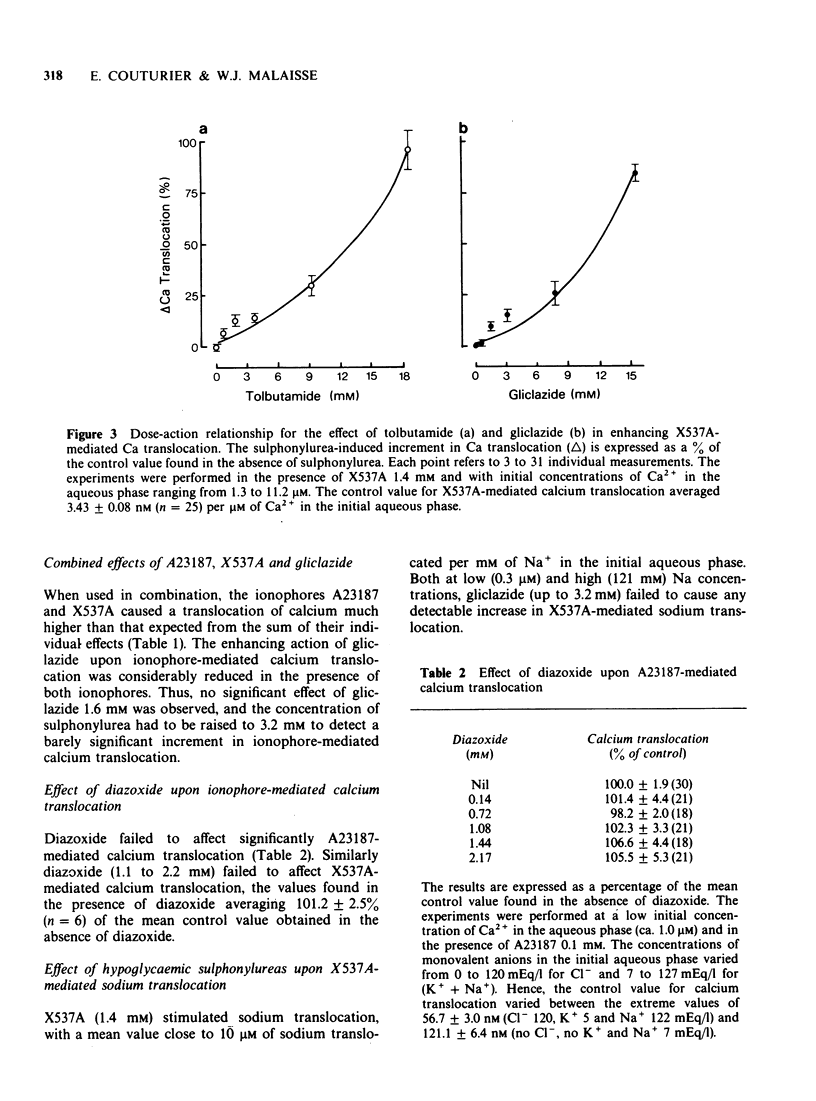
1 Hypoglycaemic sulphonylureas, such as tolbutamide and gliclazide, provoke the translocation of calcium from an aqueous medium into or across a hydrophobic region. The combined effect of sulphonylureas and antibiotic ionophores upon such a process was investigated. 2 The magnitude of the sulphonylurea-induced translocation of calcium was more marked in the presence than in the absence of A23187. Gliclazide and tolbutamide also enhanced, although less markedly, X537A-mediated calcium translocation. The effect of the sulphonylureas was even less marked in the presence of both ionophores, which acted synergistically in causing calcium translocation. 3 A non-hypoglycaemic sulphonylurea and diazoxide failed to affect ionophore-mediated calcium translocation. Gliclazide failed to enhance X537A-mediated sodium translocation. 4 It is proposed that the primary site of action of hypoglycaemic sulphonylureas upon calcium-dependent physiological processes may correspond to a drug-induced facilitation of calcium transport across the plasma membrane, as mediated by native ionophores.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Couturier E., Malaisse W. J. Ionophore-mediated cation translocation in artificial systems. II. - X537A-mediated calcium and sodium translocation. Biochimie. 1980;62(2-3):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Töljedal I. B. The pancreatic beta-cell recognition of insulin secretagogues. Inhibitory effects of a membrane probe on the islet uptake and insulin-releasing action of glibenclamide. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80827-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Ionic effects on the uptake of sulfonylurea (glibenclamide) by pancreatic islets. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Nov;8(6):427–429. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic -cell recognition of insulin secretagogues. IV. Islet uptake of sulfonylureas. Diabetologia. 1973 Jun;9(3):210–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01219785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Töljedal I. B. The pancreatic -cell recognition of insulin secretagogues. II. Site of action of tolbutamide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1384–1388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J., Brooker G. The positive inotropic action of sulfonylureas. A mechanism independent of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Diabetes. 1978 Jun;27(6):694–698. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.6.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Valverde I., Devis G., Somers G., Couturier E. Ionophore-mediated cation translocation in artificial systems. I. A23187-mediated calcium translocation. Biochimie. 1979;61(10):1185–1192. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Malaisse W. J. Ionophoretic activity in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):386–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90641-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


