Abstract
1 The effects of intracarotid injections of methionine-enkephalin (Met-enkephalin) and morphine on chemoreceptor activity recorded from the peripheral end of a sectioned carotid sinus nerve have been studied in cats anaesthetized with pentobarbitone. 2 Met-enkephalin caused a rapid, powerful, inhibition of spontaneous chemoreceptor discharge, the intensity and duration of which was dose-dependent. 3 Morphine was a less potent inhibitor of spontaneous chemoreceptor discharge, and the inhibition it evoked was rather variable and tended to be biphasic. Low doses of morphine caused a slight increase in discharge. 4 Naloxone (0.2 mg i.c.) slightly increased spontaneous discharge, greatly reduced the chemo-inhibition caused by morphine, and reduced the inhibitory effect of Met-enkephalin. A higher dose of naloxone (0.8 mg) caused a substantial reduction of the Met-enkephalin effect. 5 Chemo-excitation evoked by intracarotid injections of acetylcholine, CO2-saturated Locke solution, and sodium cyanide were only slightly and somewhat variably reduced following injections of Met-enkephalin, whereas the inhibitory effect of dopamine was potentiated. Following morphine administration, response to acetylcholine and sodium cyanide were reduced slightly, whereas those to CO2 and dopamine were potentiated. 6 Responses to acetylcholine and CO2 were slightly potentiated during infusion of Met-enkephalin (50 micrograms/min, i.c.) and the response to sodium cyanide was slightly reduced. 7 It is concluded that naloxone-sensitive opiate receptors are present in the cat carotid body; when activated they cause inhibition of spontaneous chemoreceptor discharge. The physiological role of these receptors and the identity of any endogenous ligand remains to be established.
