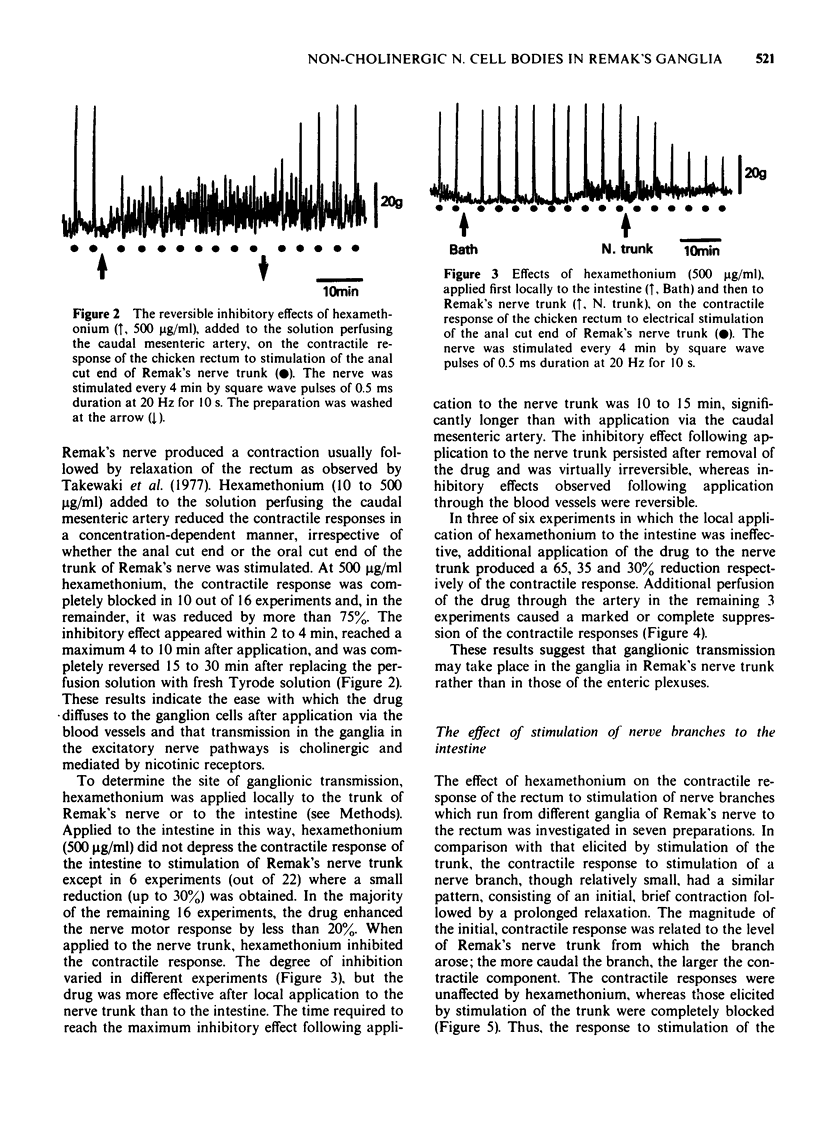
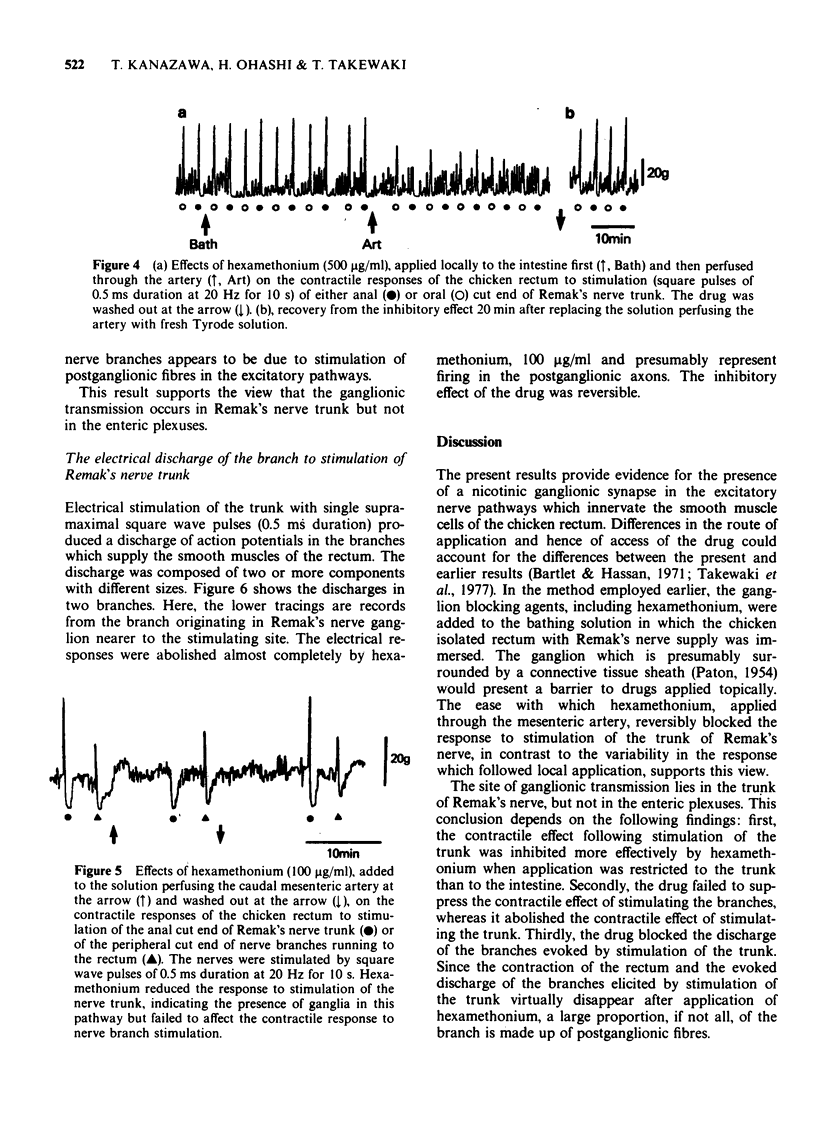
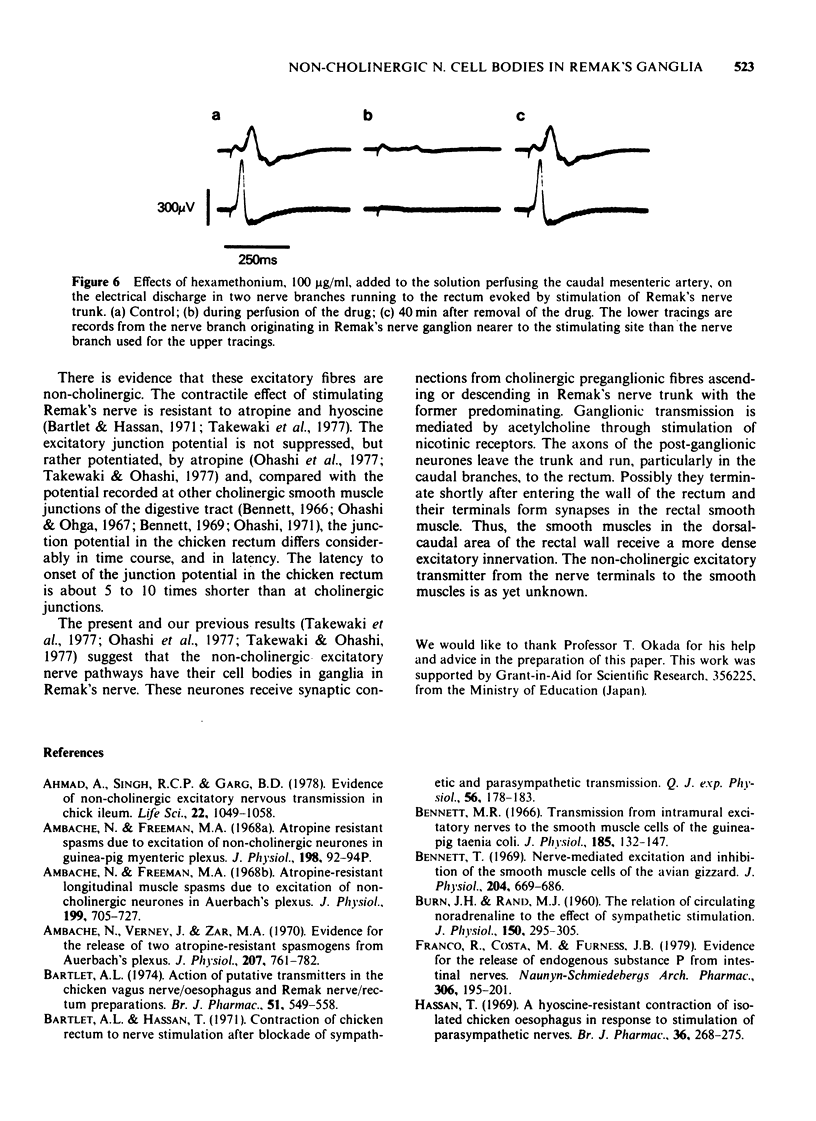
Abstract
1. A pharmacological investigation of the distribution of non-cholinergic excitatory nerve cell bodies was performed on the chicken's isolated perfused rectum with attached Remak's nerve supply. 2. Electrical stimulation of Remak's nerve trunk produced a contraction and a discharge of action potentials in the nerve branches which supply the smooth muscle of the rectum. Both responses were virtually blocked by hexamethonium when applied via the caudal mesenteric artery. 3. The contractile effect following stimulation of the nerve trunk was inhibited more effectively by hexamethonium when application was restricted to the trunk rather than to the intestine. 4. The contractile effect of stimulating the nerve branches was unaffected by hexamethonium. 5. It is concluded that ganglionic transmission, which is mediated by nicotinic receptors, occurs in the ganglia of Remak's nerve but not in ganglia of the enteric plexuses. Therefore, cell bodies of the postganglionic neurones which are considered to be non-cholinergic are located in Remak's nerve ganglia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad A., Singh R. C., Garg B. D. Evidence of non-cholinergic excitatory nervous transmission in chick ileum. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(12):1049–1058. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Freeman M. A. Atropine-resistant longitudinal muscle spasms due to excitation of non-cholinergic neurones in Auerbach's plexus. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):705–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Verney J., Zar M. A. Evidence for the release of two atropine-resistant spasmogens from Auerbach's plexus. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):761–782. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The relation of circulating noradrenaline to the effect of sympathetic stimulation. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:295–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlet A. L. Actions of putative transmitters in the chicken vagus nerve/oesophagus and Remak nerve/rectum preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;51(4):549–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlet A. L., Hassan T. Contraction of chicken rectum to nerve stimulation after blockade of sympathetic and parasympathetic transmission. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1971 Jul;56(3):178–183. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1971.sp002117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R. Transmission from intramural excitatory nerves to the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):132–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett T. Nerve-mediated excitation and inhibition of the smooth muscle cells of the avian gizzard. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R., Costa M., Furness J. B. Evidence for the release of endogenous substance P from intestinal nerves. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00507103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan T. A hyoscine-resistant contraction of isolated chicken oesophagus in response to stimulation of parasymphathetic nerves. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;36(2):268–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb09504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi H., Naito K., Takewaki T., Okada T. Non-cholinergic, excitatory junction potentials in smooth muscle of chicken rectum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;27(3):379–387. doi: 10.1254/jjp.27.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi H., Ohga A. Transmission of excitation from the parasympathetic nerve to the smooth muscle. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):291–292. doi: 10.1038/216291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. Transmission and block in autonomic ganglia. Pharmacol Rev. 1954 Mar;6(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takewaki T., Ohashi H., Okada T. Non-cholinergic and non-adrenergic mechanisms in the contraction and relaxation of the chicken rectum. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;27(1):105–115. doi: 10.1254/jjp.27.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takewaki T., Ohashi O. Non-cholinergic excitatory transmission to intestinal smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):749–750. doi: 10.1038/268749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