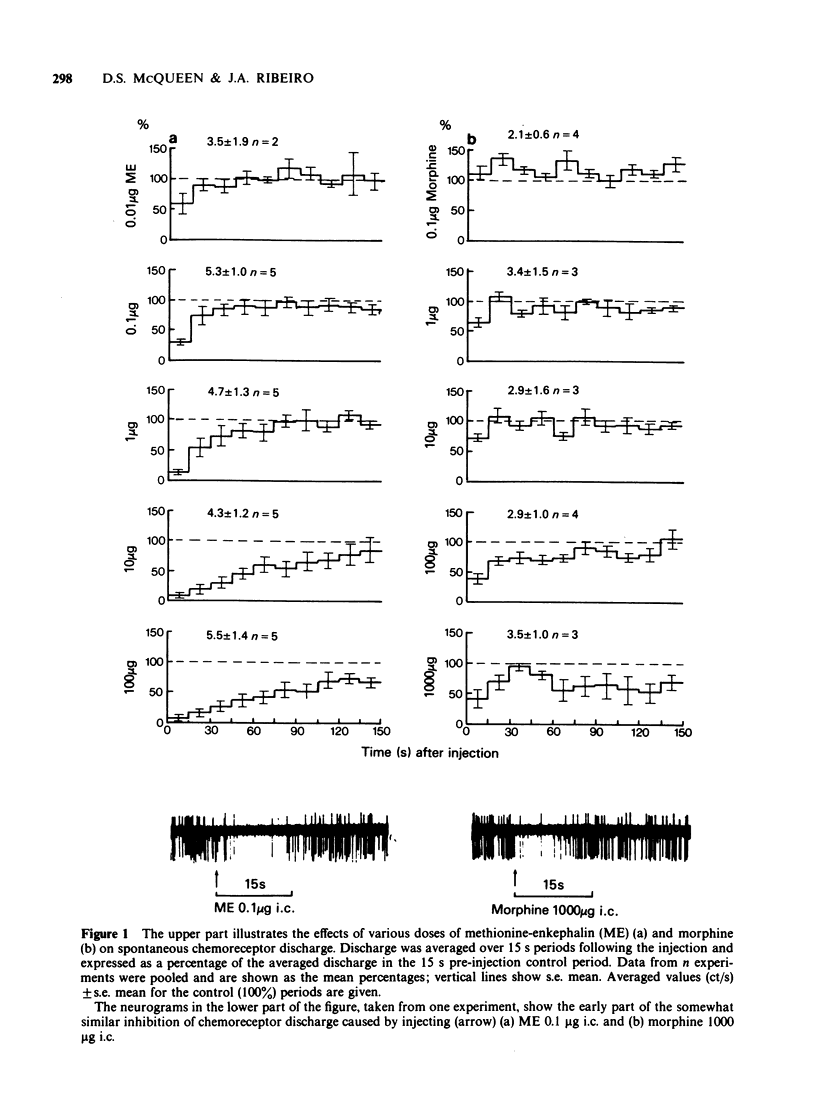
Full text
PDF

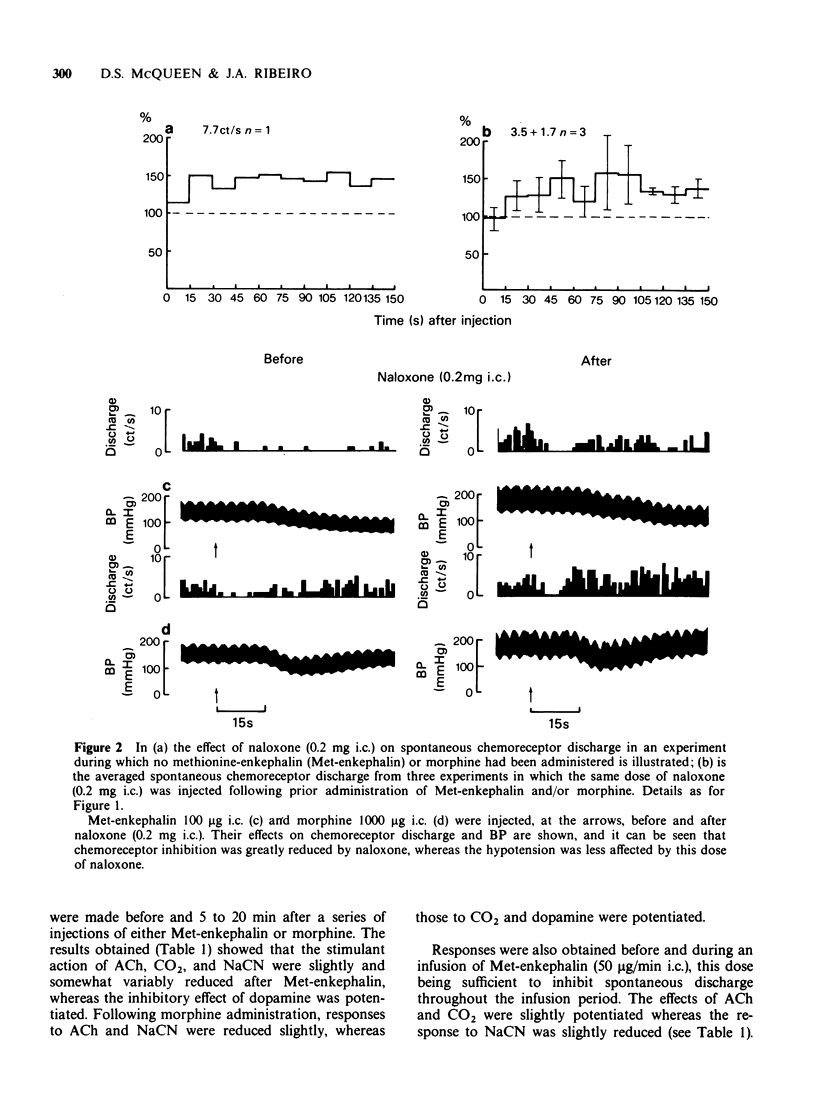
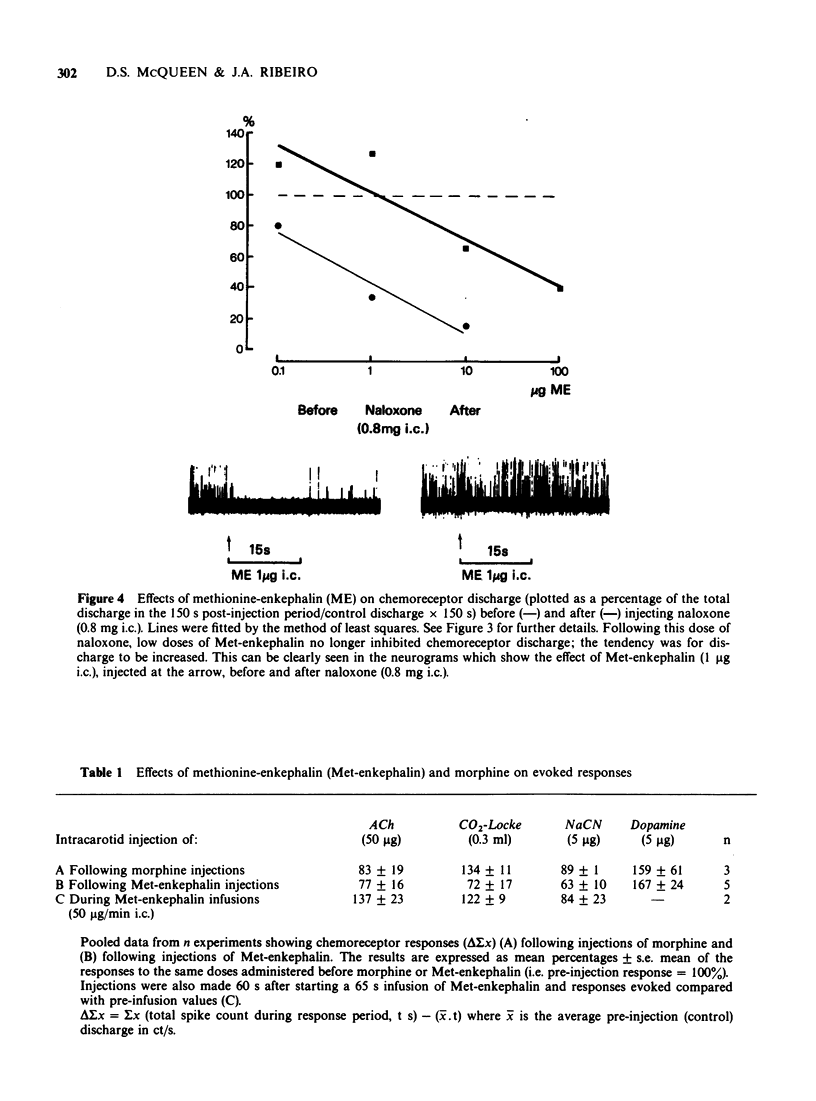



Selected References
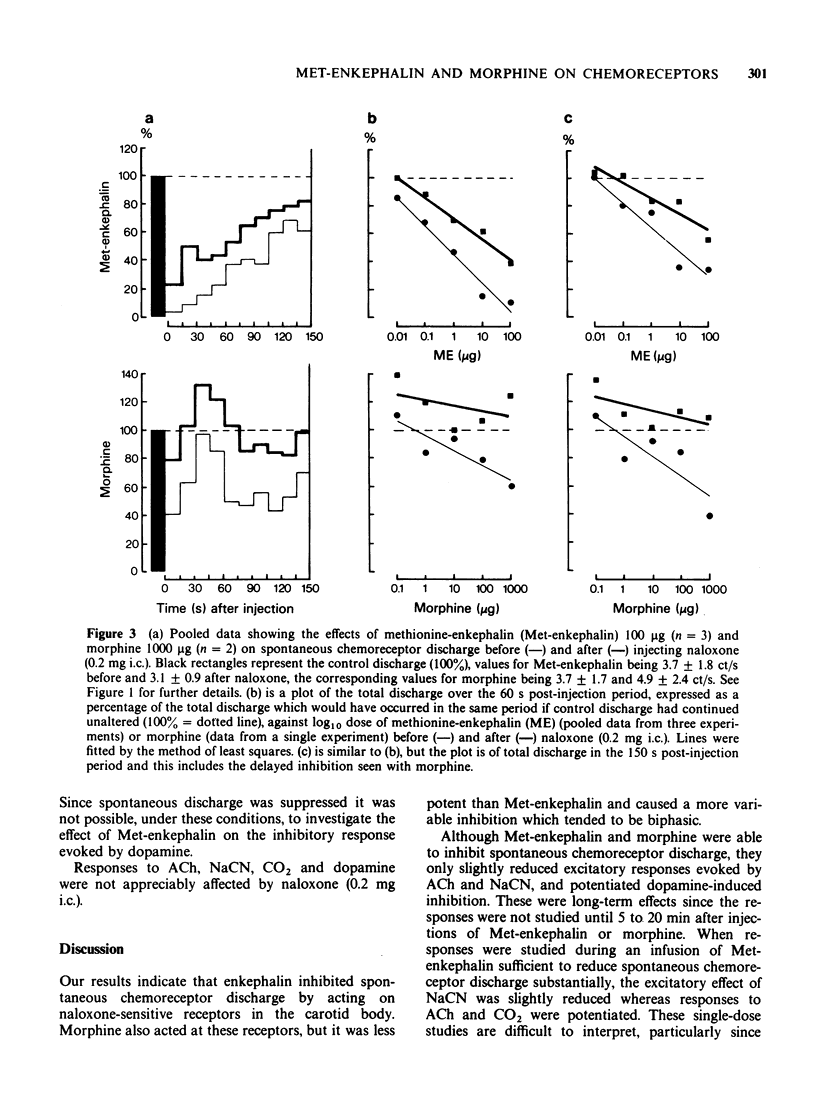
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt J. O., Freye E. Opiate antagonist reverses the cardiovascular effects of inhalation anaesthesia. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):399–400. doi: 10.1038/277399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., McQueen D. S. Substance P: a carotid body peptide. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J., McQueen D. S. Inhibitory action of dopamine on cat carotid chemoreceptors. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:425–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Enkephalins and dorsal horn neurones of the cat: effects on responses to noxious and innocuous skin stimuli. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;61(3):399–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., LEWIN J. Effect of different oxygen tensions on the carotid body in vitro. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:238–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyzaguirre C., Zapata P. Pharmacology of pH effects on carotid body chemoreceptors in vitro. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):557–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst Z., Foldes F. F., Knoll J. The influence of naloxone on barbiturate anesthesia and toxicity in the rat. Life Sci. 1977 Mar 15;20(6):921–926. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Munoz F., Cerreta K. V., Guerrero M. L., Way E. L. Effect of morphine on synaptosomal Ca++ uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Apr;209(1):132–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Munoz F., de Lourdes Guerrero M., Way E. L., Li C. H. Effect of beta-endorphin on calcium uptake in the brain. Science. 1979 Oct 5;206(4414):89–91. doi: 10.1126/science.39340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. The effects of morphine on the release of noradrenaline from the cat isolated nictitating membrane and the guinea-pig ileum myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle preparation. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;53(4):505–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Hughes J. Some thoughts on the significance of enkephalin, the endogenous ligand. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 1;17(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., LILJESTRAND G., ZOTTERMAN Y. The effect of certain autonomic drugs on the action potentials of the sinus nerve. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Sep 10;26(2-3):264–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Brase D. A., Sampath-Khanna S., Mar J. B., Way E. L., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin in vitro inhibition of striatal dopamine release. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):567–568. doi: 10.1038/264567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S. A quantitative study of the effects of cholinergic drugs on carotid chemoreceptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):515–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S. Effects of substance P on carotid chemoreceptor activity in the cat. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:31–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E., Fischbach G. D. Enkephalin inhibits release of substance P from sensory neurons in culture and decreases action potential duration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):526–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Opiates, opioid peptides and single neurones. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 23;24(17):1527–1545. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A. ATP; related nucleotides and adenosine on neurotransmission. Life Sci. 1978 Apr 24;22(16):1373–1380. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sá-Almeida A. M., Namorado J. M. Adenosine and adenosine triphosphate decrease 45Ca uptake by synaptosomes stimulated by potassium. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 15;28(8):1297–1300. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90428-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZERB J. C. The effect of morphine on the adrenergic nerves of the isolated guinea-pig jejunum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Feb;16:23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Jhamandas K. H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: antagonism by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 May;197(2):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Pinsky C., LaBella F. S. On the specificity of naloxone as an opiate antagonist. Life Sci. 1979 Nov 5;25(19):1621–1632. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Childers S. R. Opiate receptors and opioid peptides. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:35–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Is adenosine the mediator of opiate action on neuronal firing rate? Nature. 1979 Sep 20;281(5728):227–228. doi: 10.1038/281227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


